186
Chapter 9: Financial Features
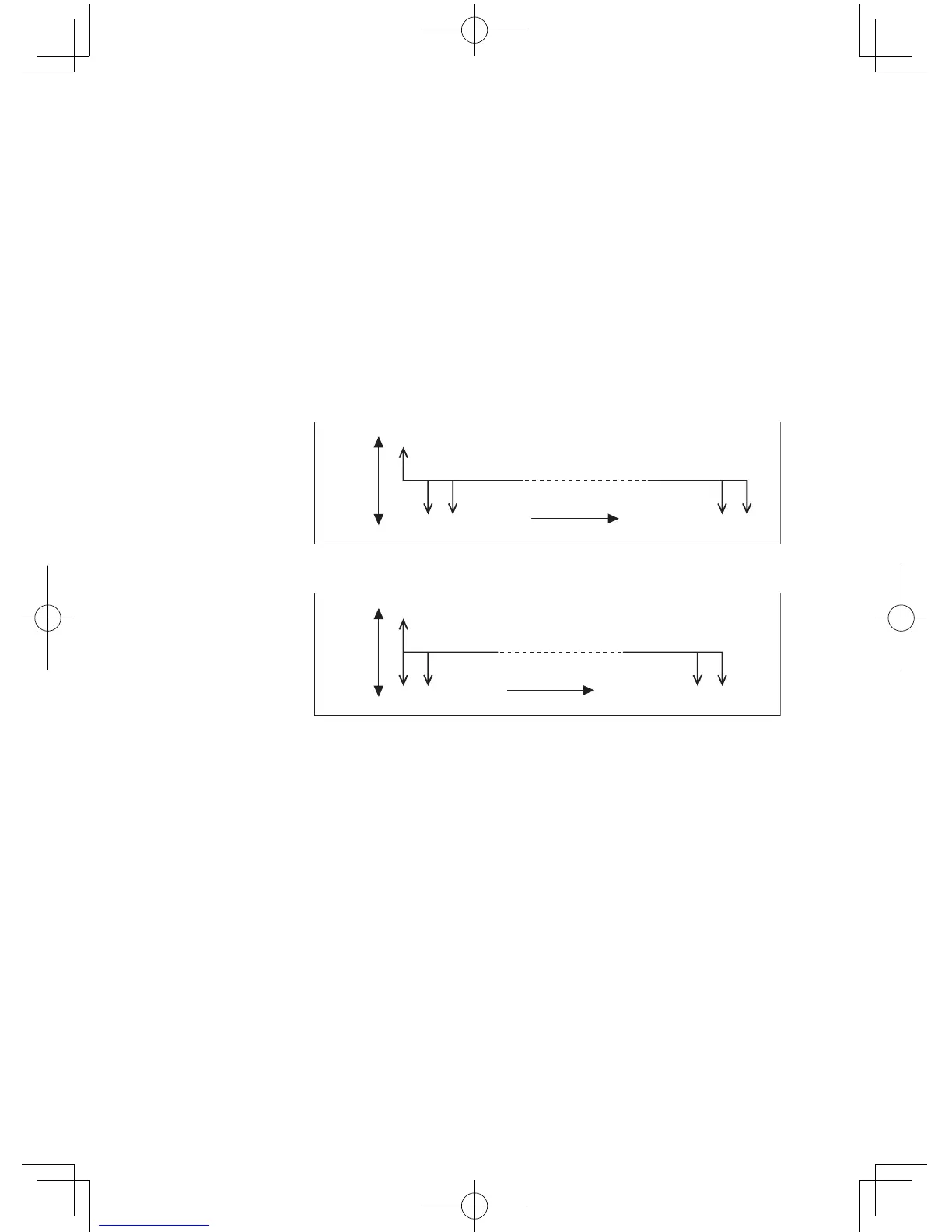
• Verticalarrowsalongthehorizontallineindicatethecashow.
AnUParrowindicatesinow(
+
)andaDOWNarrowindicates
outflow (
–
).
• Thecalculatorconsidersthecashinowforeachperiodis
constant. (Even payment.)
2. Determine the time each payment is due.
Fordepositsandloanpayments,thetimeeachpaymentisdue
(paid at the beginning or the end of the period) makes for a
different cash flow diagram.
Payment due at the end of the period
Payment due at the beginning of the period
In this case payment is due at the end of the period.
3. Determine the inflow and outflow and place the present value
(PV=$200,000)onthediagram.
Wecanconsiderthepresentvalue(PV)asaloanandthus
inow(revenue)fromthecustomer’spointofview.So,placethe
PVatthetopleftendofthediagram.Wealsocanconsiderthe
principalinteresttotal(Futurevalue)asoutow(payment).Draw
averticallinewithaDOWNarrowonthetopofthediagram.
4. Completethediagramwithinterest(I%),numberofpayment
periods(N),futurevalue(FV),andotherrequirednumbers.
Cash flow
PV
FV
PMT
Time flow
I %
NN
– 121
(
+)
(
–)
Cash flow
PV
FV
PMT
Time flow
I %
NN
– 121
(
+)
(
–)
 Loading...
Loading...