TECHNICAL INFORMATION
Copyright Trace Engineering Company, Inc.
5916 - 195th Street N.E.
Arlington, WA 98223
Telephone: 360/435-8826
Fax: 360/435-2229
www.traceengineering.com
PS Series Inverter/Charger
Part No. 3597
Rev. D: November 23, 1999
Page
99
WORKSHEET
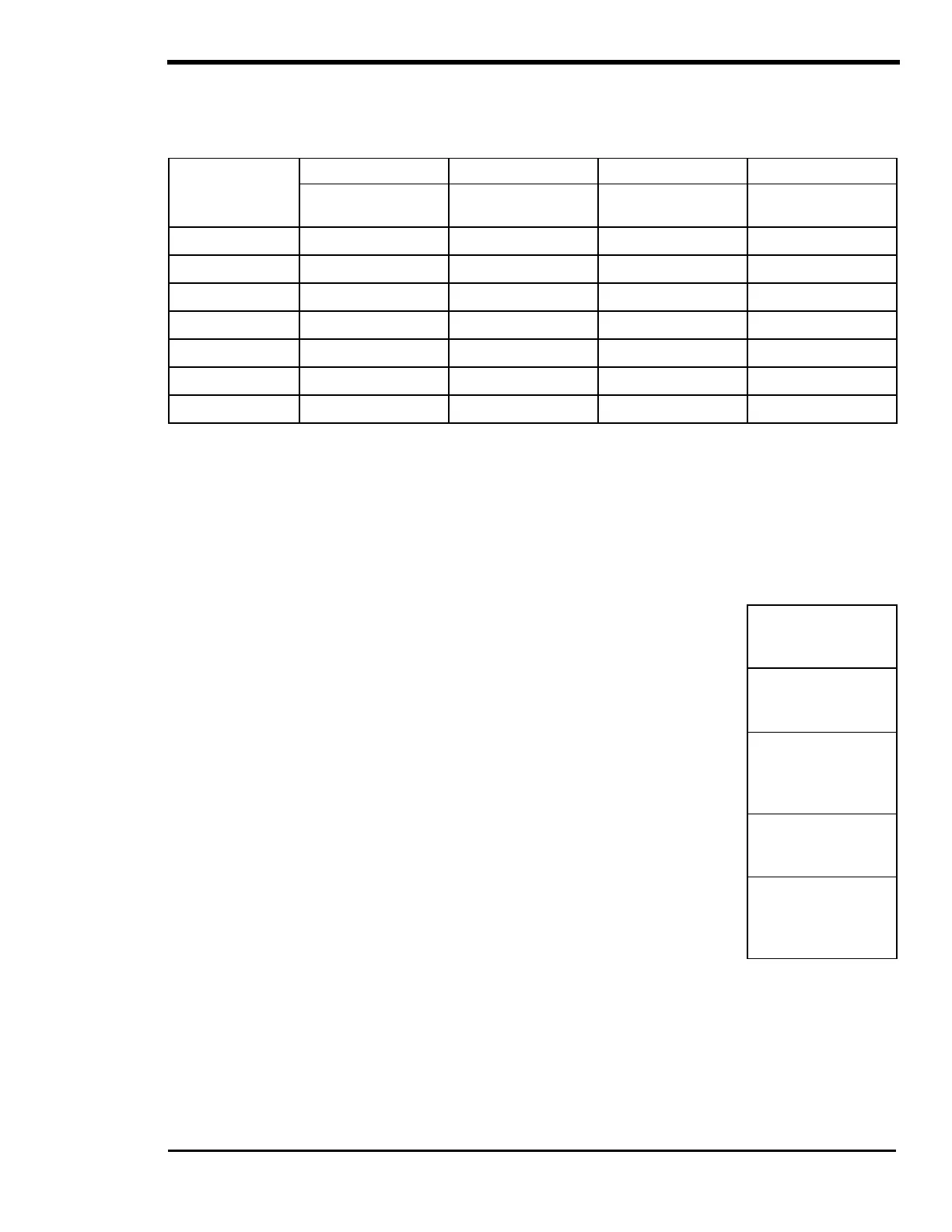
Complete the steps that follow to calculate your battery bank capacity.
STEP 1-4: Determine your Average Daily Watt-Hours Needed.
STEP 1 STEP 2 STEP 3 STEP 4
AC APPLIANCE APPLIANCE RUNNING
WATTS
(X) HOURS USED
EACH DAY
(X) DAYS USED
EACH WEEK
(÷ 7 = ) AVERAGE DAILY
WATT-HOURS NEEDED
Determine what appliances the inverter will power and enter the
Wattage of each appliance.
STEP 2: Determine the number of hours (or fractions of hours) you will use the appliance each day;
Multiply the number of days you will use the appliance during the week; this is your
Watt-Hours Needed;
Needed;
STEP 5: Total Average Daily Watt-Hours Needed to determine your Total Daily
Watt-Hours Needed.
Total Daily Watt-Hours Needed
STEP 6: Multiply your Total Daily Watt-Hours Needed (Step 5) by the number
of anticipated days of autonomy (days between charging, usually 1 to
5) to determine your Autonomy Battery Size (example used 3 days).
Autonomy Battery Size
STEP 7: Multiply your Autonomy Battery Estimate (Step 6) x 2 to allow for a
50% maximum battery discharge in normal operation and an
additional 50% for emergency situations to obtain your Rough Battery
Size in watt-hours.
Rough Battery Size Watt-Hours
STEP 8: Determine your Safe Battery Size in watt-hours. Multiply your Rough
Battery Estimate x 1.2. This allows for an efficiency of 80%. This
number is your Safe Battery Size in watt-hours
Safe Battery Size (Watt-Hours)
STEP 9: Convert your Safe Battery Size to amp-hours. Divide Safe Battery
Size by the DC system voltage (i.e., 12, 24 or 48 VDC; example used
24-volts). This number is your Safe Battery Size in amp-hours, which
is the battery bank capacity needed before recharging.
Safe Battery Size (Amp-Hours)
 Loading...
Loading...