ZED-F9P-Integration Manual
UBX-18010802 - R02
4 Receiver description Page 67 of 114
Advance Information
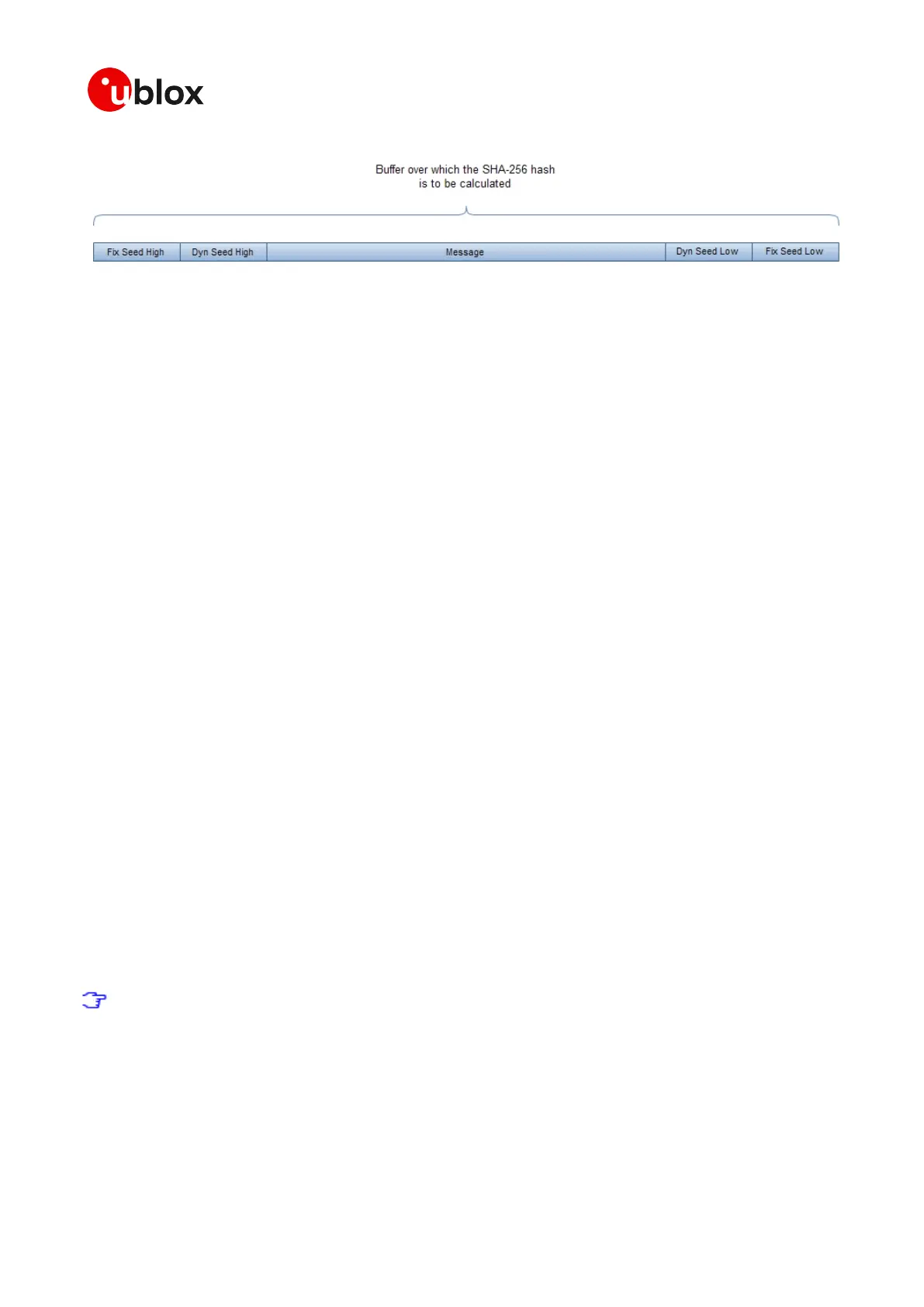
Figure 41: SHA256 hash
The result is a 256 bit (32 bytes) hash which needs to be verified with the content (field hash) of the
corresponding UBX-SEC-SIGN message.
4.15 Spoofing detection
4.15.1 Introduction
Spoofing is the process whereby someone tries to forge a GNSS signal with the intention of fooling
the receiver into calculating a different user position than the true one.
The spoofing detection feature monitors the GNSS signals for suspicious patterns indicating that
the receiver is being spoofed. A flag in UBX-NAV-STATUS message (flags2 - spoofDetState) alerts
the user to potential spoofing.
4.15.2 Scope
The spoofing detection feature monitors suspicious changes in the GNSS signal indicating external
manipulation. Therefore the detection is only successful when the signal is genuine first and when
the transition to the spoofed signal is being observed directly. When a receiver is started up
to a spoofed signal the detection algorithms will be unable to recognize the spoofing. Also, the
algorithms rely on availability of signals from multiple GNSS; the detection does not work in single
GNSS mode.
4.16 Timemark
The receiver can be used to provide an accurate measurement of the time at which a pulse was
detected on the external interrupt pin. The reference time can be chosen by setting the time source
parameter to UTC, GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, Galileo or local time in the CFG-TP-* configuration group.
The UTC standard can be set in the CFG-NAVSPG-* configuration group. The delay figures defined
with CFG-TP-* are also applied to the results output in the UBX-TIM-TM2 message.
A UBX-TIM-TM2 message is output at the next epoch if
• The UBX-TIM-TM2 message is enabled
• A rising or falling edge was triggered since last epoch on one of the EXTINT channels
The UBX-TIM-TM2 messages includes the time of the last timemark, new rising/falling edge
indicator, time source, validity, number of marks and a quantization error. The timemark is triggered
continuously.
Only the last rising and falling edge detected between two epochs is reported since the output
rate of the UBX-TIM-TM2 message corresponds to the measurement rate configured with
CFG-RATE-MEAS (see Figure below).

 Loading...
Loading...