Introduction–Driver installation and settings
11
Mac OS X users
When used with Mac OS X, the microKONTROL will automatically use Mac
OS X’s built-in MIDI driver.
For use with Mac OS X, the microKONTROL requires Mac OS X 10.2 or
later.
To set up the microKONTROL for use with Mac OS X, follow the steps
below.
1
Use a USB cable to connect the microKONTROL to your computer.
2
Turn on the power of the microKONTROL.
3
Navigate to Macintosh HD
➝
Application folder
➝
Utility folder, and
double-click “Audio MIDI Settings.”
4
Click the “MIDI Devices” tab, and verify that the
microKONTROL
is
displayed.
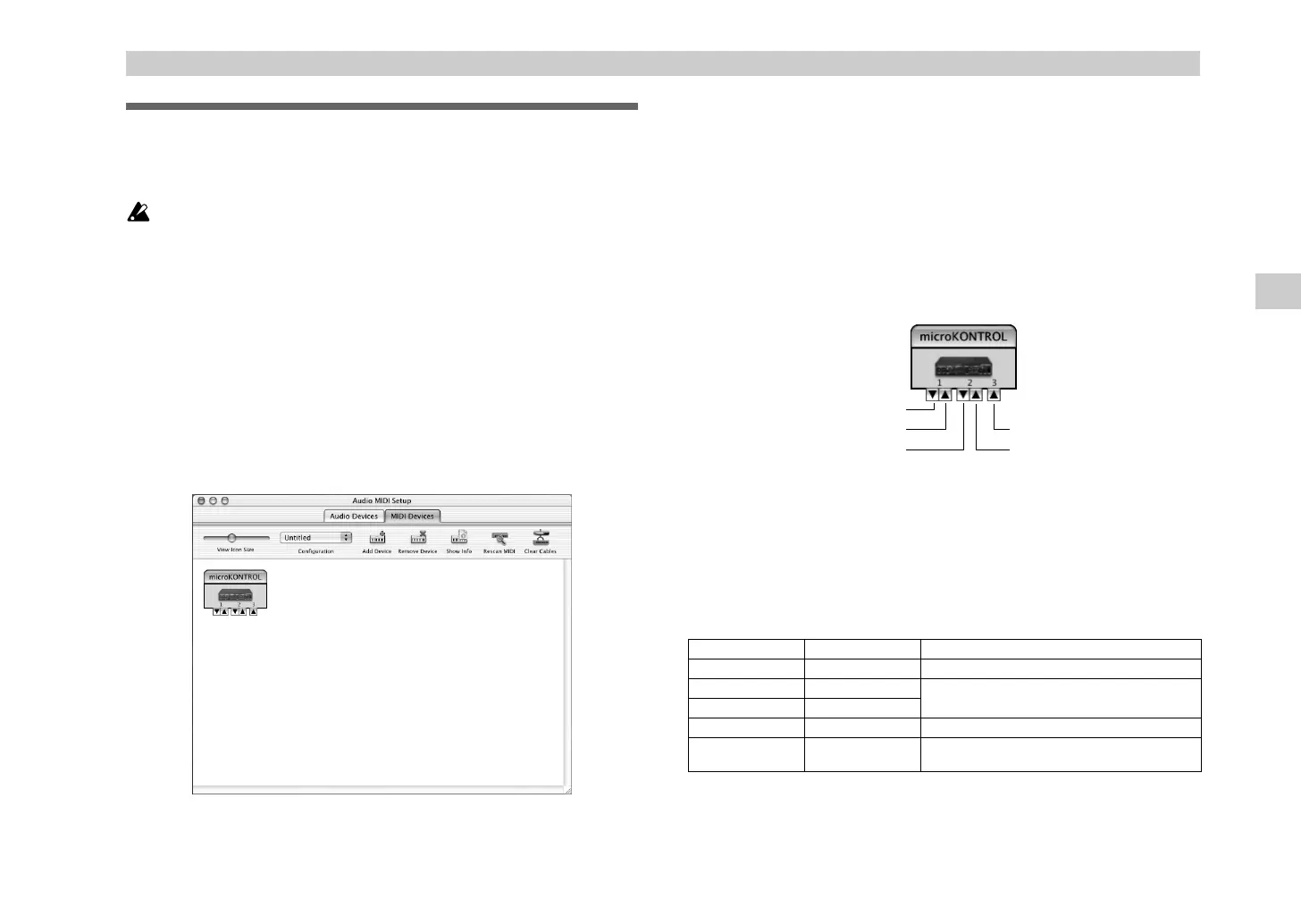
Mac OS X MIDI input and output ports
Using the Mac OS X MIDI drivers, the microKONTROL provides a total of
three MIDI inputs and two MIDI outputs, as follows:
• One port each of MIDI input and output for external devices
•Two ports of MIDI input from the microKONTROL’s own keyboard and
controllers
• One port of MIDI output dedicated to microKONTROL data dumps and
Korg Native mode
The numbers assigned to these ports are a little different between the
microKONTROL front panel and the Mac OS X MIDI drivers.
On the microKONTROL, you can set the different kinds of controllers -
keyboard, pads, sliders, encoders, and so on - to send data to either USB Port
A or Port B (
☞
p.36 “[8] PORT (USB-MIDI Port setting)”).
In the Mac OS X MIDI drivers, these same two ports correspond to Port 2
and Port 3, as shown below:
microKONTROL Mac OS X Use for...
MIDI IN Port 1 (In) MIDI input from external devices
Port A (PORT A) Port 2 (In)
microKONTROL keyboard & controllers
Port B (PORT B) Port 3 (In)
MIDI OUT Port 1 (Out) MIDI output to external devices
Dedicated port
(CTRL)
Port 2 (Out)
Data dumps to microKONTROL & Korg Native
mode
microKONTROL MIDI OUT
microKONTROL MIDI IN
microKONTROL dedicated port (CTRL)
microKONTROL port B (PORT B)
microKONTROL port A (PORT A)
Driver installation and settings
$$ !"
 Loading...
Loading...