BayStack 350 10/100/1000 Series Switches
304376-B Rev 00
1-57
Spanning Tree Considerations
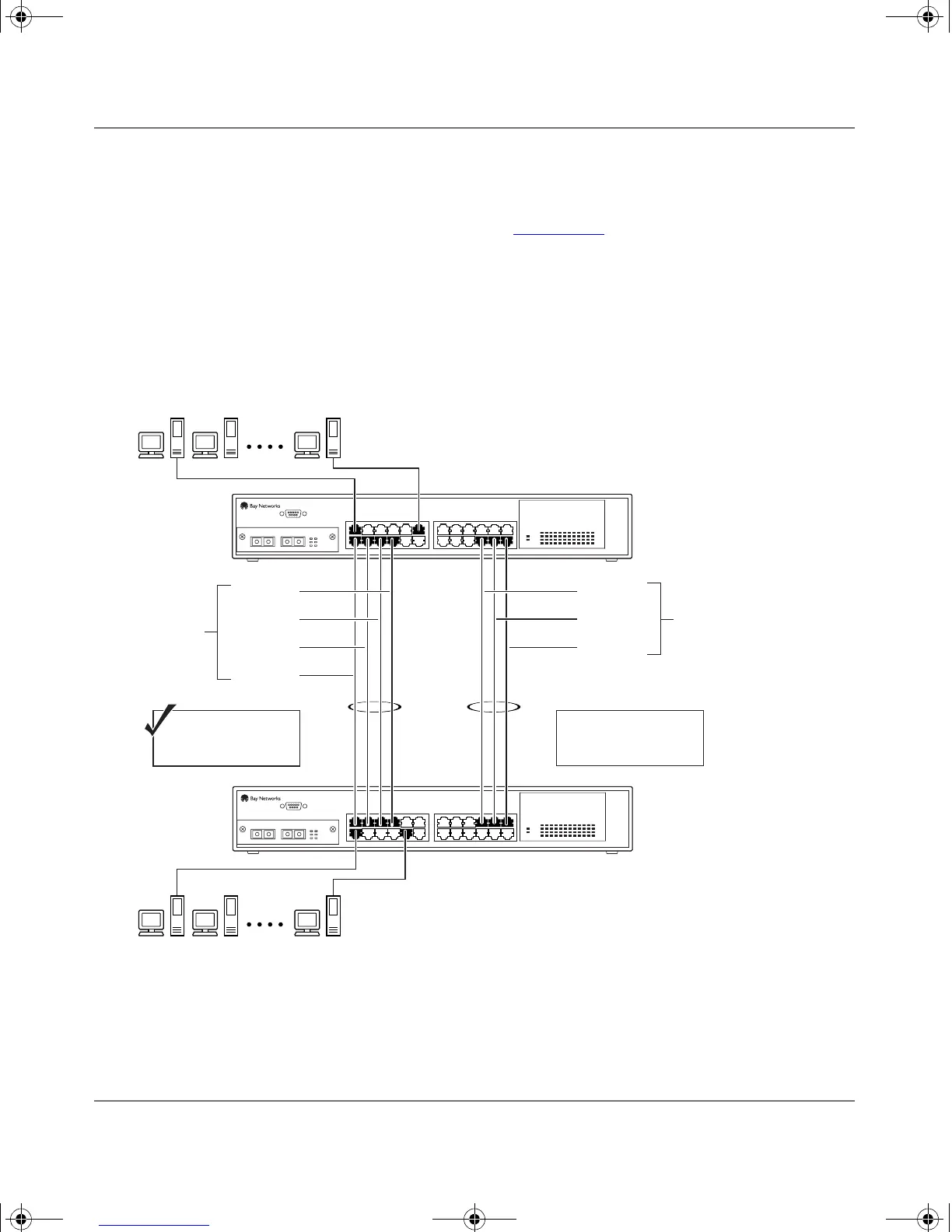
The spanning tree Path Cost parameter is recalculated based on the aggregate
bandwidth of the trunk. For example, Figure 1-39
shows a four port trunk (T1)
with two port members operating at 100 Mb/s and the other two port members
operating at 10 Mb/s. Trunk T1 provides an aggregate bandwidth of 220 Mb/s.
The Path Cost for T1 is 4 (Path Cost = 1000/LAN speed, in Mb/s). If a second
three port trunk (T2) is configured with an aggregate bandwidth of 210 Mb/s, with
a comparable Path Cost of 4, the switch software chooses the trunk with the larger
bandwidth (T1) to determine the most efficient path.
Figure 1-39. Path Cost Arbitration Example
BS35029A
T1 T2
100 Mb/s
100 Mb/s
10 Mb/s
100 Mb/s
100 Mb/s
10 Mb/s
10 Mb/s
Path Cost T1 = 4
S1
S2
Path Cost T2 = 4
Aggregate Bandwidth
220 Mb/s
Aggregate Bandwidth
210 Mb/s
kombk.book Page 57 Thursday, February 18, 1999 10:59 AM
 Loading...
Loading...