1023
3. Instructions
CS/CJ/NSJ Series Instructions Reference Manual (W474)
Failure Diagnosis Instructions
3
FAL
Example Programming
z Generating a Non-fatal Error
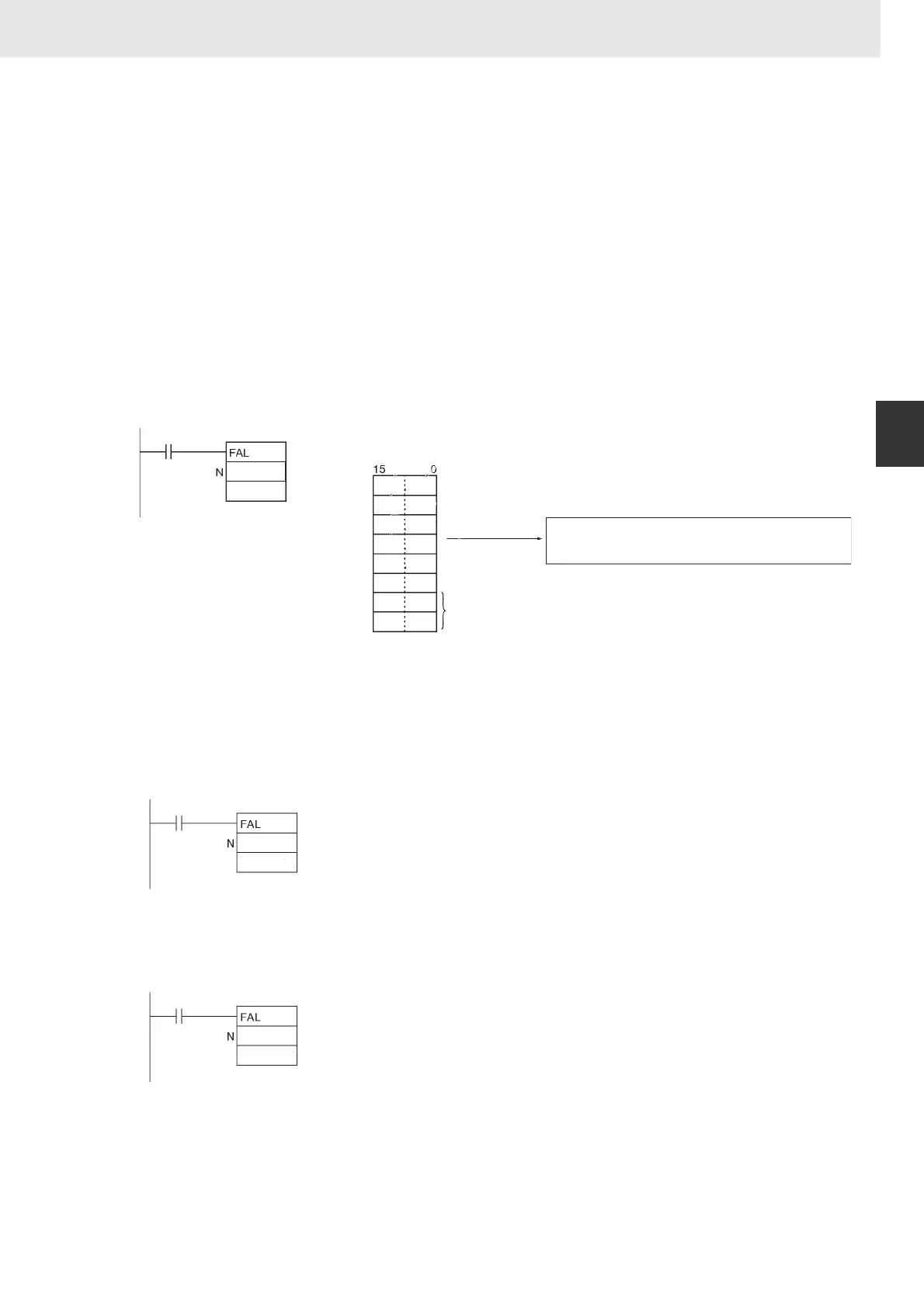
When CIO 0.00 is ON in the following example, FAL(006) will generate a non-fatal error with FAL
number 31 and execute the following processes.
1. The FAL Error Flag (A402.15) will be turned ON.
2. The corresponding Executed FAL Number Flag (A361.15) will be turned ON.
3. The corresponding error code (411F) will be written to A400.
4. The error code and the time/date that the error occurred will be written to the Error Log Area (A100
through A199).
5. The ERR Indicator on the CPU Unit will flash.
6. The ASCII message in D100 to D107 will be displayed at the Peripheral Device.
Note If a message is not required, specify a constant for S.
Note If two or more errors occur at the same time, the error code of the most serious error (with the highest error
code) will be stored in A400.
z Clearing a Particular Non-fatal Error
When CIO 0.01 is ON in the following example, FAL(006) will clear the non-fatal error with FAL number
31, turn OFF the corresponding Executed FAL Number Flag (A361.15), and turn OFF the FAL Error
Flag (A402.15).
z Clearing All Non-fatal Errors
When CIO 0.02 is ON in the following example, FAL(006) will clear all of the non-fatal errors, turn OFF
the Executed FAL Number Flags (A360.01 to A391.15), and turn OFF the FAL Error Flag (A402.15).
M:
MESSAGE
LOW VOLTAGE
4C 4F
57 20
56 4F
4C 54
41 47
45 00
31
M
Disregarded
D100
0.00
M:
D100
D101
D102
D103
D104
D105
D106
D107
M
#001F
0.01
0
Set N to 0 to clear errors.
Set M to the desired FAL
number (031(001F)).
M
0.02
0
#FFFF
Set N to 0 to clear errors.
Set M to FFFF to clear all non-fatal errors
(both FAL(006) and system errors).
 Loading...
Loading...











