Version 7.2 627 Mediant 1000B Gateway & E-SBC
User's Manual 28. SBC Overview
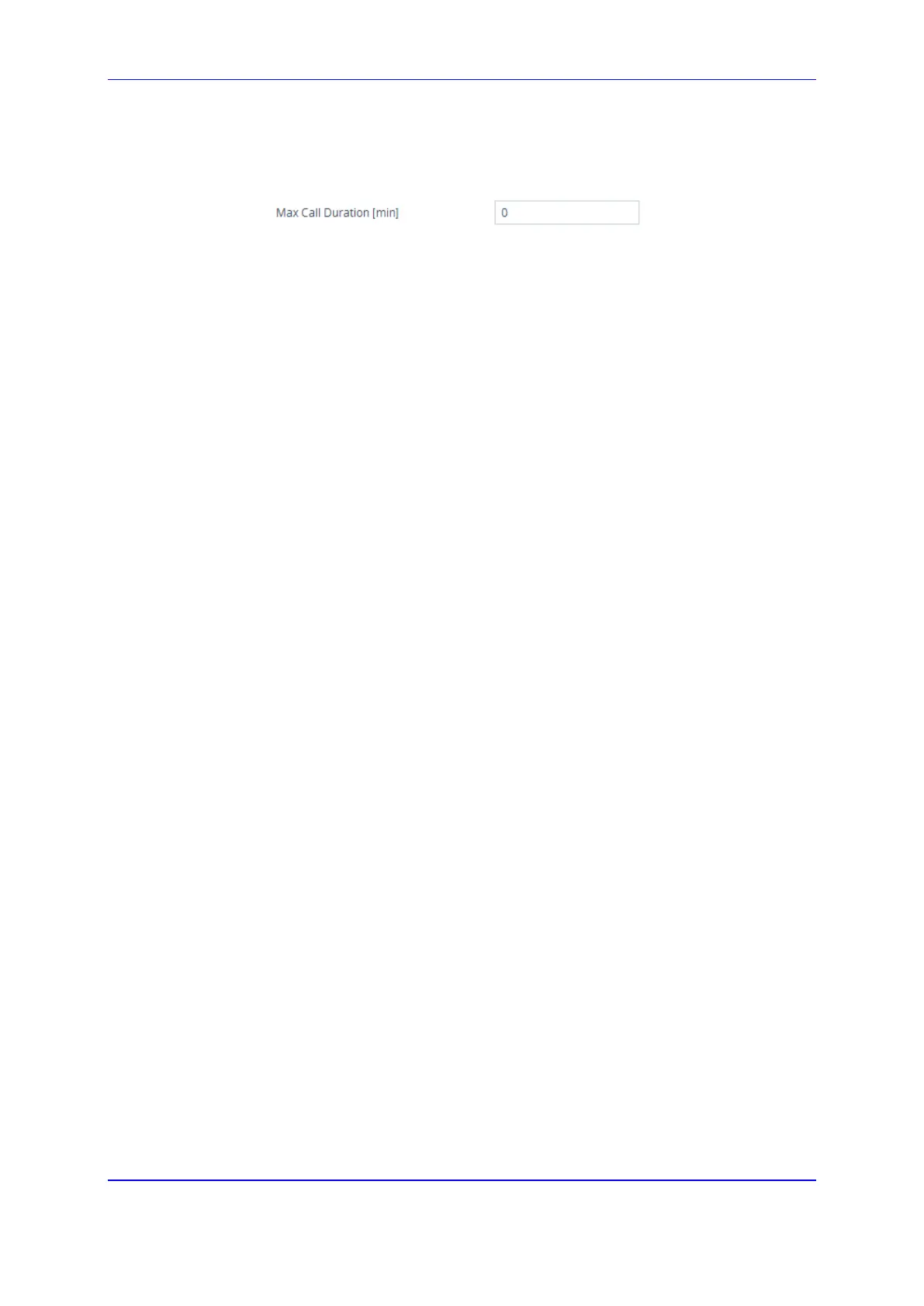
2. In the 'Max Call Duration' field (SBCMaxCallDuration), enter the maximum call
duration per SBC call:
Figure 28-6: Configuring Maximum Call Duration
3. Click Apply.
28.8 SBC Authentication
The device can authenticate SIP servers and SBC users (clients). The different
authentication methods are described in the subsequent subsections.
28.8.1 SIP Authentication Server Functionality
The device can function as an Authentication server for authenticating received SIP
message requests, based on HTTP authentication Digest with MD5. Alternatively, such
requests can be authenticated by an external, third-party server.
When functioning as an Authentication server, the device can authenticate the following
SIP entities:
SIP servers: This is applicable to Server-type IP Groups. This provides protection
from rogue SIP servers, preventing unauthorized usage of device resources and
functionality. To authenticate remote servers, the device challenges the server with a
user-defined username and password that is shared with the remote server. When the
device receives an INVITE request from the remote server, it challenges the server by
replying with a SIP 401 Unauthorized response containing the WWW-Authenticate
header. The remote server then re-sends the INVITE containing an Authorization
header with authentication information based on this username-password combination
to confirm its identity. The device uses the username and password to authenticate
the message prior to processing it.
SIP clients: These are clients belonging to a User-type IP Group. This support
prevents unauthorized usage of the device's resources by rogue SIP clients. When the
device receives an INVITE or REGISTER request from a client (e.g., SIP phone) for
SIP message authorization, the device processes the authorization as follows:
1. The device challenges the received SIP message only if it is configured as a SIP
method (e.g., INVITE) for authorization. This is configured in the IP Groups table,
using the 'Authentication Method List' parameter.
2. If the message is received without a SIP Authorization header, the device
"challenges" the client by sending a SIP 401 or 407 response. The client then
resends the request with an Authorization header (containing the user name and
password).
3. The device validates the SIP message according to the AuthNonceDuration,
AuthChallengeMethod and AuthQOP parameters.
♦ If validation fails, the device rejects the message and sends a 403
(Forbidden) response to the client.
♦ If validation succeeds, the device verifies client identification. It checks that
the username and password received from the client is the same username
and password in the device's User Information table / database (see ''SBC
User Information for SBC User Database'' on page 759). If the client is not
successfully authenticated after three attempts, the device sends a SIP 403
(Forbidden) response to the client. If the user is successfully identified, the
device accepts the SIP message request.

 Loading...
Loading...



















