3. Instructions
560
CS/CJ/NSJ Series Instructions Reference Manual (W474)
Flags
Function
z LIFO
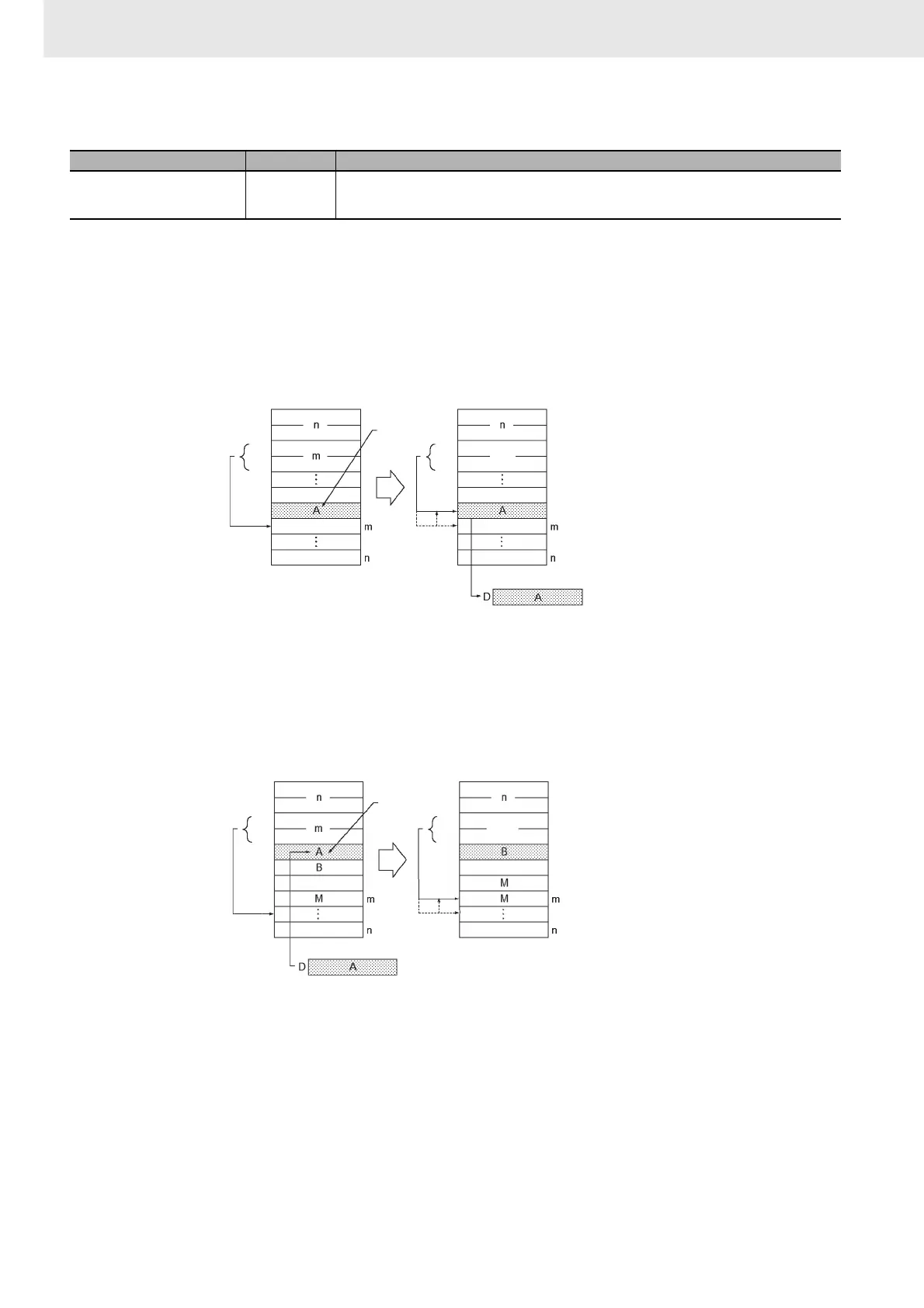
LIFO(634) reads the data from the address indicated by the stack pointer (the newest word of data in
the stack), decrements the stack pointer by one, and outputs the data to D. The word that was read is
left unchanged.
The stack must be defined in advance with SSET(630).
z FIFO
FIFO(633) reads the oldest word of data from the stack (TB+4) and outputs that data to D. Next, the
stack pointer (TB+3 and TB+2) is decremented by one, all of the remaining data in the stack is shifted
downward by one word, and the data read from TB+4 is deleted. The data at the end of the stack (the
address that was indicated by the stack pointer) is left unchanged.
The stack must be defined in advance with SSET(630).
Hint
z LIFO
Use LIFO(634) in combination with PUSH(632). After PUSH(632) has been used to write data into a
stack, LIFO(634) can be used to read data from the stack on a last-in first-out basis. After data is stored
by PUSH(632), the stack pointer indicates the address next to the last data.
z FIFO
• Use FIFO(633) in combination with PUSH(632). After PUSH(632) has been used to write data into a
stack, FIFO(633) can be used to read data from the stack on a first-in first-out basis.
• FIFO(633) reads the beginning data from the stack and deletes this data to move the next one
forward.
Name Label Operation
Error Flag ER • ON if the contents of the stack pointer (TB+3 and TB+2) is less than or equal to the PLC memory
address of first word in the data region of the stack (TB+4). (This is a stack underflow error.)
• OFF in all other cases.
TB
TB+1
TB+2
TB+3
TB
TB+1
TB+2
TB+3
m–1
m–1
m–1
Reading
A is left unchanged.
Stack
pointer
PC memory
address
PC memory
address
Newest
data
Stack
pointer
The pointer is
decremented.
m–1
TB
TB+1
TB+2
TB+3
TB
TB+1
TB+2
TB+3
TB+4
TB+4
m–1
PC memory
address
Oldest
data
Stack
pointer
PC memory
address
First-in first-out
Stack
pointer
 Loading...
Loading...











