Circuit Descriptions
3.1 Introduction
3
3-3
3.1 Introduction
Section 3.2 describes the functional block diagram shown in Figure 3-1. It provides a
quick way to get familiar with the test tool basic build-up.
Section 3.3 describes the principle of operation of the test tool functions in detail, on the
basis of the circuit diagrams shown in Figures 9-1 to 9-5.
For all measurements, input signals are applied to the shielded input banana jackets.
Traces and readings are derived from the same input signal samples.
3.2 Block Diagram
In the block diagram Figure 3-1, the test tool is divided in five main blocks. Each block
represents a functional part, build up around an Application Specific Integrated Circuit
(ASIC). A detailed circuit diagram of each block is shown in Section 9.
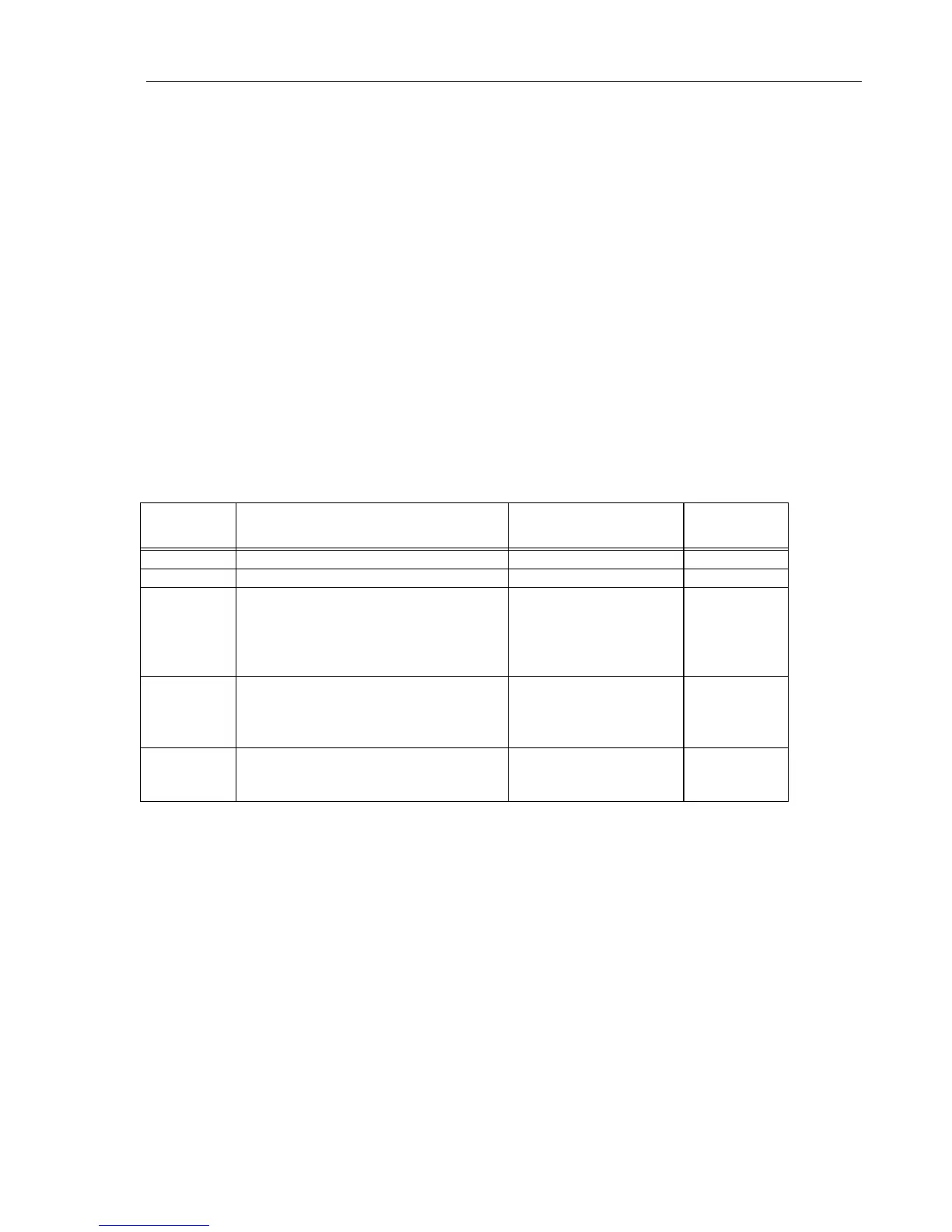
Table 3-1 provides an overview of the blocks in which the test tool is broken down, the
main block function, the ASIC name, and the applicable circuit diagram.
Table 3-1. Fluke 43B Main Blocks
Block Main Functions ASIC Circuit
Diagram
INPUT 1 Input 1 signal conditioning C(hannel)-ASIC OQ0258 Figure 9-1
INPUT 2 Input 2 signal conditioning C(hannel)-ASIC OQ0258 Figure 9-2
TRIGGER Trigger selection and conditioning
Current source for resistance, capacitance,
continuity, and diode measurements
AC/DC input coupling and Ω/F relay control
Voltage reference source
T(rigger)-ASIC OQ0257 Figure 9-3
DIGITAL Analog to Digital Conversion
Acquisition of ADC samples
Micro controller (µP-ROM-RAM)
Keyboard- and LCD control
D(igital)-ASIC MOT0002 Figure 9-4
POWER Power supply, battery charger
LCD back light voltage converter
Optical interface input
P(ower)-ASIC OQ0256 Figure 9-5
All circuits, except the LCD unit and the KEYBOARD, are located on one Printed
Circuit Board (PCB), called the MAIN PCB.
The ASIC’s are referred to as C-ASIC (Channel ASIC), T-ASIC (Trigger ASIC), P-ASIC
(Power ASIC), and D-ASIC (Digital ASIC).
3.2.1 Input 1 - Input 2 Measurement Circuits
The basic input signal for the Input 1 and Input 2 circuits (hardware) is voltage. The
reading of Input 1 is in (milli)Volts. The reading of Input 2 is in Amperes. So the
voltage on Input 2 is assumed to be supplied by a current clamp. From the measured
voltage samples the readings are calculated by the instrument firmware. For example:
power readings are calculated from the Input 1 and Input 2 voltage samples.

 Loading...
Loading...