3. Overview/functional description
○ Stroke frequency (dynamics)
○ Working temperature, viscosity fluctua-
tions due to strong temperature changes
The maximum stroke and thus the piston
capacity/metered quantity can reduce due to
these factors.
The minimum piston stroke, also referred
to as the compulsory stroke, is determined
by the position of the control bores in the
progressive metering device and the con-
trol edges on the metering piston. If only
the compulsory stroke is performed, the
metered quantity at the affected outlet is
reduced, which also increasing the effective
number of piston strokes. The theoretically
determined number of piston strokes can
therefore deviate from the actual mea-
sured value. This must be considered when
evaluating pulses on progressive metering
devices with a mounted piston detector.
The ratio of piston capacity per progres-
sive metering device outlet determines the
Maximum stroke
Maximum stroke for piston 5/2 Compulsory stroke for position of piston 5/2
Compulsory stroke
distribution ratio of the quantity of lubricant
supplied to the progressive metering device.
This distribution ratio is usually constant
under all operating conditions.
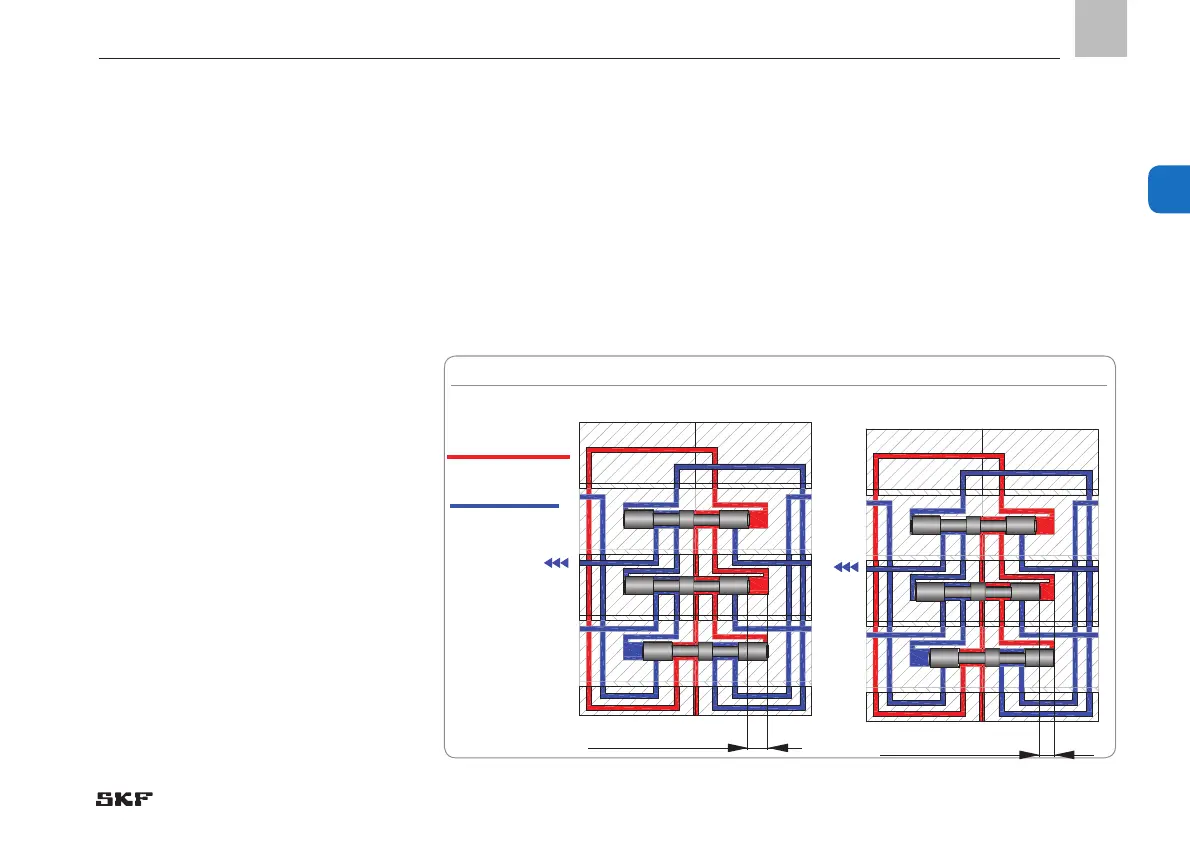
Figure 2 shows the piston positions of a
progressive metering device section at
maximum stroke and at compulsory stroke
(minimum stroke).
red = control circuit
blue = working circuit
3
Fig. 2 Maximum stroke and compulsory stroke
5
5
2
5

 Loading...
Loading...