159
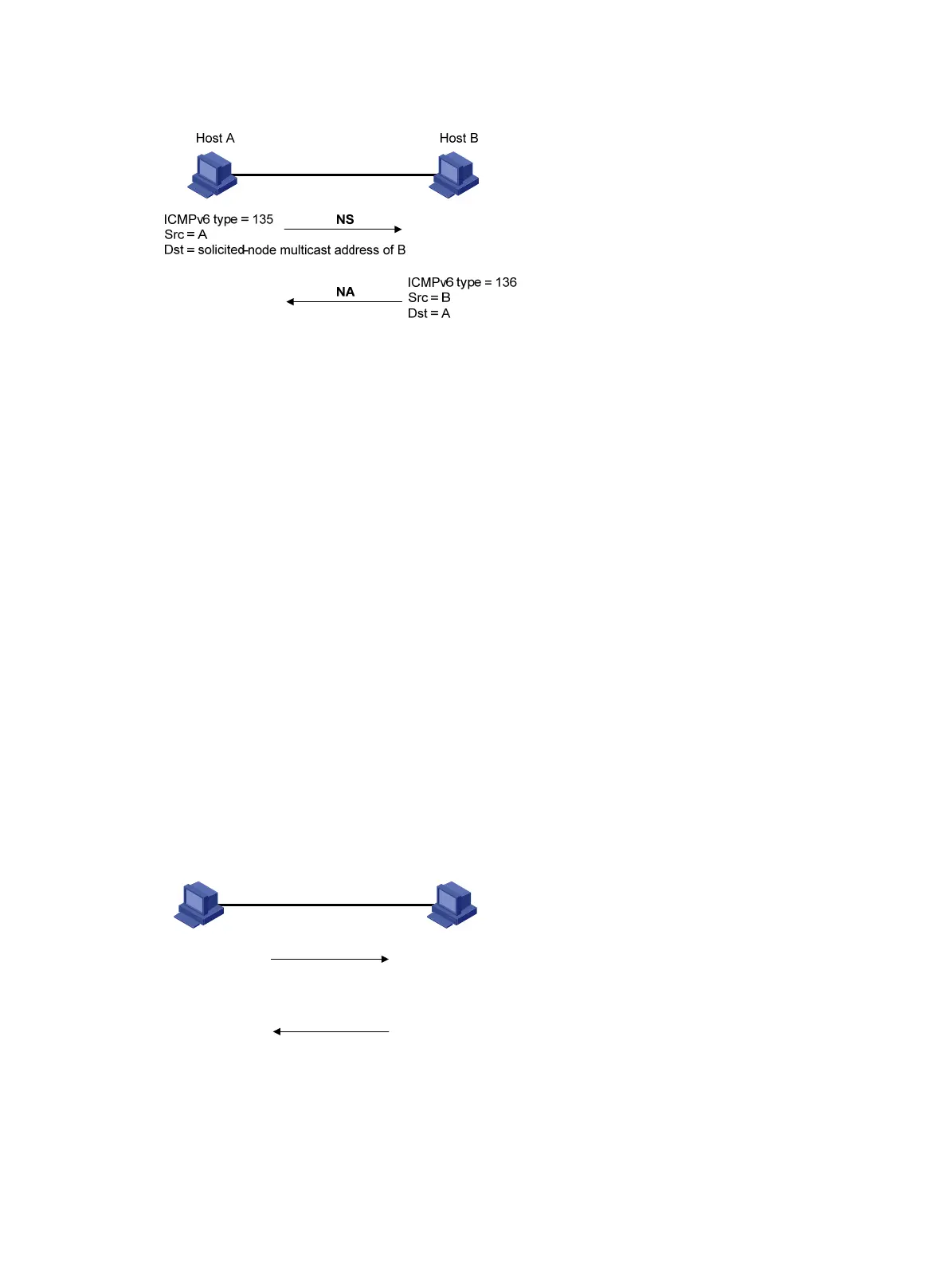
Figure 57 Address resolution
Neighbor reachability detection
After Host A acquires the link-layer address of its neighbor Host B, Host A can use NS and NA
messages to test the reachability of Host B as follows:
1. Host A sends an NS message whose destination address is the IPv6 address of Host B.
2. If Host A receives an NA message from Host B, Host A decides that Host B is reachable.
Otherwise, Host B is unreachable.
Duplicate address detection
After Host A acquires an IPv6 address, it performs Duplicate Address Detection (DAD) to check
whether the address is being used by any other node. This is similar to gratuitous ARP in IPv4. DAD
is accomplished through NS and NA messages.
The DAD procedure is as follows:
1. Host A sends an NS message. The source address is the unspecified address and the
destination address is the corresponding solicited-node multicast address of the IPv6 address
to be detected. The NS message body contains the detected IPv6 address.
2. If Host B uses this IPv6 address, Host B returns an NA message that contains its IPv6 address.
3. Host A knows that the IPv6 address is being used by Host B after receiving the NA message
from Host B. If receiving no NA message, Host A decides that the IPv6 address is not in use and
uses this address.
Figure 58 Duplicate address detection
ICMPv6 type = 135
Src = ::
Dst = FF02::1:FF00:1
NS
ICMPv6 type = 136
Src = 2000::1
Dst = FF02::1
NA
Host A Host B
2000::1

 Loading...
Loading...











