LGA775 Socket Heatsink Loading
18 Thermal and Mechanical Design Guidelines
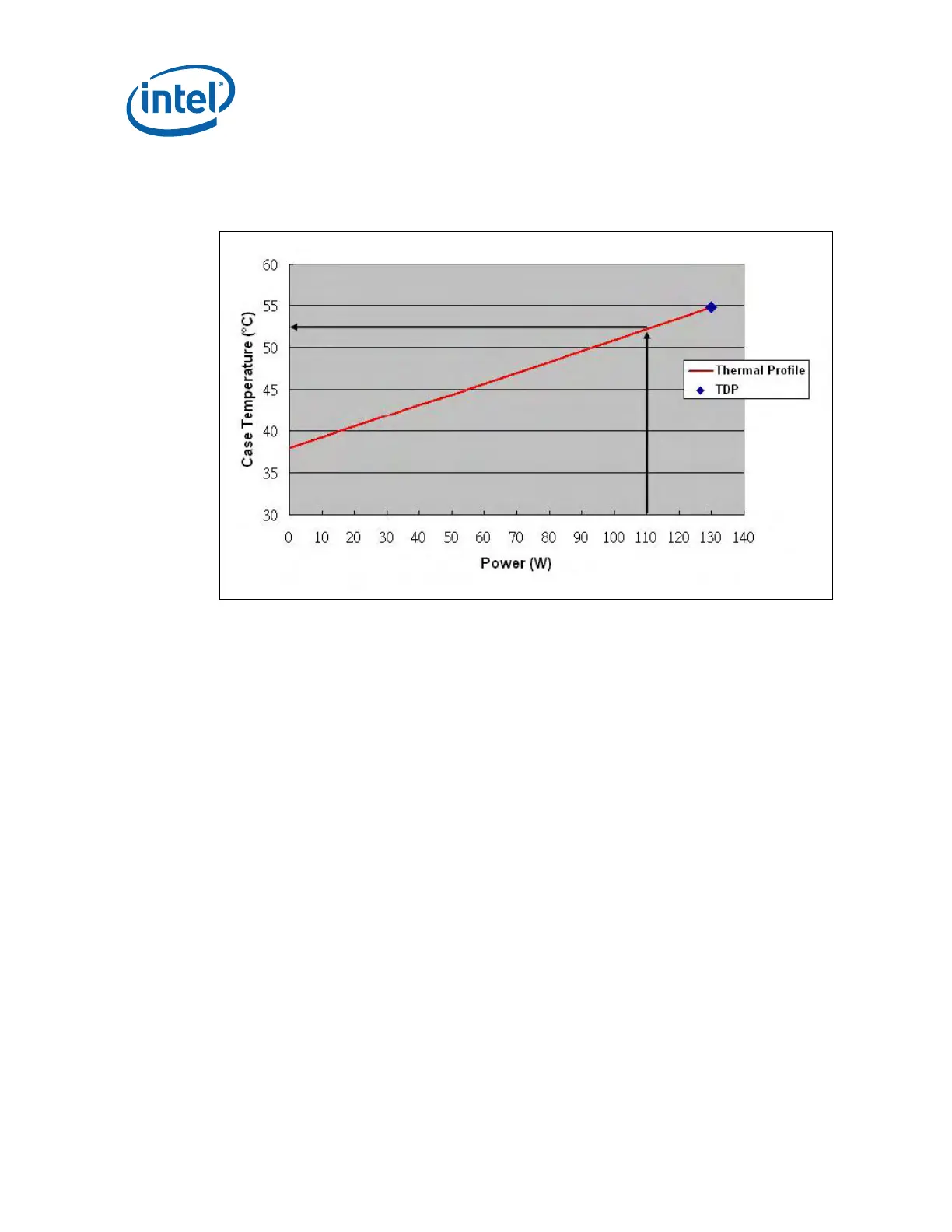
temperature. Using the example in Figure 3 for a processor dissipating 110W the
maximum case temperature is 52.2°C. See the datasheet for the thermal profile.
Figure 3. Example Thermal Profile
2.2.3 T
CONTROL
T
CONTROL
defines the maximum operating temperature for the digital thermal sensor
when the thermal solution fan speed is being controlled by the digital thermal sensor.
The T
CONTROL
parameter defines a very specific processor operating region where fan
speed can be reduced. This allows the system integrator a method to reduce the
acoustic noise of the processor cooling solution, while maintaining compliance to the
processor thermal specification.
Note: The T
CONTROL
value for the processor is relative to the Thermal Control Circuit (TCC)
activation set point which will be seen as 0 via the digital thermometer. As a result the
T
CONTROL
value will always be a negative number. See Chapter 4 for the discussion
the thermal management logic and features and Chapter 6 on Intel
®
Quiet System
Technology (Intel
®
QST).
The value of T
CONTROL
is driven by a number of factors. One of the most significant
of these is the processor idle power. As a result a processor with a high (closer to 0)
T
CONTROL
will dissipate more power than a part with lower value (farther from 0, e.g.
more negative number) of T
CONTROL
when running the same application.
The value of T
CONTROL
is calculated such that regardless of the individual processor’s
T
CONTROL
value the thermal solution should perform similarly. The higher power of
some parts is offset by a higher value of T
CONTROL
in such a way that they should
behave similarly in the acoustic performance.

 Loading...
Loading...











