D-15
SIMATIC TD 200 Operator Interface
C79000-G7076-C272-01
You can design your S7-200 program to take other actions as a result of setting the
acknowledge-notification bit. Figure D-13 shows how you can use the
acknowledge-notification bit. For this example, VB21 is assumed to be the most
significant byte of the first format word of the message.
Ladder Logic Statement List
// Resetting the acknowledge-notification
// bit and using it to enable the next
// message
LD V21.1 // When the operator acknowledges the
R V21.1,1 // message, reset the bit and enable
// the next message
MOVB . . . // Move ...
Network #
MOV_B
EN
OUT
. . .. . .
IN
V21.1 V21.1 1
R
Figure D-13Sample Program for Using the Acknowledge-Notification Bit
Edit-Notification Bit 2
The TD 200 sets the edit-notification bit to 1 after an edit. The CPU can read this
edit-notification bit value to recognize when an editable data value has been
changed. The program can then read and make use of the edited value.
Note
The edit-notification bit does not reset automatically when subsequent edits are
performed. If you want the TD 200 to detect and notify you of a second edit
operation, you must design your program to reset the edit-notification bit to zero.
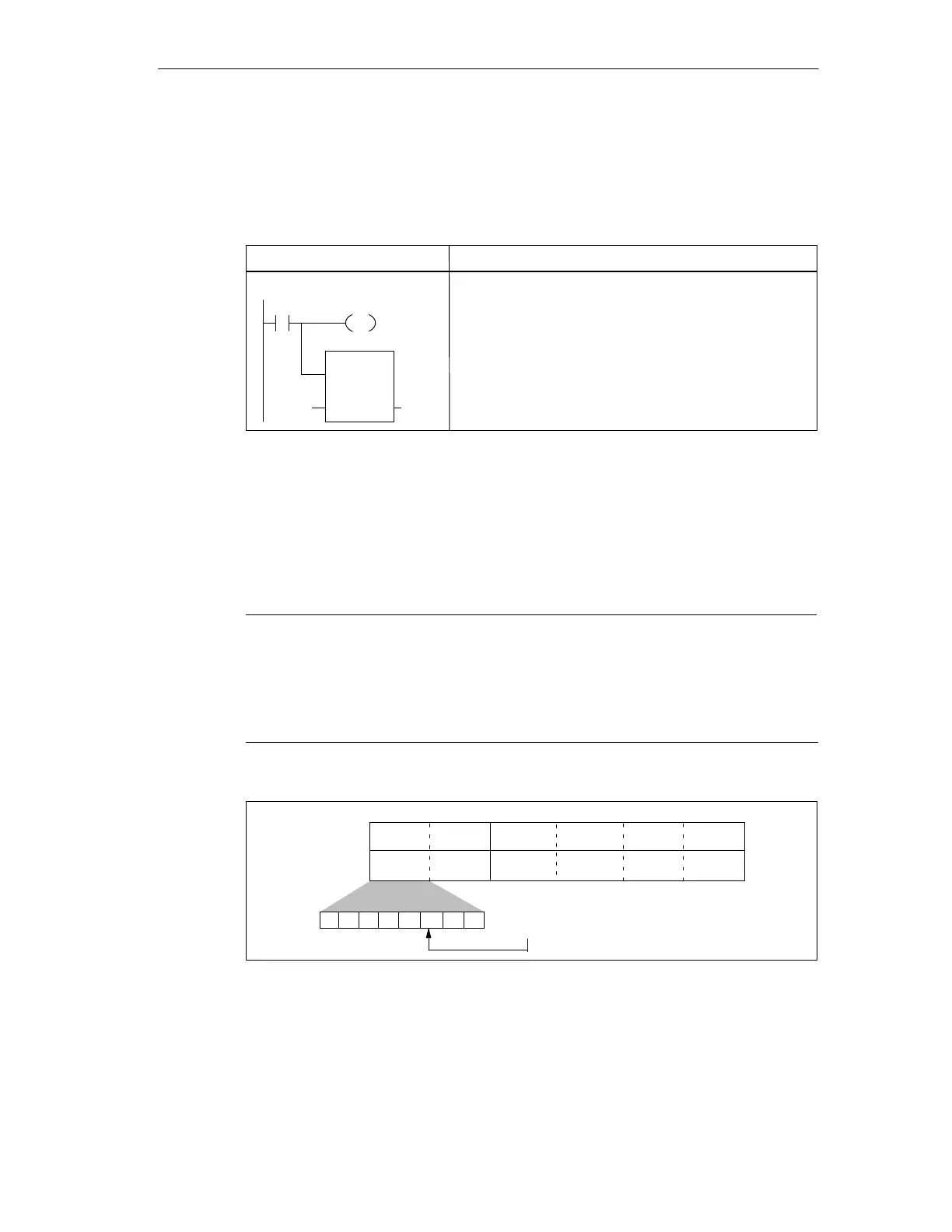
Figure D-14 shows the placement of the edit-notification bit, located in byte 0 of
the format word.
EN- Edit-Notification
0 - Not edited
1 - Message edited
Format Word Optional Data Value
Byte 0 Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3 Byte 4 Byte 5
MSB of
Format
LSB of
Format
MSB of
Data
LSB of
Data
0 0 0EPEN A
76543210
MSB LSB
AN
Figure D-14Edit-Notification Bit of Byte 0 of the Format Word
TD 200 Parameters and Messa
es

 Loading...
Loading...