Version 7.2 271 Mediant 1000B Gateway & E-SBC
User's Manual 15. Services
"additionalRoute" attribute in HTTP Get Route request) to the Routing server, sends a
new routing request to the Routing server. The Routing server may respond with a
new route destination, thereby implementing alternative routing. Alternatively, it may
enable the device to return a failure response to the previous device in the route path
chain and respond with an alternative route to this device. Therefore, alternative
routing can be implemented at any point in the route path. If the Routing server sends
an HTTP 404 "Not Found" message for an alternative route request, the device rejects
the call. If the Routing server is configured to handle alternative routing, the device
does not make any alternative routing decisions based on its alternative routing tables.
Call Status: The device can report call status to the Routing server to indicate
whether a call has successfully been established and/or failed (disconnected). The
device can also report when an IP Group (Proxy Set) is unavailable, detected by the
keep-alive mechanism, or when the CAC thresholds permitted per IP Group have
been crossed. For Trunk Groups, the device reports when the trunk's physical state
indicates that the trunk is unavailable.
Credentials for Authentication: The Routing Server can provide user (e.g., IP Phone
caller) credentials (username-password) in the Get Route response, which can be
used by the device to authenticate outbound SIP requests if challenged by the
outbound peer, for example, Microsoft Skype for Business (per RFC 2617 and RFC
3261). If multiple devices exist in the call routing path, the Routing server sends the
credentials only to the last device ("node") in the path.
To configure routing based on Routing server:
1. For each configuration entity (e.g., IP Group) that you want routing done by the
Routing server, configure the entity's 'Used By Routing Server' parameter to Used:
Figure 15-44: Configuring Entity to Use Routing Server
2. Configure an additional Security Administrator user account in the Local Users table
(see ''Configuring Management User Accounts'' on page 65), which is used by the
Routing server (REST client) to log in to the device's management interface.
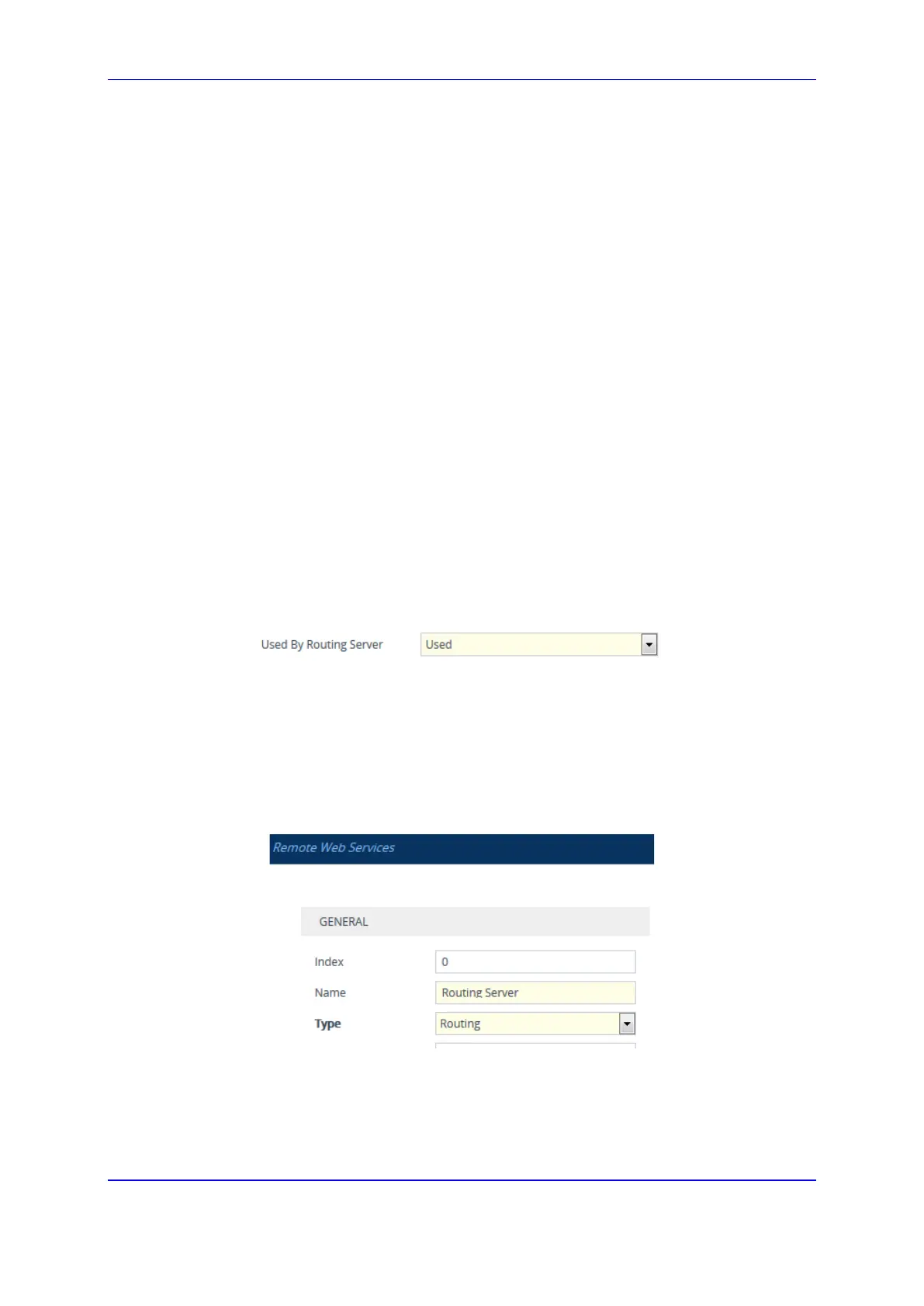
3. Configure the address and connection settings of the Routing server, referred to as a
Remote Web Service and HTTP remote host (see ''Configuring Remote Web
Services'' on page 262). You must configure the 'Type' parameter of the Remote Web
Service to Routing, as shown in the following example:
Figure 15-45: Configuring Remote Web Service for Routing Server

 Loading...
Loading...



















