5
Special Motion Commands 04.00
5.1 A
roachin
coded
ositions
CAC
CIC
CDC
CACP
CACN
5
840D
NCU 571
840D
NCU 572
NCU 573
FM-NC 810D 840Di
Siemens AG 2000. All rights reserved
5-150
SINUMERIK 840D/840Di/810D/FM-NC Programming Guide Advanced (PGA)
−
04.00 Edition
5.1 Approaching coded positions, CAC, CIC, CDC, CACP, CACN
Explanation of the commands
CAC(n)
Approach coded positions absolutely
CIC(n)
Approach coded position incrementally by n spaces in plus direction (+)
or in minus direction (–)
CDC(n)
Approach coded position via shortest possible route (rotary axes only)
CACP(n)
Approach coded position absolutely in positive direction (rotary axes only)
CACN(n)
Approach coded position absolutely in negative direction (rotary axes only)
(n)
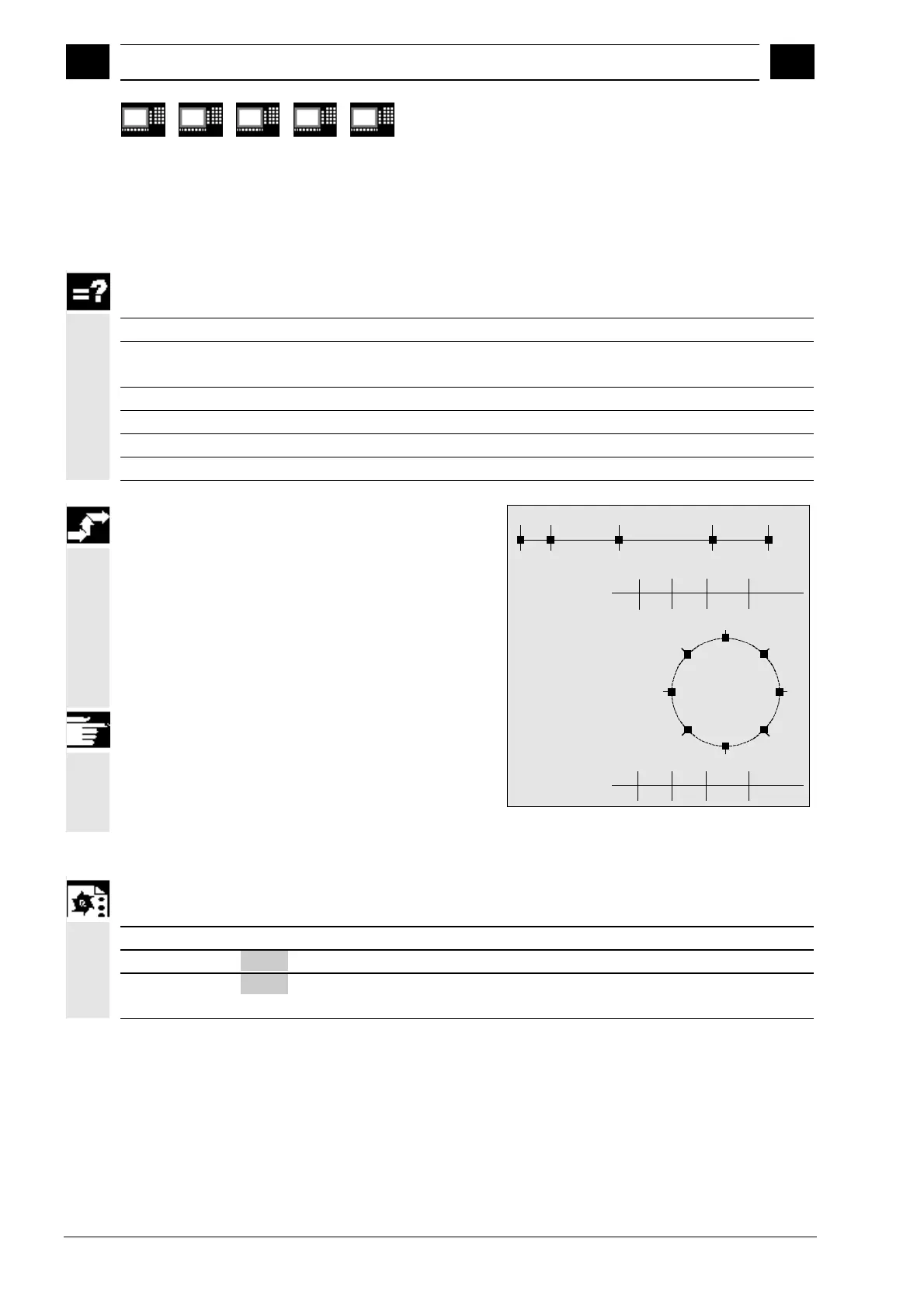
Position numbers 1, 2, ... max. 60 positions for each axis
Sequence
You can enter a maximum of 60 (0 to 59) positions
in special position tables for 2 axes
in machine data.
For an example of a typical position table see
diagram.
Further details
If an axis is situated between two positions, it does
not traverse in response to an incremental position
command with CIC (...).
It is always advisable to program the first travel
command with an absolute position value.
6
1
2
3
43210
0
0
27.3
1
40.7
2
112
3
112 mm
4
5
0
Table 1 (rotar
axis)
0
45
1
90
...
...
72
315 de
.
7
0
Table 1 (linear axis)
Position number:
Position value:
Indexin
axis:
Position number:
Position value:
Programming example
N10 FA[B]= 300
Feed for positioning axis B
N20 POS[B]= CAC (10)
Approach coded position 10 (absolutely)
N30 POS[B]= CIC (-4)
Travel 4 spaces back from the current
position

 Loading...
Loading...























