Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Tools
• A ping or traceroute command that includes the host name of a
device in the same domain as the configured domain suffix can
reach that device.
• A ping or traceroute command that includes a fully qualified
domain name can reach a device in any domain that is available
to the configured DNS server.
Example. Suppose the switch is configured with the domain suffix
mygroup.procurve.net and the IP address for an accessible DNS server. If an
operator wants to use the switch to ping a host using the DNS name “leader”
assigned to an IP address used in that domain, then the operator can use either
of the following commands:
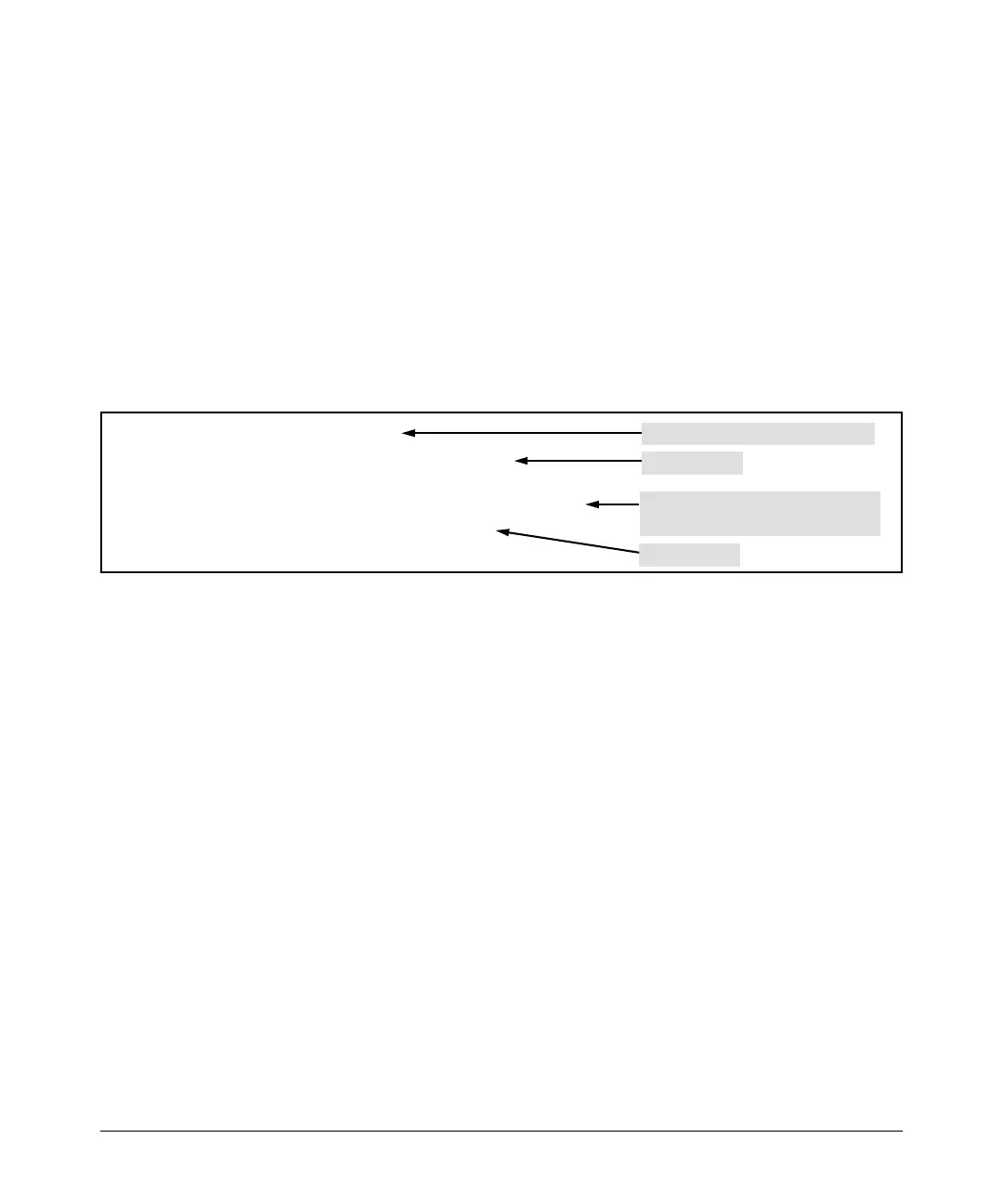
ProCurve# ping leader
Host Name for the Desired Host
10.28.229.220 is alive, time = 1 ms
Ping Response
ProCurve# ping leader.mygroup.procurve.net
Fully Qualified Domain Name for the
10.28.229.220 is alive, time = 1 ms
Desired Host
Ping Response
Figure C-19. Example of Using Either a Host Name or a Fully Qualified Domain Name
In the proceeding example, if the DNS server’s IP address is configured on the
switch, but a domain suffix is not configured, then the fully qualified domain
name must be used.
Note that if the target host is in a domain other than the domain configured
on the switch, then:
■ The host’s domain must be reachable from the switch. This requires
that the DNS server for the switch must be able to communicate with
the DNS server(s) in the path to the domain in which the target host
operates.
■ The fully qualified domain name must be used, and the domain suffix
must correspond to the domain in which the target host operates,
regardless of the domain suffix configured in the switch.
Example. Suppose the switch is configured with the domain suffix
mygroup.procurve.net and the IP address for an accessible DNS server. This
time, the operator wants to use the switch to trace the route to a host named
C-51
 Loading...
Loading...
















