Chapter 3 Functional descriptions
32 SMSO-2-02.03- 15.07.03
3.2 Components
3.2.1 General
This section contains a description of all the units imple-
mented in several of the systems, or which are used in similar
form in various systems to prepare products. These descrip-
tions form the basis of an understanding of the system de-
scriptions.
An understanding of the function of individual components and
a knowledge of the interaction between many components is
essential in order to set up and maintain the machine in such
a way that high quality products can be produced.
3.2.2 Programming
The control system monitors the operating behaviour of many
components.
Data regarding the operating status is gathered via sensors
(e.g. limit switch) and typical parameters (such as volt-
ages/times) are collected and analysed by the control system.
The switching points for these parameters can be modified via
the machine programming system/ However the actual values
and their units (e.g. 10 seconds; 1.5 A) are not displayed in
the programming dialog, but are “relative” values without di-
mensions.
Every correcting variable (e.g. grinding time) is assigned to a
relative scale containing dimensionless values from 1 to n.
These values can be modified via the programming system.
So instead of displaying a time segment in seconds, it is dis-
played in the form of a value (e.g. between 1 and 1000). For
this reason when making programming settings, we do not talk
of absolute values (e.g. 6.5 A) but of “value70” or “70 unit” The
effect of a change in value by ±1 is different for every correct-
ing variable.
3.2.3 ESD protection (electro static discharge)
Electrical and electronic components can be damaged by
static discharge. For this reason suitable protection against
electrostatic discharge must be provided for all such compo-
nents. Therefore please follow all rules and instructions to
prevent and divert static discharges. (See sections entitled
“Safety instructions” and “Functional descriptions, unit control
system”)
3.2.4 Lubricant
Some components must be lubricated when a maintenance
service takes place. There are various lubricants available for
this purpose. The service and maintenance instructions con-
tain information regarding their application with regard to qual-
ity (type of grease) and to quantity.
DANGER OF INJURY
Machine lubricants can contain materials
that are hazardous to life and can cause
symptoms of toxic poisoning or paralysis or
cause other damage to health.
They should be used in coffee machines
only where such materials do not come into
direct contact with the foodstuffs or with
the drinking water.
Always check the applicable maintenance instruc-
tions to make sure in which locations the various
types of lubricant may be used.
Label the containers concerned to make sure you
cannot get the lubricant types mixed up.
Ensure that you have an efficient working method
that will ensure that lubricants cannot, unnoticed,
come into contact with food either directly or indi-
rectly.
Food greases have a restricted consumption period,
always check the “use-by” date on the pack or con-
tainer.
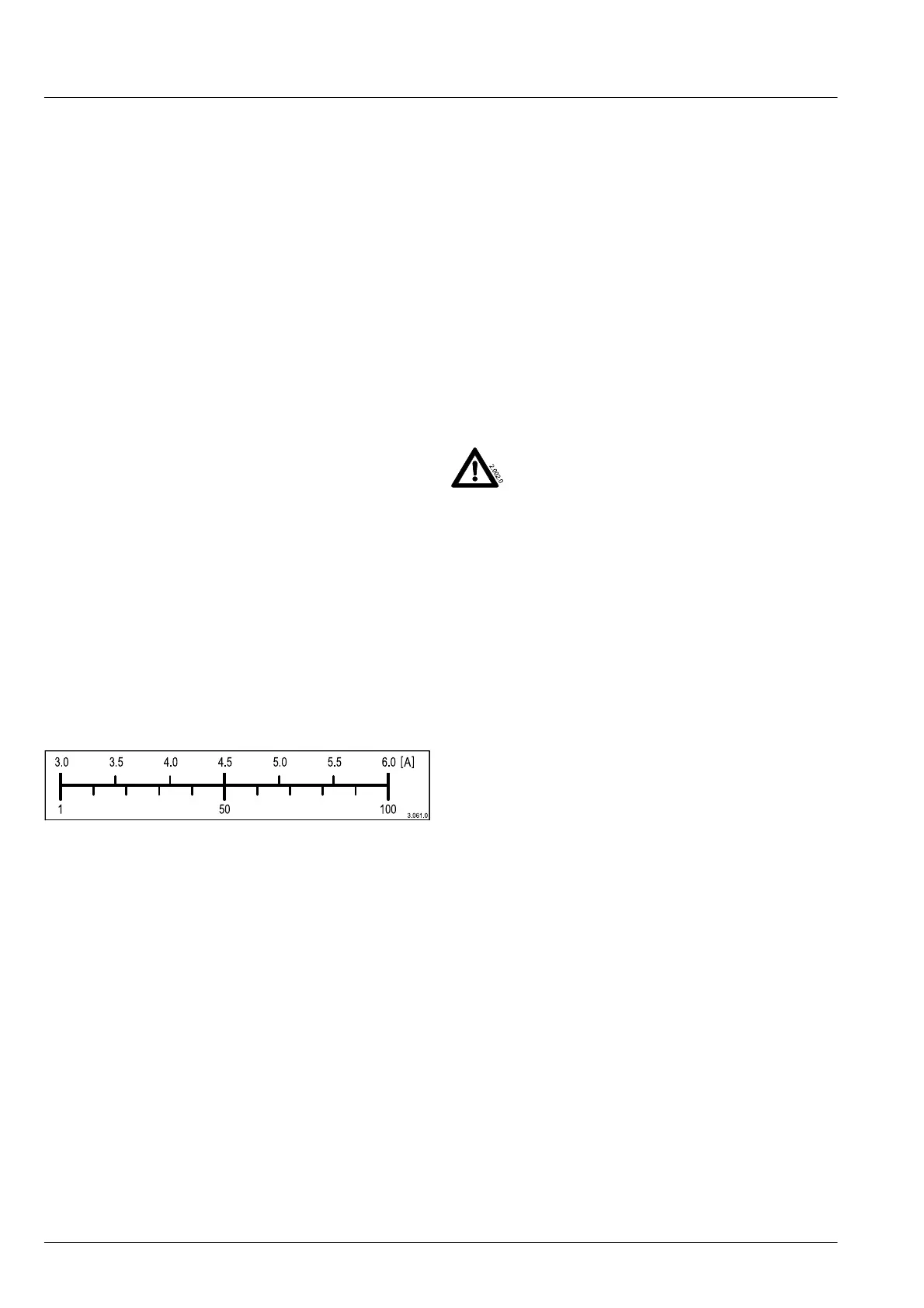
The scale shows how, for example, programming "units" are
assigned to the current strength in amperes. Because both
scales are linear, they always are interrelated with one con-
version factor.

 Loading...
Loading...











