107
Procedure
# Configure a mapping between host name host.com and IP address 10.1.1.2.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip host host.com 10.1.1.2
# Verify that the device can use static domain name resolution to resolve domain name host.com
into IP address 10.1.1.2.
[Sysname] ping host.com
Ping host.com (10.1.1.2): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for host.com ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.200/2.000/0.400 ms
Example: Configuring dynamic domain name resolution
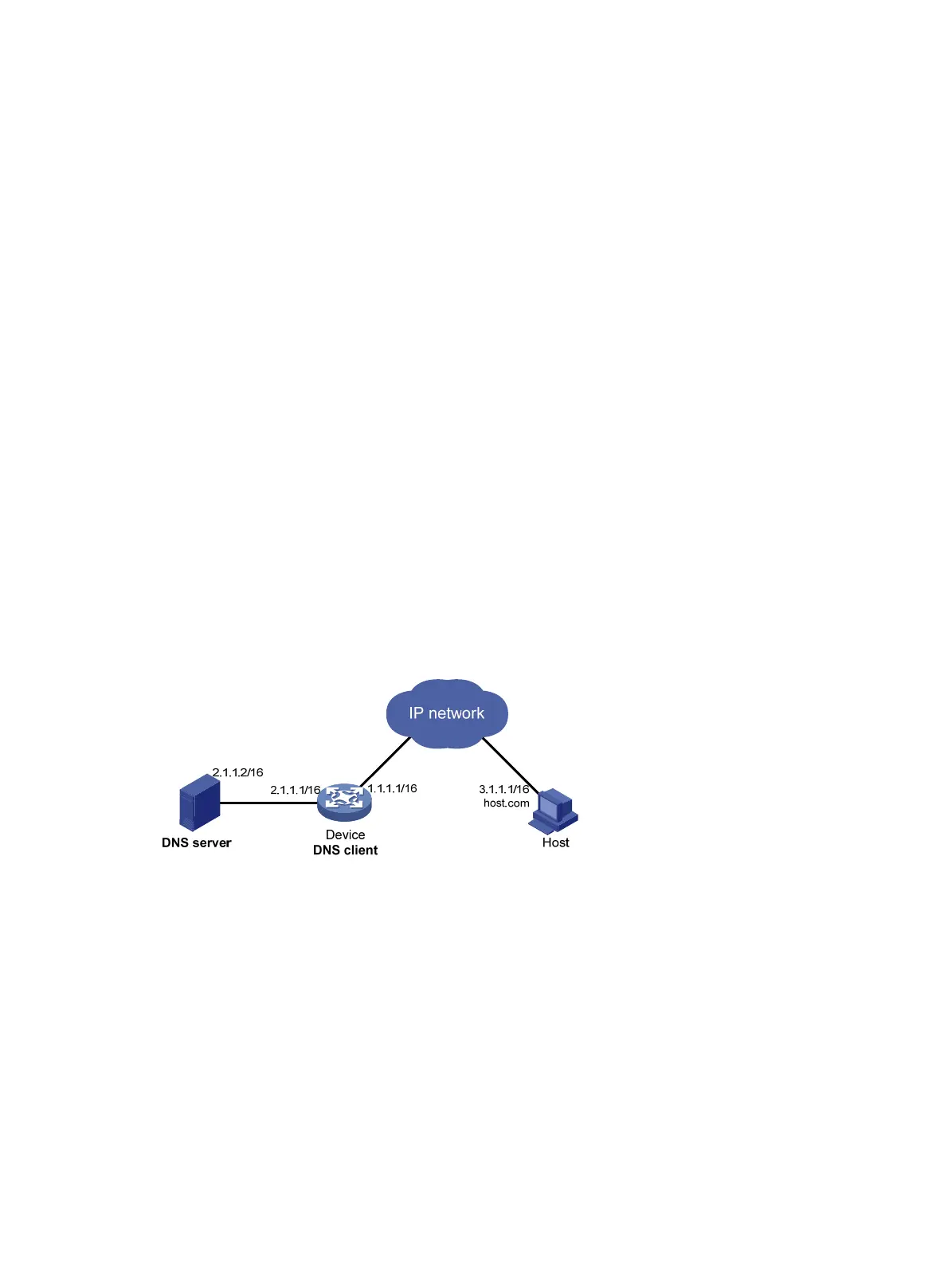
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 38, configure the DNS server to store the mapping between the host's domain
name host and IPv4 address 3.1.1.1/16 in the com domain. Configure dynamic IPv4 DNS and DNS
suffix com on the device so that the device can use domain name host to access the host.
Figure 38 Network diagram
Procedure
Before performing the following configuration, make sure that:
• The device and the host can reach each other.
• The IP addresses of the interfaces are configured as shown in Figure 38.
1. Config
ure the DNS server:
The configuration might vary by DNS server. The following configuration is performed on a PC
running Windows Server 2008 R2.
a. Select Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > DNS.
The DNS server configuration page appears, as shown in Figure 39.
b. Right-cli
ck Forward Lookup Zones, select New Zone, and then follow the wizard to create
a new zone named com.

 Loading...
Loading...











