LTE3311 Series User’s Guide
91
CHAPTER 10
NAT
10.1 Overview
NAT (Network Address Translation - NAT, RFC 1631) is the translation of the IP address of a host in
a packet. For example, the source address of an outgoing packet, used within one network is
changed to a different IP address known within another network.
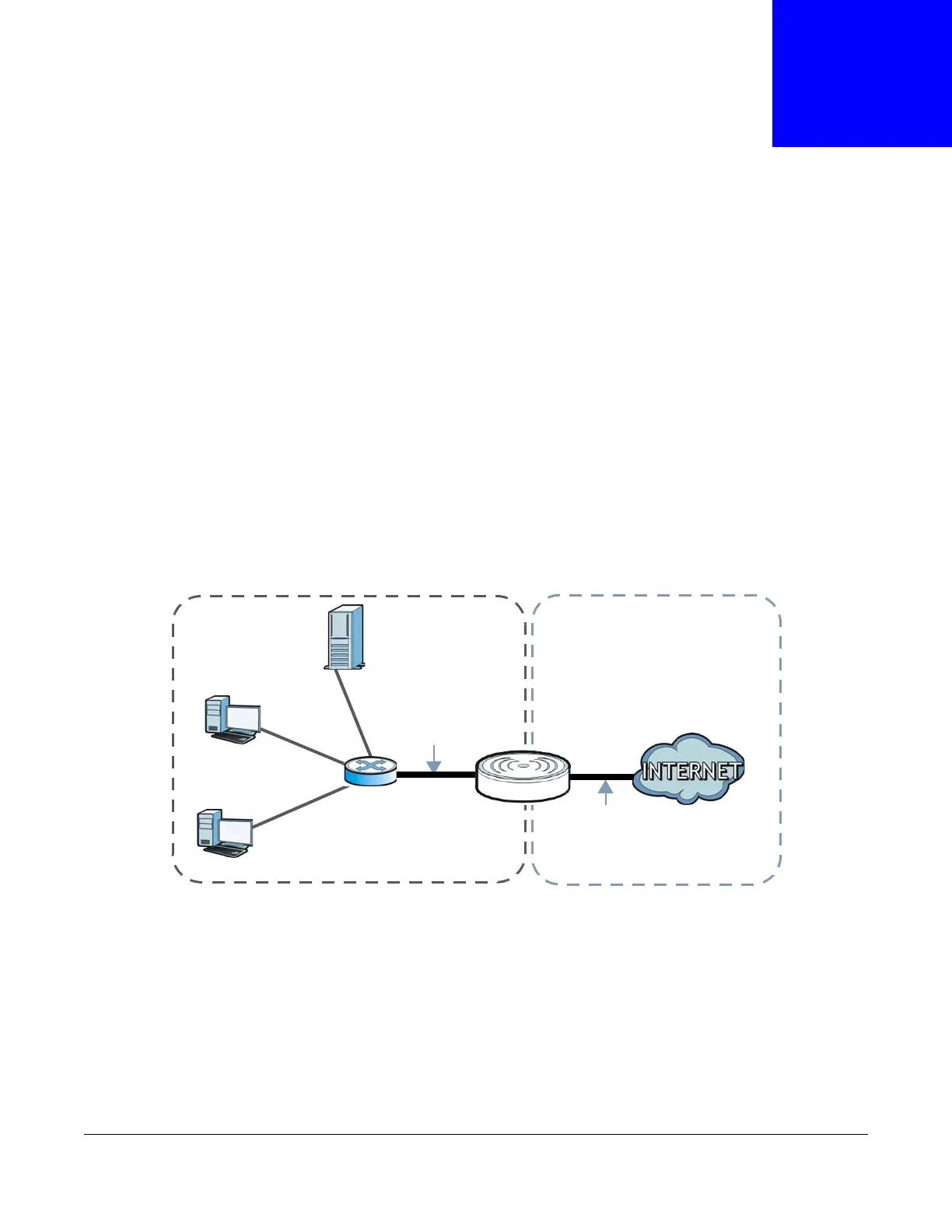
The figure below is a simple illustration of a NAT network. You want to assign ports 21-25 to one
FTP, Telnet and SMTP server (A in the example), port 80 to another (B in the example) and assign
a default server IP address of 192.168.1.35 to a third (C in the example).
You assign the LAN IP addresses to the devices (A to D) connected to your LTE3311. The ISP
assigns the WAN IP address. The NAT network appears as a single host on the Internet. All traffic
coming from A to D going out to the Internet use the IP address of the LTE3311, which is
192.168.1.1.
Figure 55 NAT Example
Note: You must create a firewall rule in addition to setting up NAT, to allow traffic from
the WAN to be forwarded through the LTE3311.
10.1.1 What You Can Do
•Use the General screen to enable NAT (Section 10.2 on page 92).
•Use the Port Forwarding screen to set a default server and change your LTE3311’s port
forwarding settings to forward incoming service requests to the server(s) on your local network
(Section 10.3 on page 92).
A: 192.168.1.33
B: 192.168.1.34
C: 192.168.1.35
IP address
192.168.1.1
WANLAN
assigned by ISP
FTP, Telnet, SNMP
Port 80
Ports 21 to 25

 Loading...
Loading...











