ES User’s Guide 3-81
Making Measurements
Measuring Impedance Magnitude
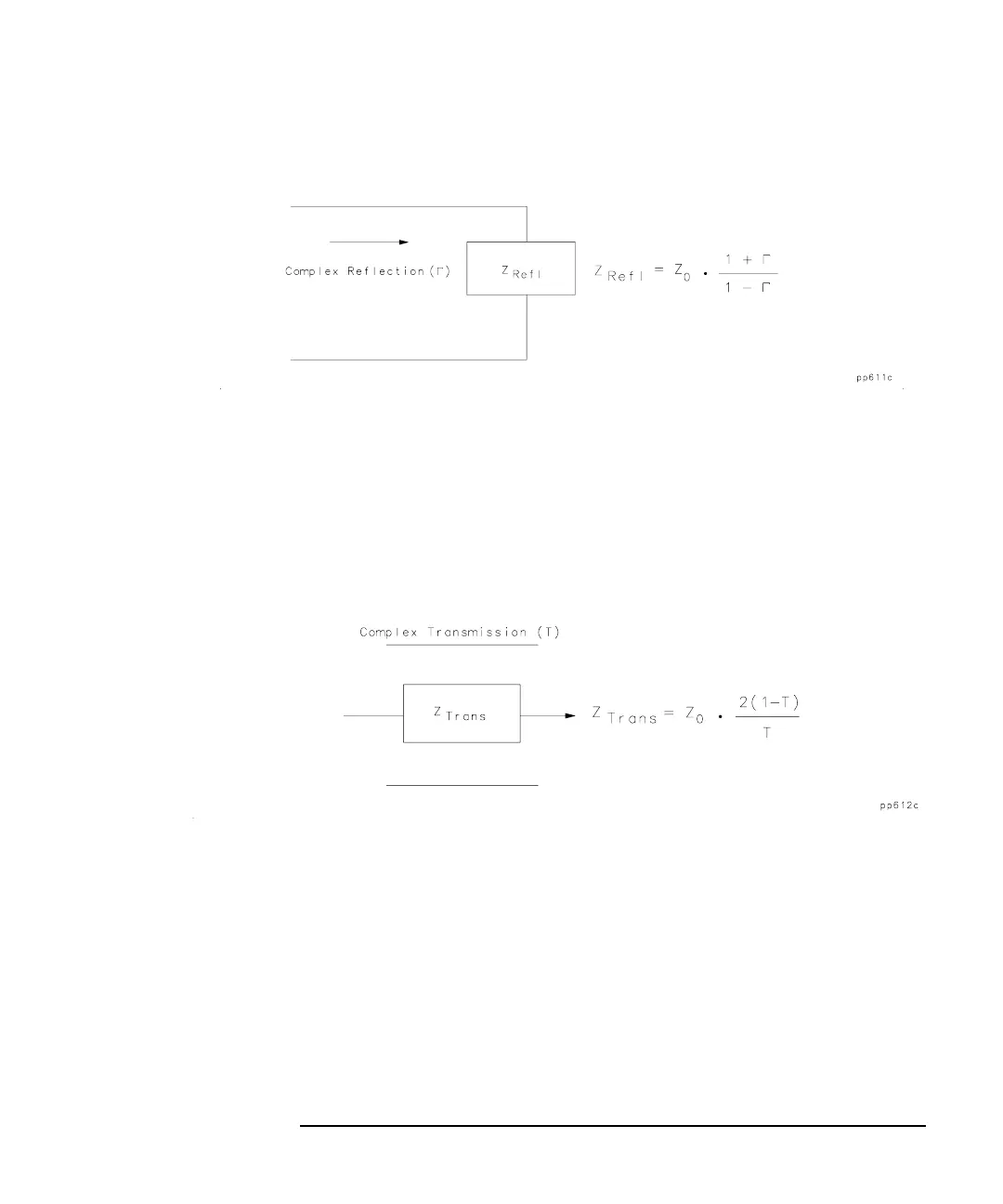
Figure 3-36 Impedance Calculation for Reflection Measurements
How the Transmission Measurement Works
In a transmission measurement, the data can be converted to its
equivalent mathematical series impedance using the model and
equations shown in Figure 3-37.
Figure 3-37 Impedance Calculation for Transmission Measurements
In the formula shown above, T is the complex transmission response.
The complex impedance, Z
Trans
, is computed based on T and Z
0
. The
analyzer displays the magnitude of Z
Trans
. This is not the same as a
two-port Z-parameter conversion, as only the measured parameter is
used in the equations.
Chapter 6 provides information about all of the calibrations available for
transmission measurements. A two-port calibration is the most accurate
form of error correction for transmission measurements since it accounts
for all of the major sources of systematic error. Another possible
calibration choice for a transmission measurement is the enhanced
response calibration. However, since the enhanced response calibration

 Loading...
Loading...