7-4
To Control External GPIB Devices
Agilent B2200 control example
To send command
Value 1
Value 2
Value 3
Value 4
{0}
{1}
{2}
{3}
Programming image:
*RST
:ROUT:FUNC ACON
(enters “SMU1” to StringPort)
:ROUT:SYMB:PORT {0},”{1}”
:ROUT:SYMB:PORT? {0}
(reads string data)
*OPC?
(reads operation complete flag)
(enters “OUT1” to StringCh)
:ROUT:SYMB:CHAN {0},{2},”{1}”
:ROUT:SYMB:CHAN? {0},{2}
(reads string data)
*OPC?
(reads operation complete flag)
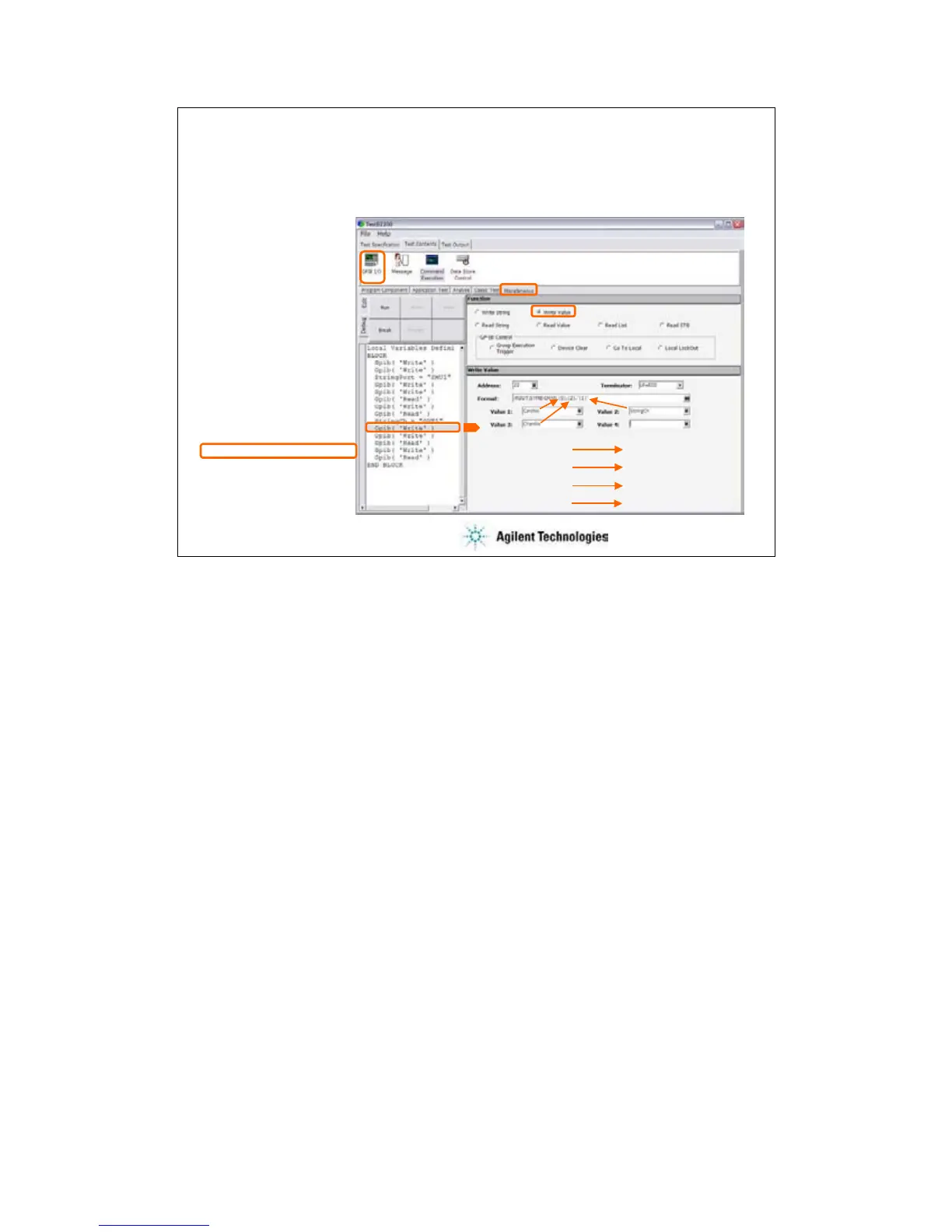
This slide shows an example setup of the GPIB I/O statement. This is a component of the test
contents used to control the Agilent B2200 switching matrix.
This example uses the Write Value function to send the following command to the B2200.
:ROUT:SYMB:CHAN {0},{2},”{1}”
where, {0} is CardNo, {1} is StringCh, and {2} is ChanNo.
The followings are the reference of the setup editor.
•Address: GPIB address of the device
•Terminator: EOI, LF, CR/LF, LF+EOI, CR/LF+EOI, or NONE (no terminator)
•Format: Command (header and parameters) sent to the device
•Value 1: Value for {0}
•Value 2: Value for {1}
•Value 3: Value for {2}
•Value 4: Value for {3}
{0}. {1}, {2}, and {3} are variable available in the Format field only.
Note:
Use double quotes to enter a string to a local variable by using the Assign statement.
 Loading...
Loading...