PAGE 41
8.2 8.2
8.2 8.2
8.2
ZEROZERO
ZEROZERO
ZERO
Procedure (first-time sensor calibration only) Procedure (first-time sensor calibration only)
Procedure (first-time sensor calibration only) Procedure (first-time sensor calibration only)
Procedure (first-time sensor calibration only)
Zero the sensor if it is being calibrated for the first time. If not, disregard this subsection and
proceed with calibrating the sensor span (Section 4.3, 4.4 or 4.5).
NOTE: When using a new sensor, always perform a “RESET CALIBRATE” using the TEST/
MAINT menu (Section 9.8)
before zeroing and calibrating.
1. Make sure that the sensor is dry before zeroing.
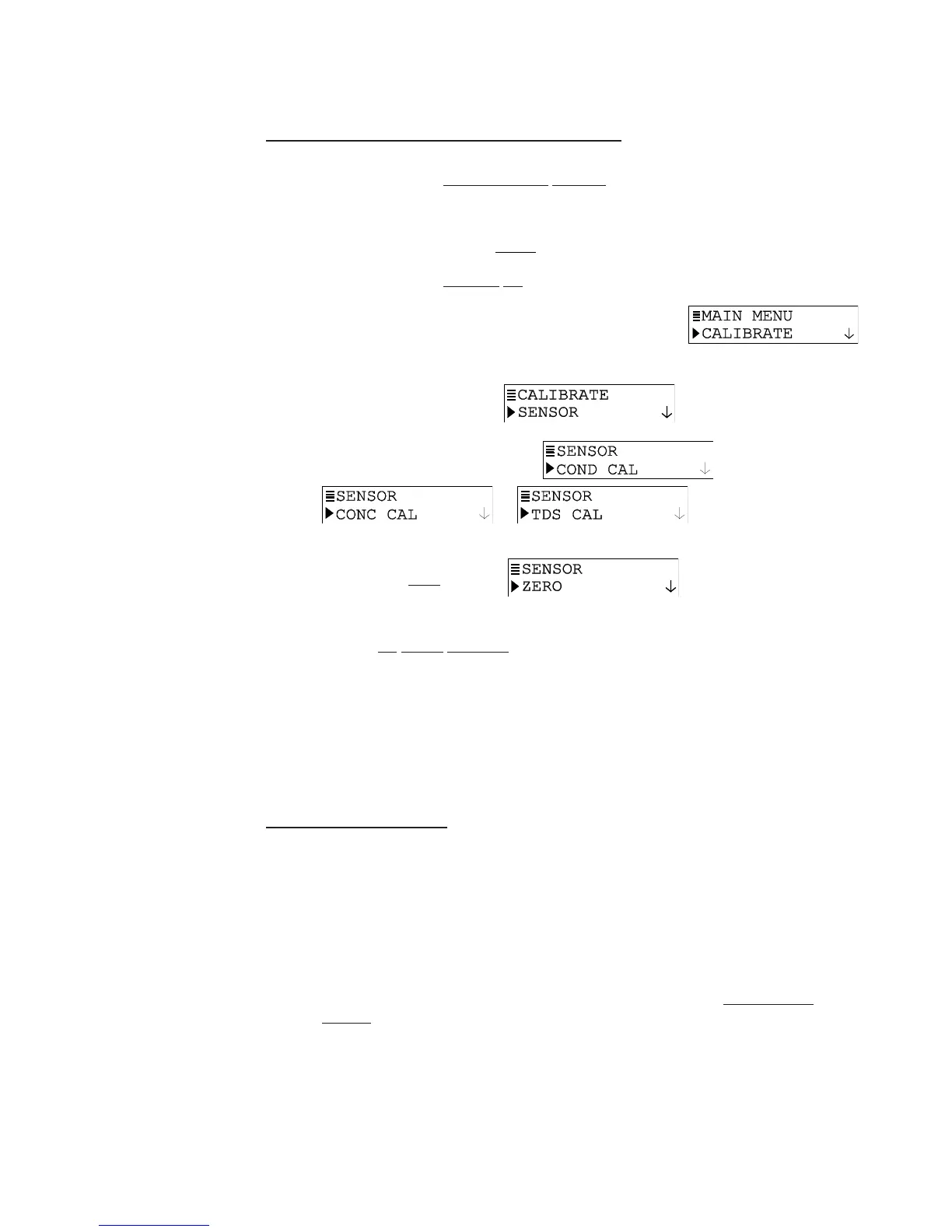
2. Press MENU key to display a “MAIN MENU” screen. If the
screen is not showing, use
ØØ
ØØ
Ø or
××
××
× key to display it.
3. Press ENTER key to display
.
4. Press ENTER key again to display
,
, or (displayed screen depends
on selected measurement).
5. Press
ØØ
ØØ
Ø key twice to display .
6. Press ENTER key to display the “ZERO: IN DRY AIR?” screen.
7. With the dry sensor held in air, press ENTER key again to start automatic zeroing.
NOTE: During zeroing, the analog output is automatically “held” at the last measured value.
8. After the “ZERO: CONFIRM ZERO OK” screen appears, press ENTER key to end
zeroing.
9. After the “ZERO: CONFIRM ACTIVE?” screen appears, press ENTER key to return the
analog output to its active state (MEASURE screen appears).
This completes zeroing the sensor.
8.3 Conductivity Calibration8.3 Conductivity Calibration
8.3 Conductivity Calibration8.3 Conductivity Calibration
8.3 Conductivity Calibration
After zeroing the sensor (first-time sensor calibration only), calibrate the sensor span using one
of these methods:
• COND CAL Method: This method requires removing the sensor from the process,
immersing it into a conductivity reference solution, and entering a reference for
temperature compensation, and the known linear % per °C slope and conductivity
value of the reference solution.
• SAMPLE CAL Method: This method allows keeping the sensor installed in the
process, but requires you to obtain a process sample, determine its value by laboratory
analysis or comparison reading, and enter that value.
• ELECTRONIC CAL Method: This method requires that the sensor be removed from
the process and utilizes a decade resistance box to simulate conductivity rather than
an actual solution.
 Loading...
Loading...