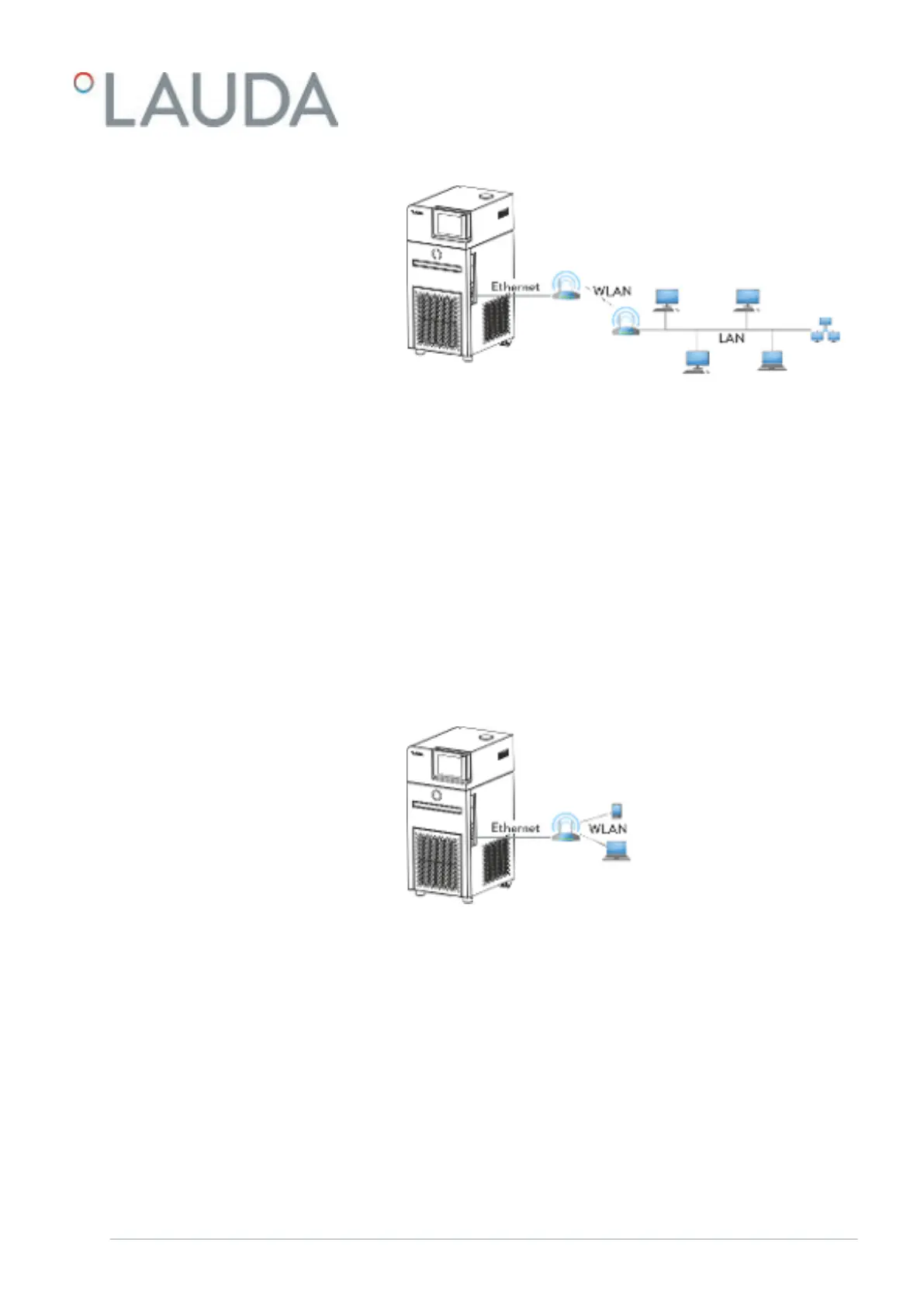
Fig. 16: Connected via LAN and WLAN
Fig. 16 illustrates the connection between the LAUDA constant tem-
perature equipment and a LAN network with control station via a WLAN.
Here, the constant temperature equipment is connected to a WLAN router
using a standard Ethernet cable. The WLAN router must be configured
so that it establishes a connection to a LAN via another WLAN router.
This kind of connection is called a WLAN bridge. Refer to the instructions
accompanying the relevant router for information on configuring WLAN
routers.
It cannot be controlled simultaneously by two control stations.
Advantages of this connection:
The constant temperature equipment can be controlled by any control
station/PC.
The constant temperature equipment can be contacted by radio and
operated from a remote location.
Fig. 17: Connected via WLAN
Fig. 17 illustrates direct communication between the control station/PC and
the LAUDA constant temperature equipment via a WLAN. The WLAN
router must be configured as an access point. Refer to the instructions
accompanying the router for information on configuring the WLAN router.
Advantages of this connection:
The constant temperature equipment can be contacted by radio and
operated from a remote location.
It is possible to use a short Ethernet cable.
No LAN network required.
Connected via LAN and WLAN
Connected via WLAN
V6 PRO bath thermostats and circulation thermostats 37 / 156
 Loading...
Loading...



