INSTALLATION
Copyright Trace Engineering Company, Inc.
5916 - 195th Street N.E.
Arlington, WA 98223
Telephone: 360/435-8826
Fax: 360/435-2229
www.traceengineering.com
PS Series Inverter/Charger
Part No. 3597
Rev. D: November 23, 1999
Page
21
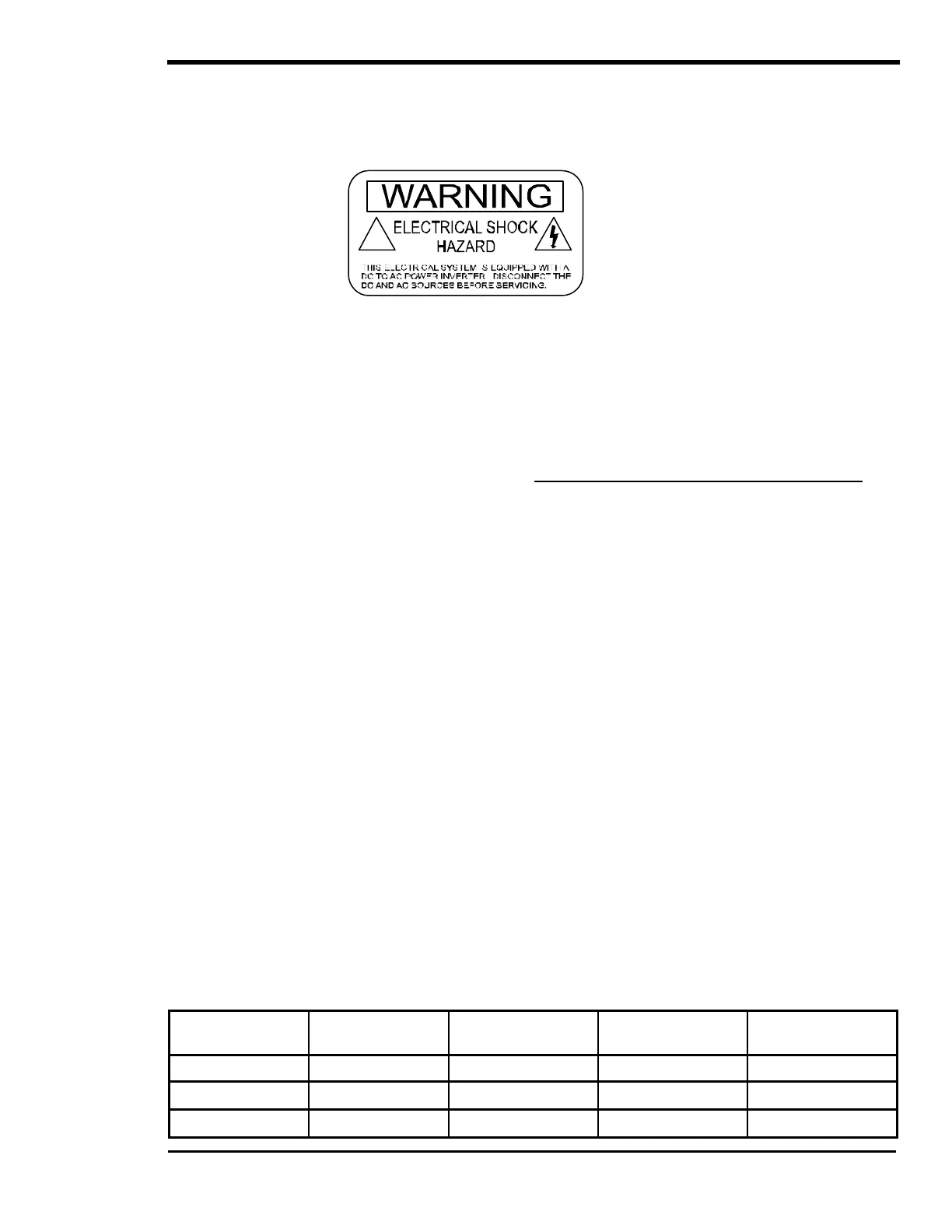
WARNING LABEL
A warning label is provided to inform all personnel that an inverter is installed in your electrical system.
This label should be installed at the electrical panel that is being powered by the inverter. Be cautious
until the inverter is disconnected from your electrical system.
Figure 12, Warning Label
DC WIRING
This section describes DC cabling requirements and recommendations including cable sizing, DC
conductor ampacity ratings, overcurrent devices, terminals and lugs, and inverter terminal connections.
WARNING! Battery cables that are very small will melt and burn the first time the inverter is
operated at high power levels. The inverter's maximum peak current requirements are high. If
battery cables are too small and/or connections are loose, efficiency and maximum output power
are degraded. Small cables or loose connections may cause dangerous overheating and a fire.
BATTERY CABLE SIZING
The larger the battery cables the better. Undersized cables result in additional stress on the inverter,
lower efficiency, reduced surge power and lower peak output voltage. Don't use cables that are too small
and degrade the efficiency that we have worked so hard to achieve and you have paid so much to own.
Also, don’t use cables that are too long - the shorter the better. The lower the DC system voltage, the
shorter the cables need to be. If long cables are required, either oversize them substantially, or switch to
a higher voltage system, such as 24 vdc or 48 vdc. On 12-vdc system, cables may need to be doubled up
(paralleled) to get maximum performance from the inverter.
NOTE: Do not separate the positive and negative cables - taping them together in parallel is best. This
reduces the inductance of the wire resulting in a better waveform and reduces the current in the inverter's
filter capacitors. Make the battery cables as short as possible.
Although large cables may seem expensive, spending an additional $100 or more to ensure the
performance of your inverter is a wise investment. Using cables that are too small is like putting cheap
tires on a high performance sports car - the results will be disappointing.
If the system is expected to operate at the inverter’s continuous power level rating for long periods of time
(over an hour), larger disconnects and cables may be required. Most systems do not operate at full
capacity for periods exceeding an hour and can operate satisfactorily with the following cable and
disconnects shown. If your system includes enormous batteries or has a very large DC source able to
continuously power the inverter (such as a hydroelectric plant, etc.) then increasing the disconnect and
cable sizes may be required to prevent nuisance tripping of a breaker or blowing of fuses.
The following table gives recommended minimum cable sizes for various cable lengths and inverter
voltages. These recommendations may not meet all local or NEC code requirements. Use only copper
cables.
Table 2, Minimum Recommended Battery Cable Size Vs. Cable Length
INVERTER MODEL
TYPICAL DC
AMPS
1 TO 3 FEET
ONE WAY
3 TO 5 FT
ONE WAY
5 TO 10 FT
ONE WAY
PS2512 267 amps #4/0 AWG / 67.4 mm
2
#4/0 AWG / 107 mm
2
Not Recommended
PS2524/PS2524E 134 amps #2/0 AWG / 67.4 mm
2
#2/0 AWG / 67.4 mm
2
#4/0 AWG / 107 mm
2
PS2212E 235 amps #2/0 AWG / 67.4 mm
2
#4/0 AWG / 107 mm
2
#4/0 AWG / 107 mm
2
!
 Loading...
Loading...