1 of 24
Jun 2001
Detectors
Agilent 6890 Gas Chromatograph Service Manual
330 Thermal Conductivity Detector
(TCD)
Theory of operation
The TCD responds to any compounds whose thermal conductivity is different
from the thermal conductivity of the carrier gas alone. The TCD cell is a dual
channel device, with an empty flow path and a path containing a detector
filament. A switching valve alternates between sending the column effluent
(containing analytes) through the empty and the active flow paths. When the
column effluent flows through the empty channel, a pure stream of reference
gas maintains an equilibrium through the filament path. The reference gas is
used to compare thermal conductivity changes caused by the column effluent.
A gas with high thermal conductivity, such as helium, is used as the carrier/
make-up/reference gas. When the analyte is present in the gas stream, the
thermal conductivity drops, and less heat is lost to the cavity wall. Under
constant applied voltage, a silicon nitride coated filament in the TCD cell will
heat up and its resistance will increase. This change is what is recorded and
measured for the chromatogram.
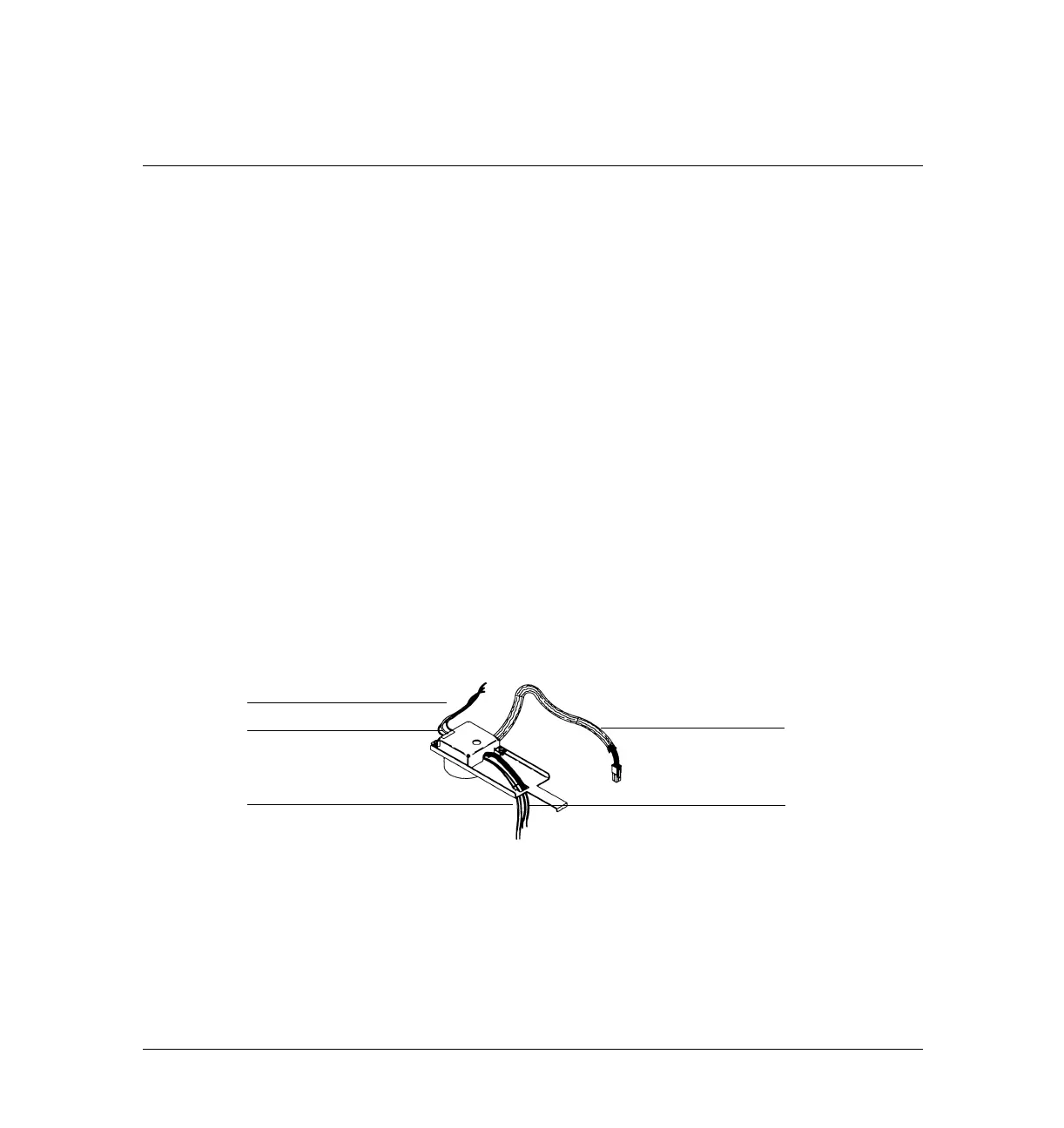
Figure 330-1 The Thermal Conductivity Detector (TCD)
Pneumatic lines
Detector body
Heater/sensor cable
Filament leads
∆ PRT leads
(under cover)

 Loading...
Loading...