99
Configuring DNS
About DNS
Domain Name System (DNS) is a distributed database used by TCP/IP applications to translate
domain names into IP addresses. The domain name-to-IP address mapping is called a DNS entry.
Types of DNS services
DNS services can be static or dynamic. After a user specifies a name, the device checks the static
name resolution table for an IP address. If no IP address is available, it contacts the DNS server for
dynamic name resolution, which takes more time than static name resolution. To improve efficiency,
you can put frequently queried name-to-IP address mappings in the local static name resolution
table.
Static domain name resolution
Static domain name resolution means manually creating mappings between domain names and IP
addresses. For example, you can create a static DNS mapping for a device so that you can Telnet to
the device by using the domain name.
Dynamic domain name resolution
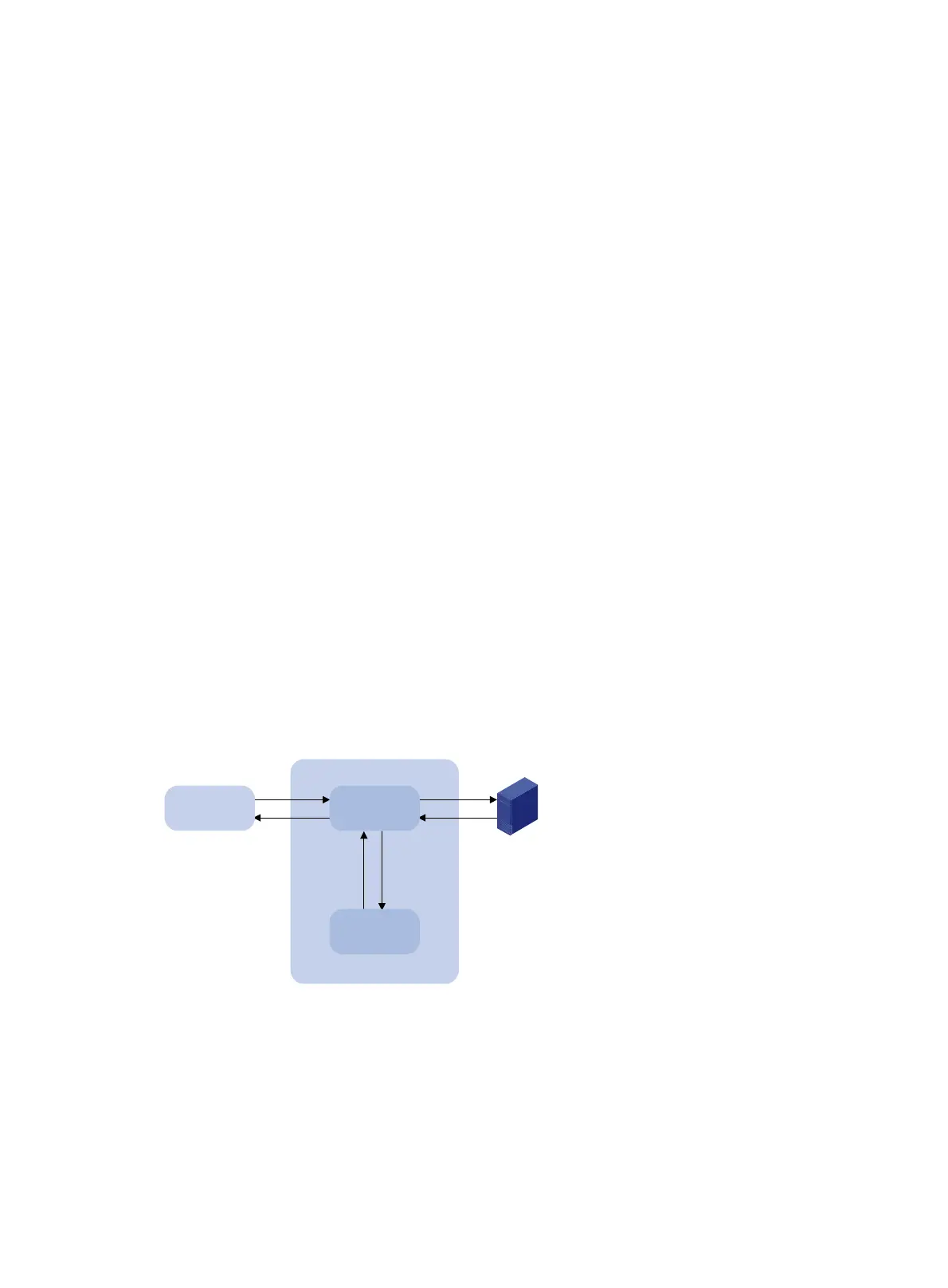
Architecture
Figure 34 shows the relationship between the user program, DNS client, and DNS server. The DNS
client includes the resolver and cache. The user program and DNS client can run on the same device
or different devices. The DNS server and the DNS client usually run on different devices.
Figure 34 Dynamic domain name resolution
The device can function as a DNS client, but not a DNS server.
If an alias is configured for a domain name on the DNS server, the device can resolve the alias into
the IP address of the host.
Resolution process
The dynamic domain name resolution process is as follows:
1. A user program sends a name query to the resolver of the DNS client.
Request
Response Response
Request
SaveRead
DNS client
DNS server
Resolver
Cache
User
program

 Loading...
Loading...











