7 | What you should know before commissioning STOBER
20
02/2020 | ID 442516.07
7.2.2 Parameter types and data types
In addition to topic-based sorting in individual groups, all parameters belong to a certain data type and parameter type. The
data type of a parameter is displayed in the parameter list, properties table. The connections between parameter types,
data types and their value range can be found in the following table.
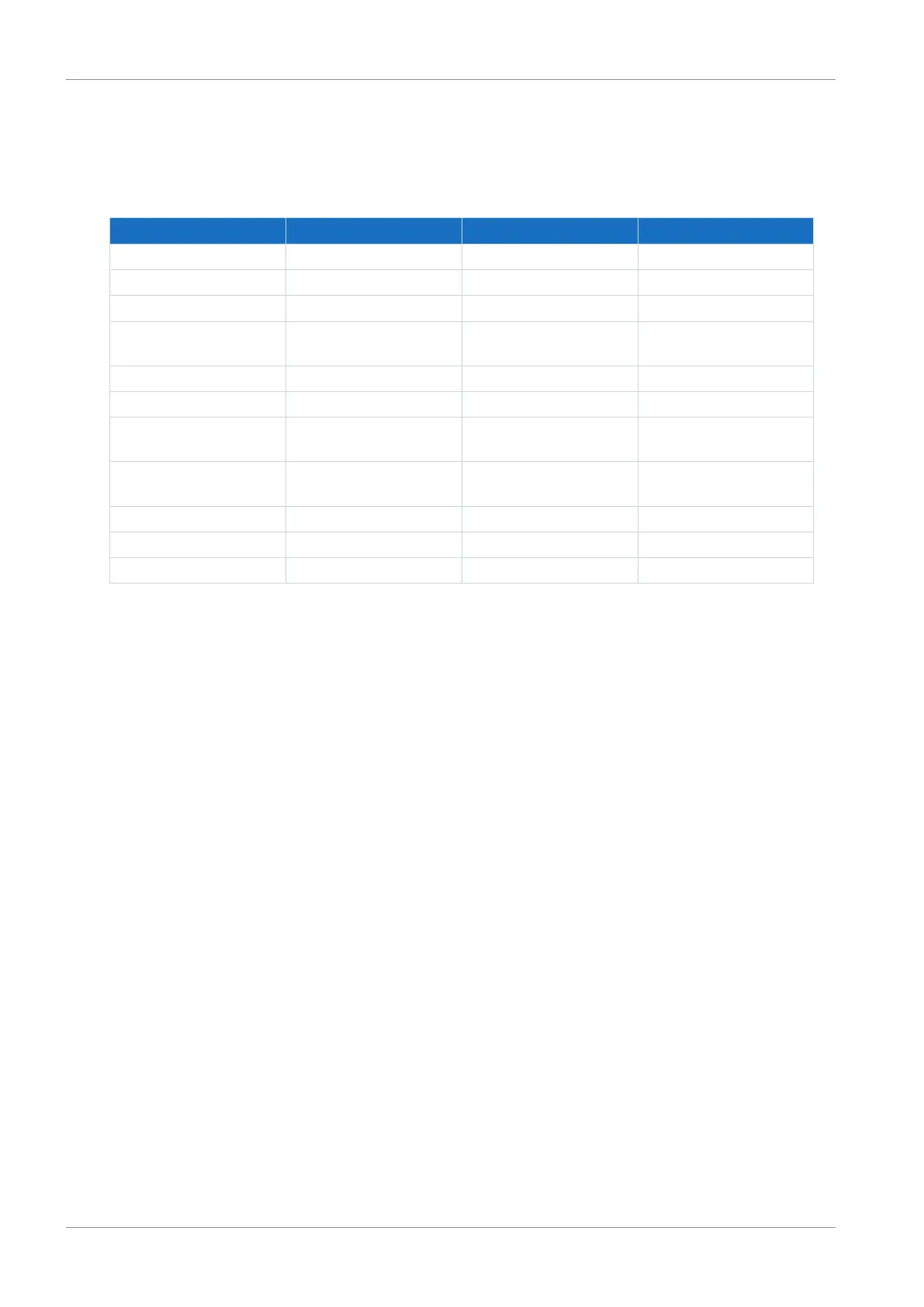
Type Style Value range (decimal)
INT8 Integer or selection 1 byte (signed) -128 – 127
INT16 Integer 2 bytes (1 word, signed) -32768 – 32767
INT32 Integer or position 4 bytes (1 word, unsigned) -21474836480 – 2147483647
BOOL Binary number 1 bit (internal:
LSB in 1 byte)
0, 1
BYTE Binary number 1 byte (unsigned) 0 – 255
WORD Binary number 2 bytes (1 word, unsigned) 0 – 65535
DWORD Binary number or parameter
address
4 bytes (1 word, unsigned) 0 – 4294967295
REAL32 Floating-point number Floating point (1 word,
unsigned)
In accordance with ANSI/
IEEE 754
STR8 Text Text (8 characters) –
STR16 Text Text (16 characters) –
STR80 Text Text (80 characters) –
Tab. 3: Parameters – Data types, styles, possible values
Parameter types – Use
§ Integer, floating-point number
For general computing processes
Example: Set and actual values
§ Selection
Numeric value to which a direct meaning is assigned
Example: Sources for signals or set values
§ Binary number
Bit-oriented parameter information that is collected in binary
Example: Control and status words
§ Position
Integer combined with associated units and decimal places
Example: Actual and set values of positions
§ Velocity, acceleration, deceleration, jerk
Floating-point number combined with the associated units and decimal places
Example: Actual and set values for velocity, acceleration, deceleration, jerk
§ Parameter address
Corresponds to the storage location of another parameter
Example: Indirect read sources for analog and digital outputs and for fieldbus mapping
§ Text
Outputs or messages
Example: Displays

 Loading...
Loading...