Air Supply Equipment
70-6925 131
Humidistats
and
Thermostats Controllers Sensors Relays Switches Actuators Valves Accessories
Engineering
Guide
Cross
Reference
outdoor air is available. After the air is compressed, cooling and
settling actions in the tank condense some of the excess
moisture and allow fallout of the larger oil droplets generated by
the compressor pump.
A high pressure safety relief valve which opens on excessively
high tank pressures is also required. A hand valve or automatic
trap periodically blows off any accumulated moisture, oil
residue, or other impurities that collect in the bottom of the tank.
Air Drying Techniques
General
Air should be dry enough to prevent condensation.
Condensation causes corrosion that can block orifices and
valve mechanisms. In addition, dry air improves the ability of
filters to remove oil and dirt.
Moisture in compressed air is removed by increasing pressure,
decreasing temperature, or both. When air is compressed and
cooled below its saturation point, moisture condenses. Draining
the condensate from the storage tank causes some drying of
the air supply, but an air dryer is often required.
An air dryer is selected according to the amount of moisture in
the air and the lowest temperature to which an air line will be
exposed. For a chart showing temperature and moisture
content relationships at various air pressures, refer to the
General Engineering Data section.
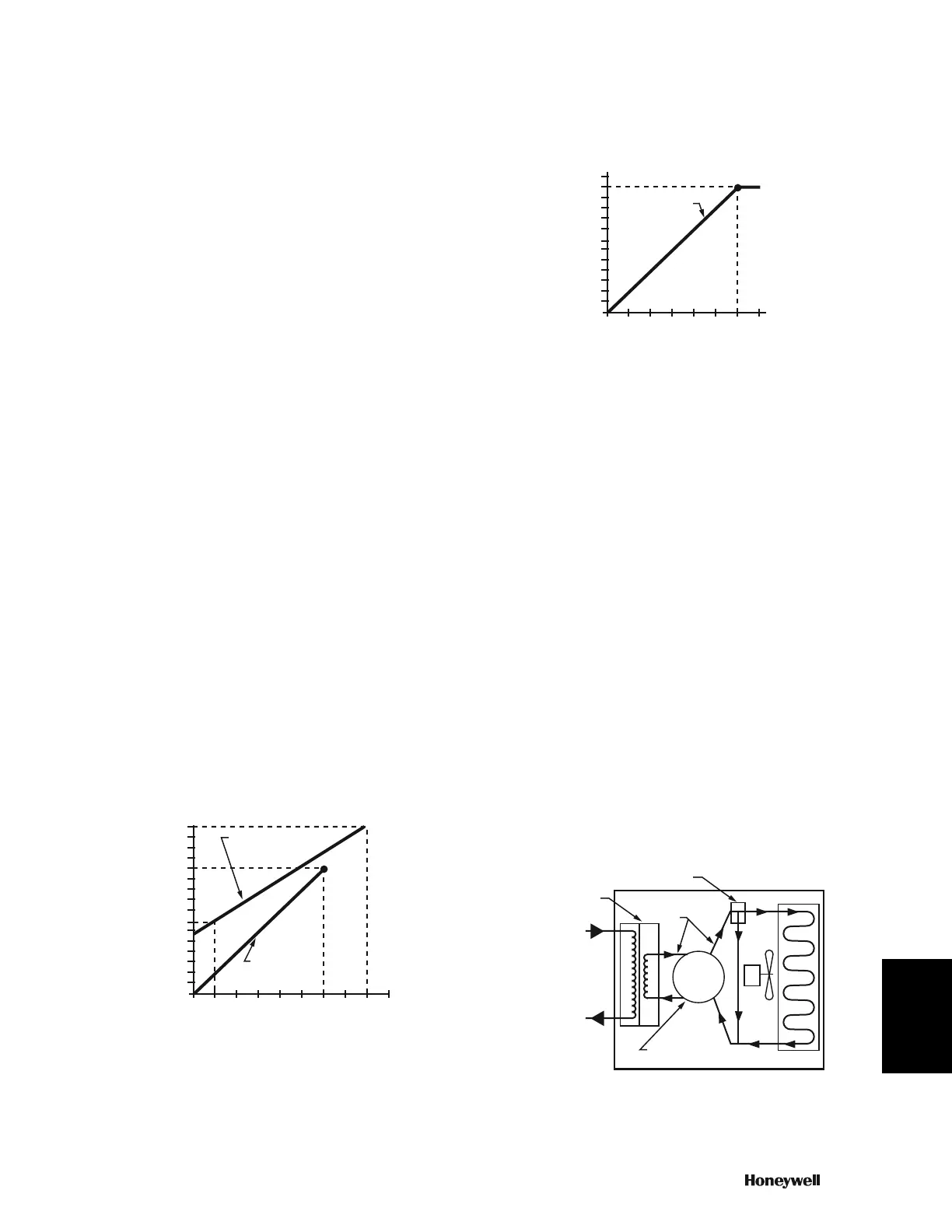
Dry Air Requirement
The coldest ambient temperature to which tubing is exposed is
the criterion for required dryness, or dew point. Dew point is the
temperature at which moisture starts to condense out of the air.
The coldest winter exposure is normally a function of outdoor
air temperature. Summer exposure is normally a function of
temperature in cold air ducts or air conditioned space. The
typical coldest winter application is an air line and control device
(e.g., damper actuator) mounted on a rooftop air handling unit
and exposed to outdoor air temperatures (Fig. 12). The second
coldest winter exposure is an air line run in a furred ceiling or
outside wall.
Fig. 12. Winter Dew Point Requirement.
A typical summer minimum dew point application is a cold air
plenum. Figure 13 shows a 50F plenum application along with
winter requirements for a year-round composite.
Fig. 13. Twelve-Month Composite
Dew Point Requirement.
CONDENSING DRYING
The two methods of condensing drying are high-pressure
drying and refrigerant drying.
High-Pressure Drying
High-pressure drying may be used when main air piping is kept
away from outside walls and chilling equipment. During
compression and cooling to ambient temperatures, air gives up
moisture which then collects in the bottom of the storage tank.
The higher the tank pressure, the greater the amount of
moisture that condenses. Maintaining a high pressure removes
the maximum amount of moisture. The compressor should
have a higher operating pressure than is required for air supply
purposes only. However, higher air pressure requires more
energy to run the compressor. The tank must include a manual
drain valve or an automatic trap to continually drain off
accumulated moisture. With tank pressures of 70 to 90 psi, a
dew point of approximately 70F at 20 psi can be obtained.
Refrigerant Drying
Lowering air temperature reduces the ability of air to hold water.
The refrigerated dryer (Fig. 14) is the most common means of
obtaining dry, compressed air and is available in several
capacities. It provides the greatest system reliability and
requires minimal maintenance.
Fig. 14. Typical Refrigerant Dryer Airflow Diagram.
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
-10
-10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
C1098
OUTDOOR AIR TEMPERATURE (F)
REQUIRED MAXIMUM
DEWPOINT OF MAIN AIR (F)
24
TUBING IN
FURRED
CEILING
TUBING AT
OUTDOOR AIR
TEMPERATURE
50
40
30
20
10
0
-10
-10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60
C1099
OUTDOOR AIR TEMPERATURE (F)
REQUIRED MAXIMUM
DEWPOINT OF MAIN AIR (F)
SUMMER REQUIREMENT
COLD AIR PLENUM
WINTER
REQUIREMENT
AT OUTDOOR AIR
TEMPERATURE
HOT GAS
BYPASS
CONTROL
HEAT
EXCHANGER
AIR IN
AIR OUT
REFRIGERANT
LINES
REFRIGERATION
UNIT
CONDENSOR
REFRIGERANT DRYER
C1888

 Loading...
Loading...











