3 Web-based Management
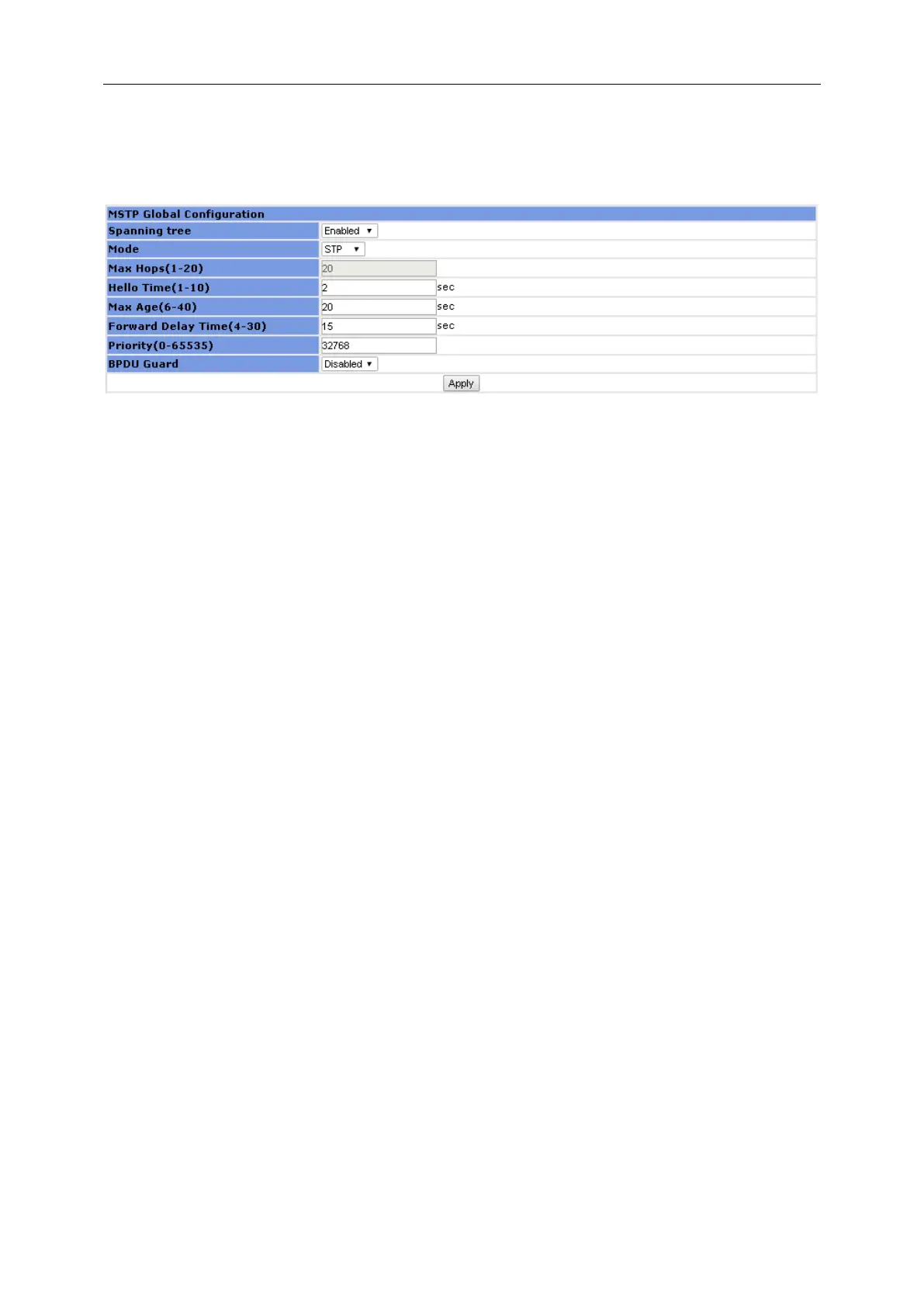
3.7.1 Global Configuration
Before configuring STP, make sure STP is enabled
This page sets bridge configurations: Mode, Max Hops, Hello Time, Max Age, Forward
Delay Time, Priority, and BPDU Guard.
Mode: Three spanning tree modes are supported: STP, RSTP, and MSTP.
Max Hops: This value is in the range of 1 to 20, and is 20 by default.
This parameter is used in MSTP mode only to limit the size of MST domain, and the root
switch of the instance always sends a BPDU (or M-record) with a cost of 0 and the hop count
of the maximum value. When a switch receives this BPDU, it decrements the received
remaining hop count by one and propagates this value as the remaining hop count in the
BPDUs it generates. When the count reaches zero, the switch discards the BPDU and ages
the information held for the port. By default, this value is set to 20.
Hello Time: This value is in the range from 1 to 10 seconds, and is 2 seconds by default.
A root bridge regularly sends out configuration BPDUs to maintain the stability of the existing
spanning tree. If the switch does not receive a BPDU packet in a specified period, the
spanning tree will be recalculated at BPDU packet times out. When a switch becomes to a
root bridge, it regularly sends BPDUs at the interval specified by this hello time. A
non-root-bridge switch adopts the interval specified by this hello time.
Max Age: This value is in the range of 6 to 40 seconds, and is 20 seconds by default.
MSTP is capable of detecting link failures and automatically restoring redundant links to the
forwarding state. In CIST, switches use max age parameter to determine whether a received
configuration BPDU times out. Spanning trees will be recalculated if a configuration BPDU
received by a port times out.
Forward Delay Time: This value is in the range of 4 to 30 seconds, and is 15 seconds by
default.
To prevent the occurrence of a temporary loop, when a port changes its state from discarding
to forwarding, it undergoes an intermediate state and waits for a specific period of time to
synchronize with the state transition of the remote switches. This state transition period is
determined by Forward Delay Time configured on the root bridge, and applies to all non-root
bridges.
 Loading...
Loading...