1-8
Catalyst 6500 Series Content Switching Module Configuration Note
OL-4612-01
Chapter 1 Product Overview
Traffic Flow
Traffic Flow
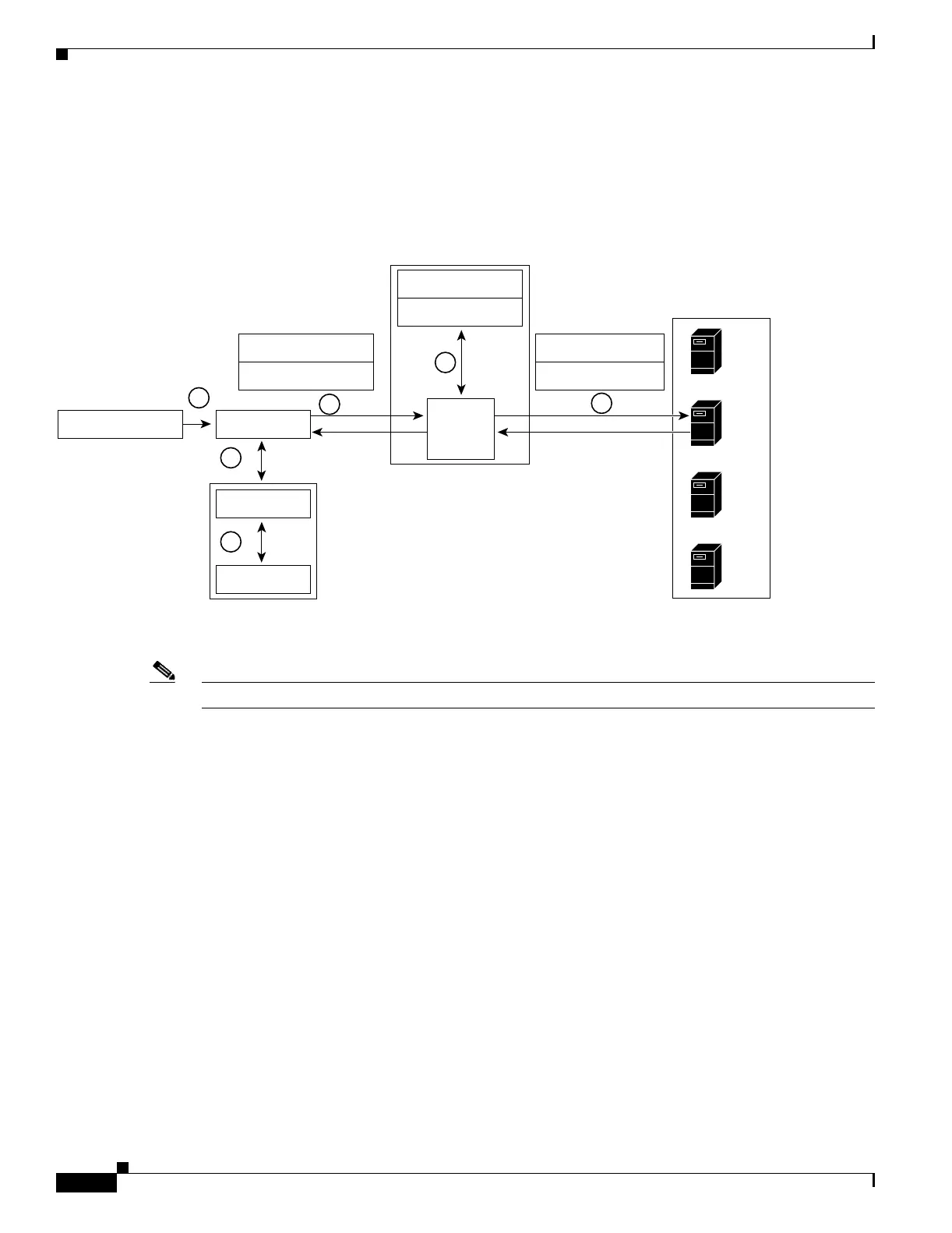
This section describes how the traffic flows between the client and server in a CSM environment.
(See Figure 1-3.)
Figure 1-3 Traffic Flow Between Client and Server
Note The numbers in Figure 1-3 correspond to the steps in the following procedure.
When you enter a request for information by entering a URL, the traffic flows as follows:
1. Yo u en te r a U R L . (Figure 1-3 shows www.example.com as an example.)
2. The client contacts a DNS server to locate the IP address associated with the URL.
3. The DNS server sends the IP address of the virtual IP (VIP) to the client.
4. The client uses the IP address (CSM VIP) to send the HTTP request to the CSM.
5. The CSM receives the request with the URL, makes a load-balancing decision, and selects a server.
For example, in Figure 1-3, the CSM selects a server (X server) from the www.example.com server
pool, replacing its own VIP address with the address of the X server (directed mode), and forwards
the traffic to the X server. If the NAT server option is disabled, the VIP address remains unchanged
(dispatch mode).
6. The CSM performs Network Address Translation (NAT) and eventually TCP sequence numbers
translation.
www.example.com
www.example.com
www.example.com
www.example.com
client
DNS
IP address
IP address
IP address
IP address
Content
Switching
Module
W
Server
X
Server
Y
Server
Z
Server
www.example.com
Server pool
1
2
3
4
5
6
47528

 Loading...
Loading...

















