Agilent 1260 Infinity DAD and MWD User Manual 105
How to optimize the Detector
5
Optimizing for Sensitivity, Selectivity, Linearity and Dispersion
Peak width (response time)
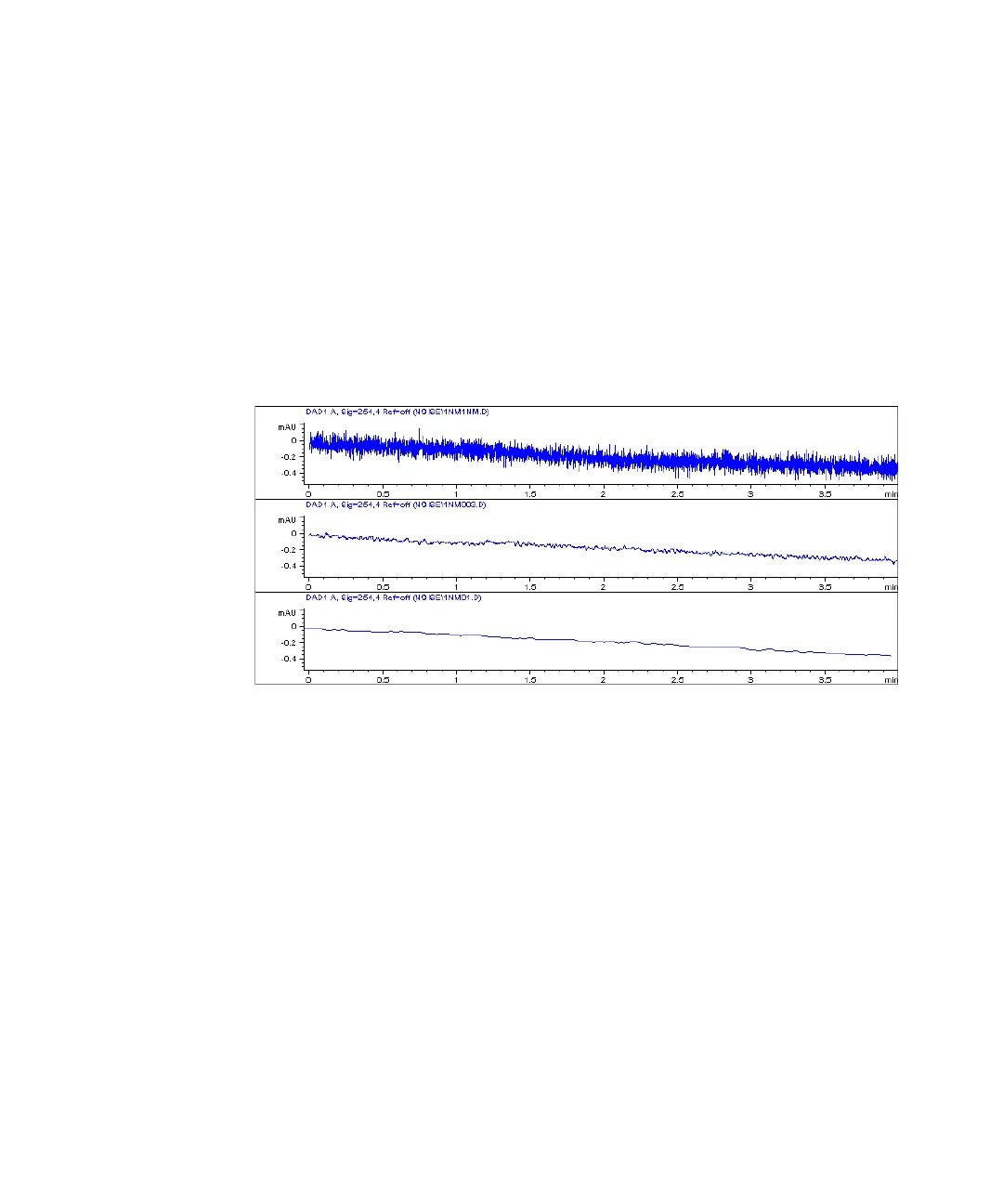
Response time describes how fast the detector signal follows a sudden change
of absorbance in the flow cell. The detector uses digital filters to adapt
response time to the width of the peaks in your chromatogram. These filters
do not affect peak area nor peak symmetry. When set correctly, such filters
reduce baseline noise significantly (Figure 34 on page 105), but reduce peak
height only slightly. In addition, these filters reduce the data rate to allow
optimum integration and display of your peaks and to minimize disk space
required to store chromatograms and spectra.
Figure 34 Influence of Response Time on Signal and Noise
Table 17 on page 106 lists the filter choices of the detector. To get optimum
results, set peak width as close as possible to a narrow peak of interest in your
chromatogram. Response time will the be approximately 1/3 of the peak
width, resulting in less than 5 % peak-height reduction and less than 5 %
additional peak dispersion. Decreasing the peak width setting in the detector
will result in less than 5 % gain in peak height but baseline noise will increase
by a factor of 1.4 for a factor of 2 response-time reduction. Increasing peak
width (response time) by factor of two from the recommended setting
(over-filtering) will reduce peak height by about 20 % and reduce baseline
noise by a factor of 1.4. This gives you the best possible signal-to-noise ratio,
but may affect peak resolution.
8QILOWHUHG
5HVSRQVHWLPH
PLQ
5HVSRQVHWLPH
PLQ

 Loading...
Loading...











