8
DAILY MCA2014 4x4 ‒ BODYBUILDER INSTRUCTIONS
CHASSIS INTERVENTIONS
2.2 DRILLS ON THE CHASSIS
– Printed 603.95.994 – 1 Ed. - Base 05/2015
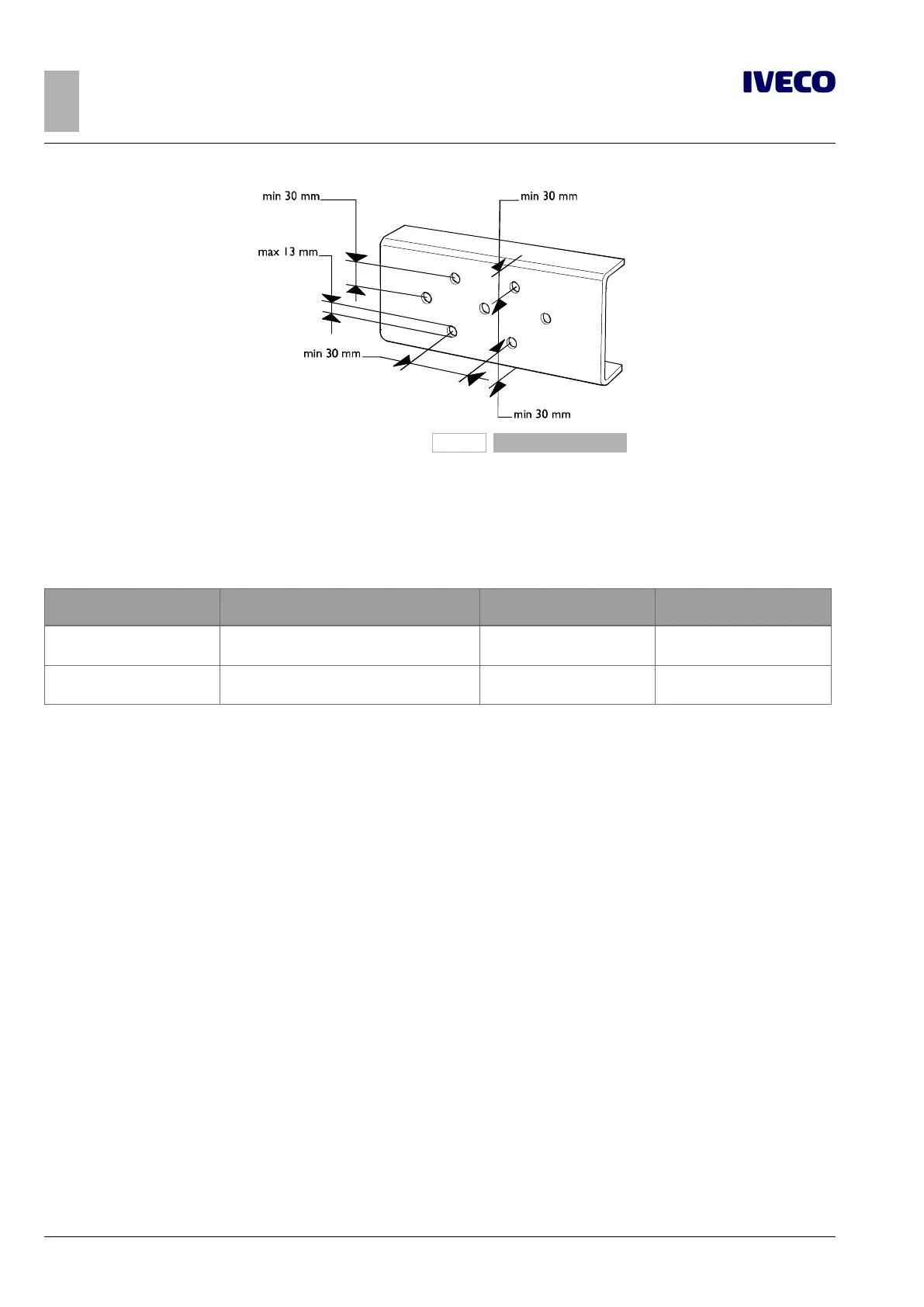
102420
Figure 2
Screws and nuts
We generally recommend the use of the same type and class of screws and nuts as those employed for similar anchorages on the
original vehicle (see Table 2.3).
Table 2.3 - Screws resistance classes
Resistance class Use
Breaking strength
[N/mm
2
]
Yield stress
[N/mm
2
]
8.8
Intermediate resistance screws (crossbars, shear
resistant plates, brackets)
800 640
10.9
High resistance screws (springs supports, stabiliser
bars and shock absorbers)
1000 900
Screws classed 8.8 and 10.9 must be well cleaned and, for applications using a screw with a diameter of ≤ 6 mm; we recommend
protection FeZnNi 7 IV.
Screw treatment allowed is Geomet or zinc coating. Geomet treated screws are discouraged when using them in welding opera-
tions.
Use flange headed screws and nuts if there is sufficient space.
Use nuts with an anti-unscrewing system and keep in mind that the tightening torque must be applied to the nut.
Sealing holes by welding
If new holes are located near old holes (see Figure 2), these last can be welded shut.
Good results are obtained by:
● chamfering the outer edge of the hole;
● applying a copper plate on the inner edge of the side member to hold the welding material;
● welding the side member on both sides with elimination of all residual material.
Holes of 20 mm diameter can be sealed off by using chamfered washers welded on both sides.

 Loading...
Loading...