Device components and controls
LD500 V2.03 Seite 9 von 67
9 Overview and application description of the different sensor types
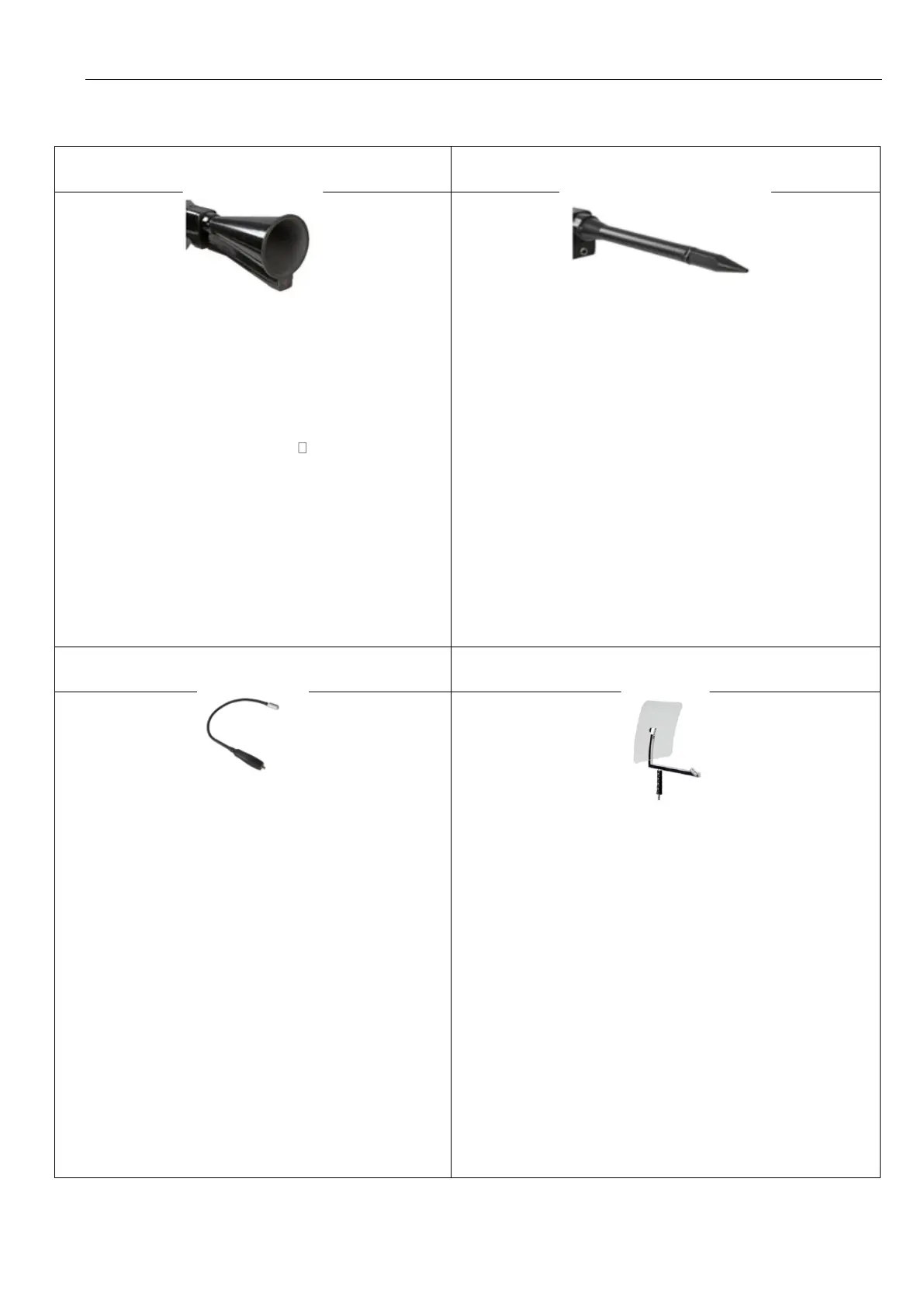
Acoustic trumpet (standard tool)
The acoustic trumpet bundles incident ultrasonic
waves, thereby extending the range of the device. This
behaviour makes it ideal for medium distances.
The leakage can be heard from large distances, for
precise detection, the user must approach the leakage
and consistently follow the "loudest" point. Individual
compressed air components are then checked for
precise detection.
Quantification distance (distance) 1 – 6 m
Use of acoustic trumpet:
• Average distance to pipe/component 0.2 - 6 m
• Low interfering noise
• Leakage freely accessible
• Use at distances of up to 6 metres if no
parabolic mirror available
The straightening tube permits only very few ultrasonic
waves to pass in the direction of the ultrasonic transducer,
allowing leakages to be located very precisely.
For this reason, the use of the straightening tube is
recommended for small distances, for the precise detection
of the corresponding leakage.
Quantification distance: 0…0,2 m
Use of focus tube:
• Short distance to pipe/component 0.05 m
• Pipe/component freely accessible
• Pipes and components to be inspected are very
close together
• Medium to high noise
• Use when no gooseneck available
The gooseneck should be used if the pipes and
components to be inspected are physically very close.
In addition, the shape of the gooseneck can be flexibly
adapted to easily inspect hard-to-reach pipes and
components.
The sensitivity of the gooseneck has been reduced to
dampen noise. This makes it ideal for target-ed, local
testing of compressed air components at high noise
levels, for example in systems using pneumatic
cylinders and in compressed air distribution cabinets
Quantification distance → 0 …0.05m
Use of gooseneck:
• Short distance to pipe/component 0.05 m
• Leakage not freely accessible
• Medium to high ultrasonic noise
• Pipes and components to be inspected are
very close together
The parabolic mirror bundles horizontally incident
ultrasound in its focal point where the ultrasonic transducer
is located. On the one hand, this leads to a considerable
amplification of the measured ultrasound (high range) and,
on the other hand, to a very precise directional behaviour,
since ultra-sound that does not incident horizontally is
reflected by the reflector.
The combination of these two characteristics enables the
parabolic mirror to precisely locate leaks at large distances.
Quantification distance → 3 – 12 m
Use of parabolic mirror:
• Large distance to pipe/components 3 – 15 m
• Interfering noise
• Leakage not freely accessible (behind a fence)
• Near leaks (superimposition))

 Loading...
Loading...