8
{ A VN interface of an ENode.
{ A VFC interface of another FCF switch.
2. After the virtual link is established, the FCF switch encapsulates the FC frame in an FCoE frame and
sends it out.
3. After receiving the FCoE frame, the FCF switch removes its Ethernet header to send the original FC
frame to the upper layer for processing.
How FIP works
FIP establishes and maintains virtual links between a VFC interface and a VN interface or between VFC
interfaces.
FIP uses Discovery Solicitation packets and Discovery Advertisement packets. Discovery Advertisement
packets include the following types:
• Solicited Discovery Advertisement—A reply for a Discovery Solicitation.
• Unsolicited Discovery Advertisement—Periodically sent to advertise the presence of a virtual link or
maintain an existing virtual link.
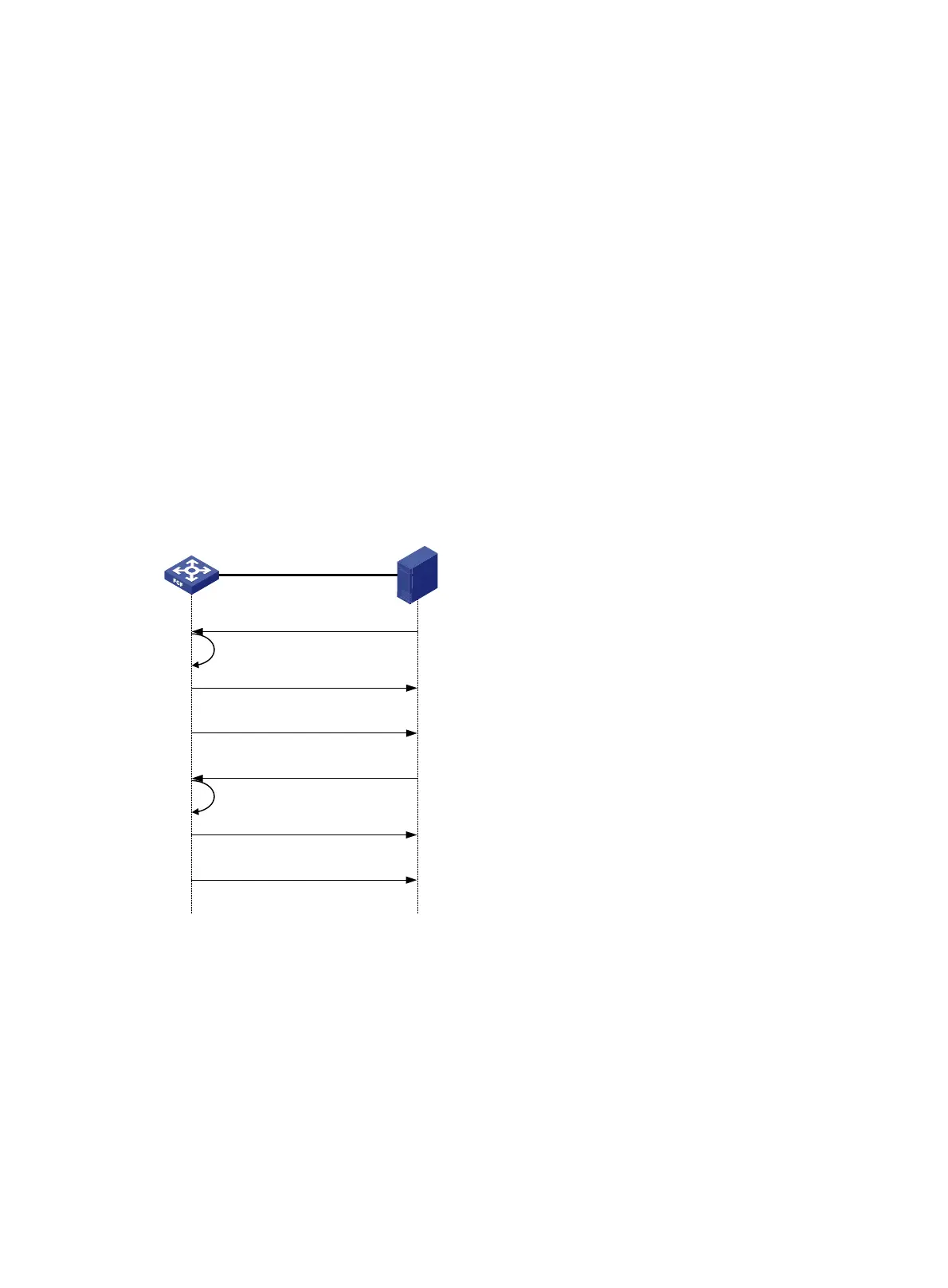
The following example shows how a virtual link is established between an FCF switch and an ENode.
Figure 9 FIP operation
As shown in Figure 9, the following workflow is used to establish a virtual link:
1. The ENode sends a Discovery Solicitation containing its FCoE MAC address.
2. After receiving the Discovery Solicitation, the FCF switch acts differently depending on whether the
receiving VFC interface is bound to an FCoE MAC address.
{ If it is not bound to an FCoE MAC address, the switch learns the FCoE MAC address and replies
with a solicited Discovery Advertisement. The fcf priority field of the solicited Discovery
Advertisement transports the FCF priority of the VFC interface.
{ If it is bound to an FCoE MAC address, the switch identifies whether the FCoE MAC address
carried in the Discovery Solicitation matches the bound FCoE MAC address.
(1) Send Discovery Solicitation
Learn FCoE MAC address
FCF
ENode
(2) Send solicited Discovery
Advertisement
(3) Send solicited Discovery
Advertisements periodically
(4) Send FLOGI request
Check FCoE MAC address
(5) Send FLOGI LS_ACC
(6) Send solicited Discovery
Advertisements periodically

 Loading...
Loading...





