10.18
ELECTRICAL
9923412 - 2012 Sportsman 400/500 and EFI Tractor Service Manual
© Copyright 2011 Polaris Sales Inc.
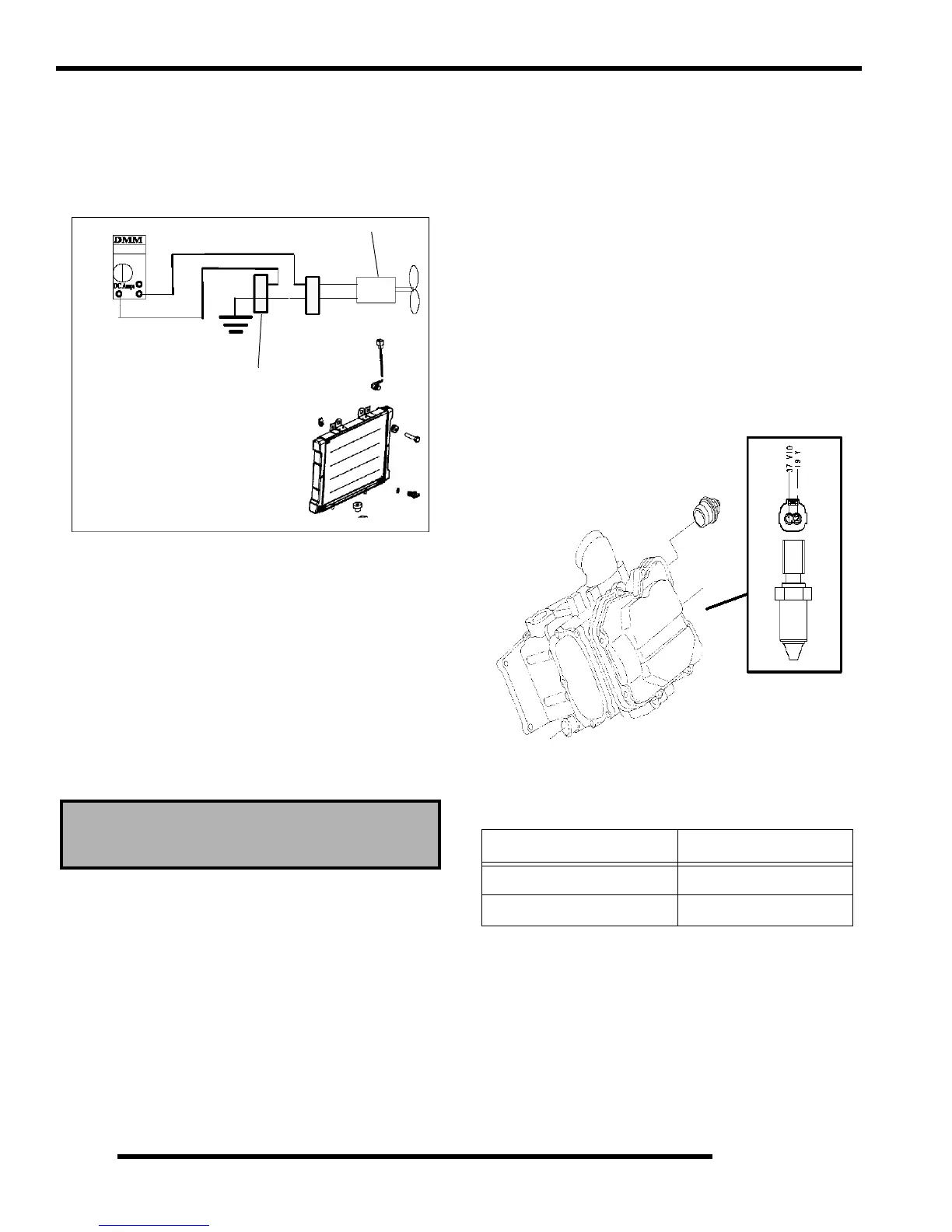
Fan Motor Current Draw Test
A current draw test will provide a good indication of fan
motor condition. A worn or damaged fan motor will draw
more current, which causes a reduction in blade speed
and reduced cooling.
1. Disconnect the harness from the coolant sensor
(EF
I).
2. Connect a DC ammeter in-line on the fan switch
harness wires.
See illustration.
(H.O. Models - An inductive ammeter is required)
3. Be sure fan blade is f
ree to rotate.
4. Turn ignition key and engine stop switch to “ON”
p
osition. Read the current draw on ammeter with fan
running.
(H.O. Models - Direct 12 Vdc to fan required)
5. If the fan motor draws more than 10 Amps, replace the
mo
tor.
NOTE: Fan motor current draw specification may
v
ary on Sportsman H.O. and EFI models.
Coolant Temperature Sensor - EFI
The coolant temperature sensor can be tested using an
ohmmeter.
If the ECT circuit is open, the engine Hot light and fan will
both co
me on. With the engine at an ambient temperature
of 68
°F (20°C), disconnect lead and measure the
resistance of sensor between the two ECT terminals and
compare to the specification listed.
1. With the engine and temperature sensor at room
t
emperature (68
°F = 20°C), disconnect the harness
connector.
2. With the meter in the ohm
s mode, place the meter
leads onto the sensor contacts.
3. Use the Temperature / Resistance
table to determine
if the sensor needs to be replaced.
NOTE: If the coolant temperature sensor or circuit
ma
lfunctions the radiator fan will default to 'ON'.
NOTE: The fan may not function or operation may
be de
layed if coolant level is low or if air is trapped in
the cooling system. Verify the cooling system is full
and purged of air. Refer to Maintenance Chapter 2
for cooling system information.
Fan Motor Current Draw:
Should Be Less Than 10 Amps
Connect Ammeter
Between OG/Black Pins
OG/Blk
Fan
Brn
OG/Blk
Fan
Harness
Table 10-1: EFI Sensor
TEMPERATURE F (C) RESISTANCE
68F (20 C)
37.3 k
212F (100 C)
2.1 k

 Loading...
Loading...











