9
08.97 Path Traversing Behavior
9.1 Tan
ential control TANG
TANGON
TANGOF
9
840D
NCU 572
NCU 573
810D 840Di
Siemens AG 2000. All rights reserved
SINUMERIK 840D/840Di/810D/FM-NC Programming Guide Advanced (PGA) – 04.00 Edition
9-303
Function
A rotary axis (= following axis) follows the
programmed path of two leading axes. The following
axis is located at a defined offset angle to the path
tangent.
Applications
Tangential control can be used in applications such
as:
•
Tangential positioning of a rotatable tool during
nibbling
•
Follow-up of the tool orientation on a band saw
•
Positioning of a dresser tool on a grinding wheel
(see diagram)
•
Positioning of a cutting wheel for glass or paper
working
•
Tangential infeed of a wire in five-axis welding
•
…
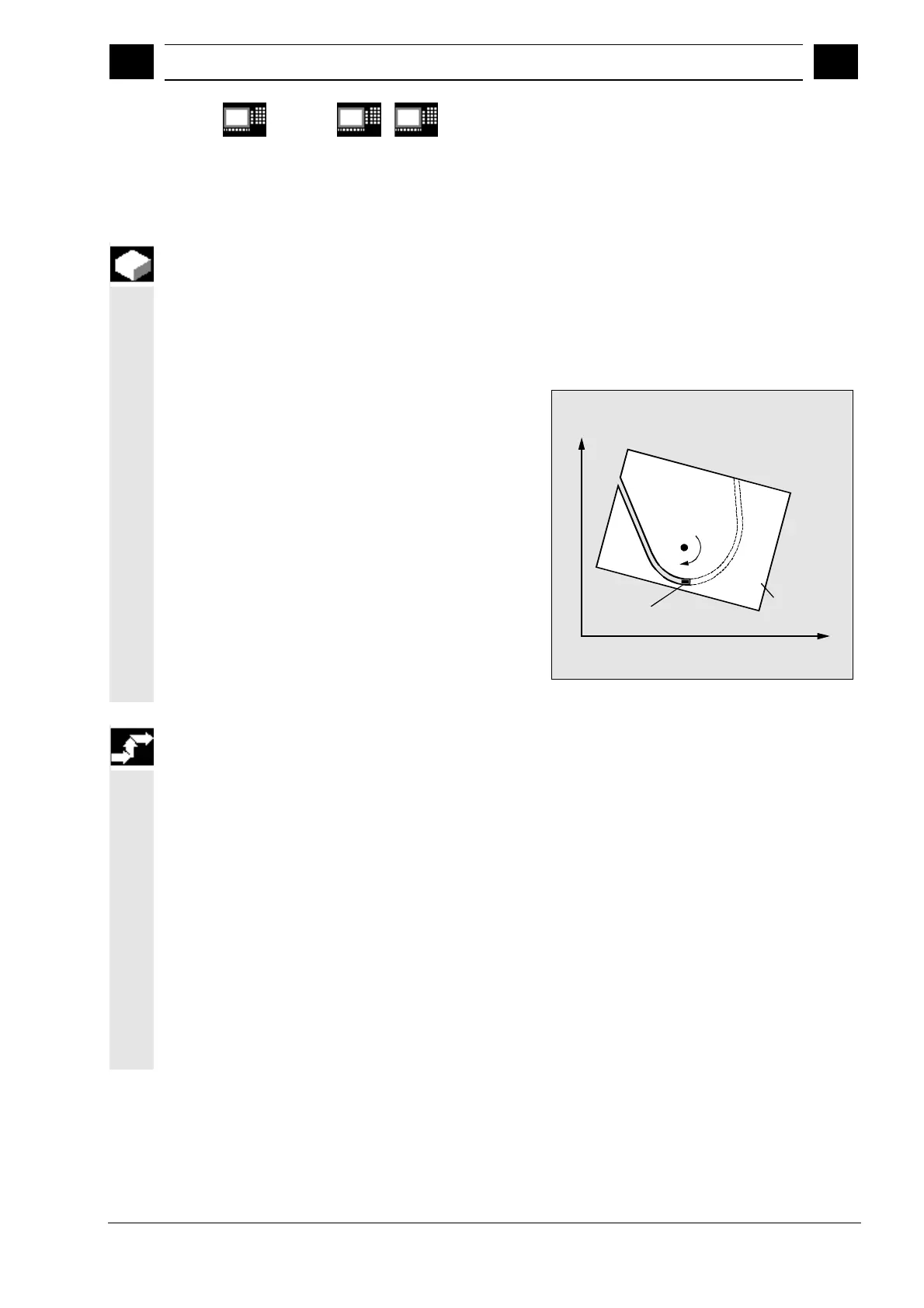
Y
X
Band saw
Workpiece
Sequence
Defining following axis and leading axis
TANG is used to define the following and leading
axes.
A coupling factor specifies the relationship between
an angle change on the tangent and the following
axis. Its value is generally 1 (default).
The follow-up can be performed in the basic
coordinate system "B" (default) or the workpiece
coordinate system "W".
Example:
TANG(C,X,Y,1,"B")
Meaning:
Rotary axis C follows geometry axes X and Y.

 Loading...
Loading...






















