route. Their policy might be to use the IGP-learned path as the preferred path and to use the eBGP-learned
path when the IGP path is down. See Figure 3: Back Door Example , on page 43.
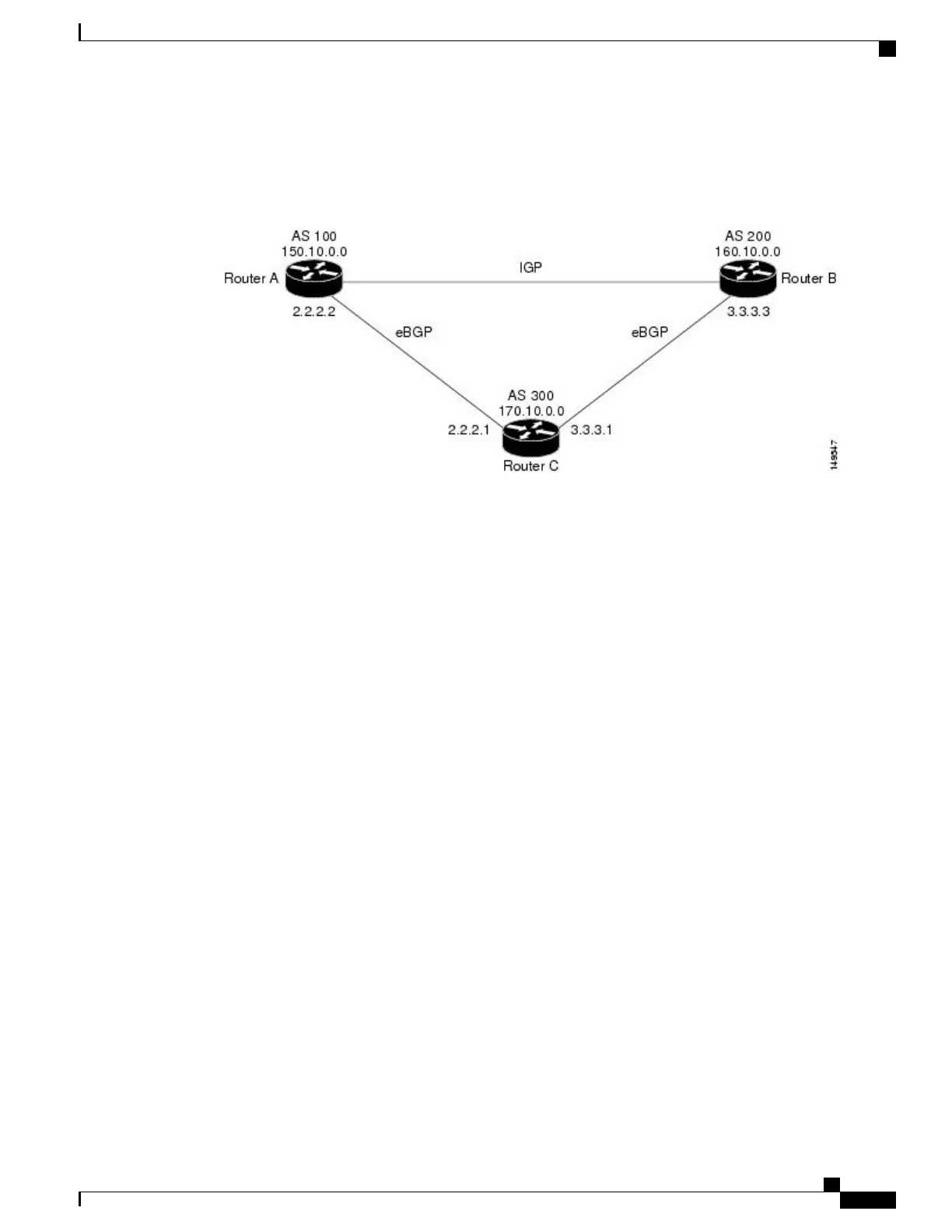
Figure 3: Back Door Example
In Figure 3: Back Door Example , on page 43, Routers A and C and Routers B and C are running eBGP.
Routers A and B are running an IGP (such as Routing Information Protocol [RIP], Interior Gateway Routing
Protocol [IGRP], Enhanced IGRP, or Open Shortest Path First [OSPF]). The default distances for RIP, IGRP,
Enhanced IGRP, and OSPF are 120, 100, 90, and 110, respectively. All these distances are higher than the
default distance of eBGP, which is 20. Usually, the route with the lowest distance is preferred.
Router A receives updates about 160.10.0.0 from two routing protocols: eBGP and IGP. Because the default
distance for eBGP is lower than the default distance of the IGP, Router A chooses the eBGP-learned route
from Router C. If you want Router A to learn about 160.10.0.0 from Router B (IGP), establish a BGP back
door. See .
In the following example, a network back-door is configured:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config)# router bgp 100
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# address-family ipv4 unicast
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-af)# network 160.10.0.0/16 backdoor
Router A treats the eBGP-learned route as local and installs it in the IP routing table with a distance of 200.
The network is also learned through Enhanced IGRP (with a distance of 90), so the Enhanced IGRP route is
successfully installed in the IP routing table and is used to forward traffic. If the Enhanced IGRP-learned
route goes down, the eBGP-learned route is installed in the IP routing table and is used to forward traffic.
Although BGP treats network 160.10.0.0 as a local entry, it does not advertise network 160.10.0.0 as it normally
would advertise a local entry.
Multiprotocol BGP
Multiprotocol BGP is an enhanced BGP that carries routing information for multiple network layer protocols
and IP multicast routes. BGP carries two sets of routes, one set for unicast routing and one set for multicast
routing. The routes associated with multicast routing are used by the Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM)
feature to build data distribution trees.
Cisco ASR 9000 Series Aggregation Services Router Routing Configuration Guide, Release 5.1.x
OL-30423-03 43
Implementing BGP
Multiprotocol BGP

 Loading...
Loading...











