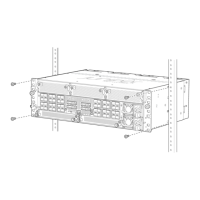
Figure 6: ACX1100 Interface Port Mapping
g017874
0/0/0
0/0/1 0/0/2 0/0/3
0/0/4
0/0/5 0/0/6 0/0/7
GE
0/1/0
0/1/1
0/1/2 0/1/3
0/1/0
0/1/1 0/1/2 0/1/3
CONSOLE/AUX
COMBO PORTS
FPC 0, PIC 0
GE 0/0/0-0/0/7
FPC 0, PIC 1
GE 0/1/0-0/1/3
Related
Documentation
ACX1000 and ACX1100 Universal Access Router Overview on page 3•
Packet Flow on ACX Series Routers
The class-of-service (CoS) architecture for ACX Series routers is in concept similar to
that for MX Series routers. The general architecture for ACX Series routers is shown in
Figure 7 on page 8.
Figure 7: ACX Series Router Packet Forwarding and Data Flow
Incoming packet
Ingress classification
In order of
decreasing precedence:
MF classification (DFW)
Fixed classification
BA classification
Queuing Egress rewrite
Outgoing packet
g006408
Buffering Scheduling
Based on the model, ACX Series routers contain a built-in Routing Engine and Packet
Forwarding Engine and can contain both T1/E1 and Gigabit Ethernet Ports.
The Packet Forwarding Engine has one or two “pseudo” Flexible PIC Concentrators.
Because there is no switching fabric, the single Packet Forwarding Engine takes care of
both ingress and egress packet forwarding.
Fixed classification places all packets in the same forwarding class, or the usual multifield
(MF) or behavior aggregate (BA) classifications can be used to treat packets differently.
BA classification with firewall filters can be used for classification based on IP precedence,
DSCP, IEEE, or other bits in the frame or packet header.
However, the ACX Series routers can also employ multiple BA classifiers on the same
physical interface. The physical interfaces do not have to employ the same type of BA
classifier. For example, a single physical interface can use classifiers based on IP
precedence as well as IEEE 802.1p. If the CoS bits of interest are on the inner VLAN tag
of a dual-tagged VLAN interface, the classifier can examine either the inner or outer bits.
(By default, the classification is done based on the outer VLAN tag.)
Eight queues per egress port support scheduling using the weighted deficit round- robin
(WDRR) mechanism, a form of round-robin queue servicing. The supported priority levels
are strict-high and default (low). The ACX Series router architecture supports both
weighted random early detect (WRED) and weighted tail drop (WTD).
Copyright © 2017, Juniper Networks, Inc.8
ACX1000 and ACX1100 Universal Access Router Hardware Guide

 Loading...
Loading...