6 Parameter Settings and Functions
© Copyright Reserved Autonics Co., Ltd. 75
6.3.3 PID control [PAR3 → C-MD → PID]
PID control is a combination of proportional (P), integral (I), and derivative (D) controls and offers
superb control over the control subjects, even with a delay time.
Proportional control (P) implements smooth,
hunting-free control; integral control (I) automatically corrects offsets;
and derivative control (D) speeds up the response to disturbance. Through these actions, PID
control realizes ideal temperature control.
Applied PID Control Technique
Proportional Control (P): Select PID control and set the integral and derivative time to 0000.
Proportional Integral Control (PI): Select PID control and set the derivative time to 0000.
Proportional Derivative Control (PD): Select PID control and set the integral time to 0000.
Multi SV: Use the same PID time constant for the values of SV0 to SV3.
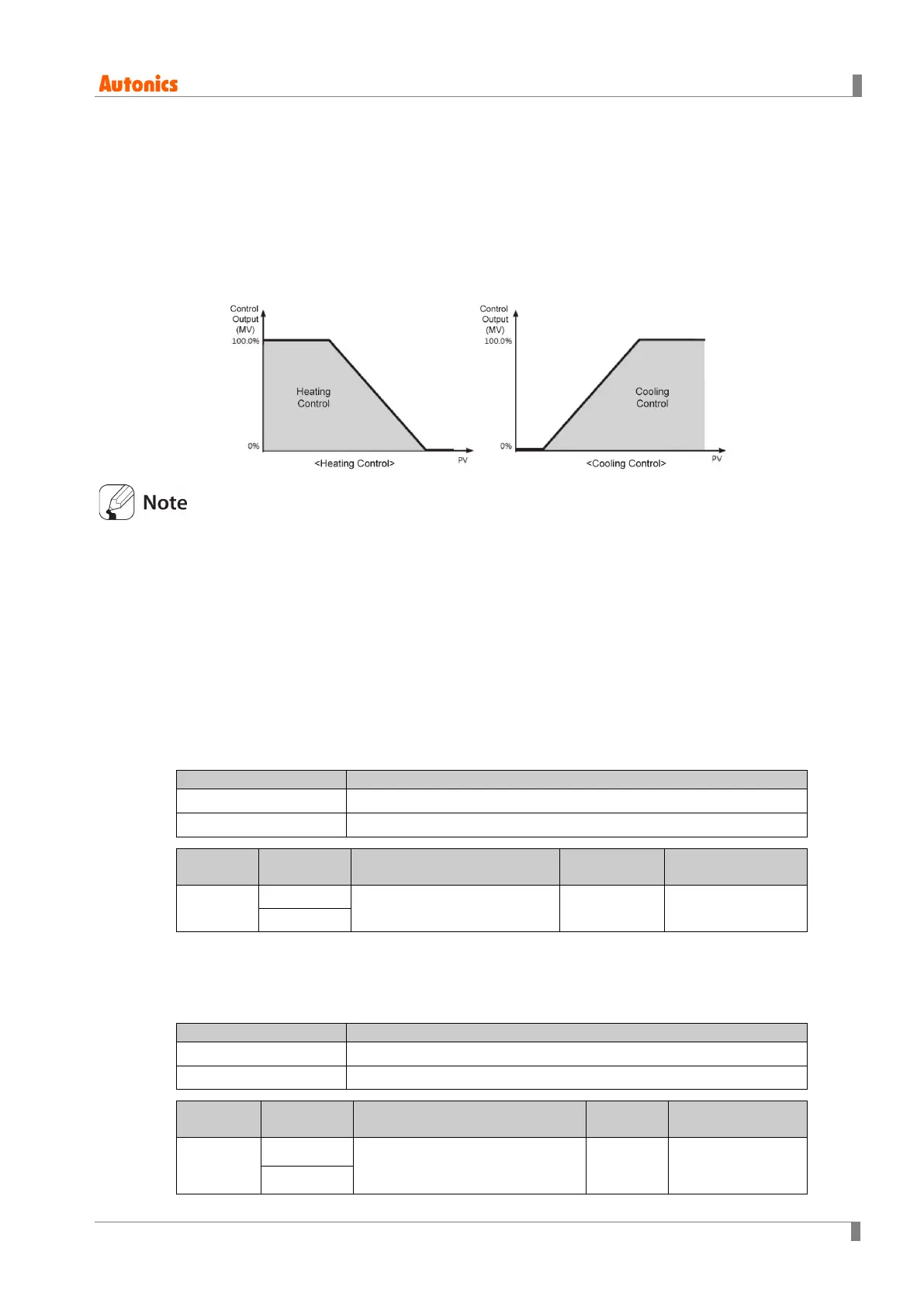
6.3.3.1 Proportional band settings [PAR2 → H-P/C-P]
When present value (PV) is within the Proportional Band (P), the ON/OFF ratio needs to be
adjusted during the proportional period (T). The defined proportional control (time proportional
control) section is called as the proportional band.
H-P
Heating proportional band
C-P
Cooling proportional band
Parameter Setting range
Unit
PAR2
H-P
00)1 to 99(9 01)0
Temperature: ℃/℉
C-P
6.3.3.2 Integral time settings [PAR2 → H-I/C-I]
MVs from integral and proportional operation become the same when deviation is consistent.
The time taken for the two MVs to match is called the integral time.
H-I
Heating integral time
C-I Cooling integral time
Parameter Setting range
Unit
PAR2
H-I
0000 to 9999 0000 Sec
C-I
 Loading...
Loading...











