2.3 Differential Protection
71
7SD610 Manual
C53000-G1176-C145-4
Pickup Value of the
Differential Current
The current sensitivity is set with address 1210 I-DIFF>. It is determined by the
entire current flowing into a protected zone in case of a fault. This is the total fault
current regardless of how it is distributed between the ends of the protected object.
This pickup value must be set to a value that is higher than the total steady-state shunt
current of the protected object. For cables and long overhead lines, the charging
current is to be considered in particular. It is calculated from the operational capaci-
tance:
I
C
= 3.63 · 10
–6
· U
N
· f
N
· C
B
' · s
with
I
C
Charging current to be calculated in A primary
U
Nom
Nominal voltage of the network in kV primary
f
N
Nominal frequency of the network in Hz
C
B
' Per unit line length service capacitance of the line in nF/km or nF/mile
s Length of the line in km or miles
Considering the variations of voltage and frequency, the value set should be at least
2 to 3 times higher than the calculated charging current. Moreover, the pickup value
should not be less than 15 % of the operating rated current. The operating rated
current either derives from the rated apparent power of a transformer in the protected
area (as described in 2.1.4.1 under margin heading „topological data for transformers
is described in the protection zone (optional)“, or from the addresses 1104
FullScaleCurr. according to Section 2.1.4.1 under margin heading „Rated Values
of Protected Lines“. It must be equal at all ends of the protected object.
If setting is performed from a personal computer using DIGSI, the parameters can be
set either as primary or as secondary quantities. If secondary quantities are set, all
currents must be converted to the secondary side of the current transformers.
Calculation Example:
110 kV single-conductor oil-filled cable
Cross section = 240 mm
2
Rated frequency f
N
= 50 Hz
Length s = 16 km
Service capacitance C
B
' = 310 nF/km
Current transformer, transformer ratio 600 A/5 A
From that the steady-state charging current is calculated:
I
C
= 3.63 · 10
–6
· U
N
· f
N
· C
B
' · s = 3.63 · 10
–6
· 110 · 50 · 310 · 16 = 99 A
For the setting with primary values at least the double value is to be set, i.e.:
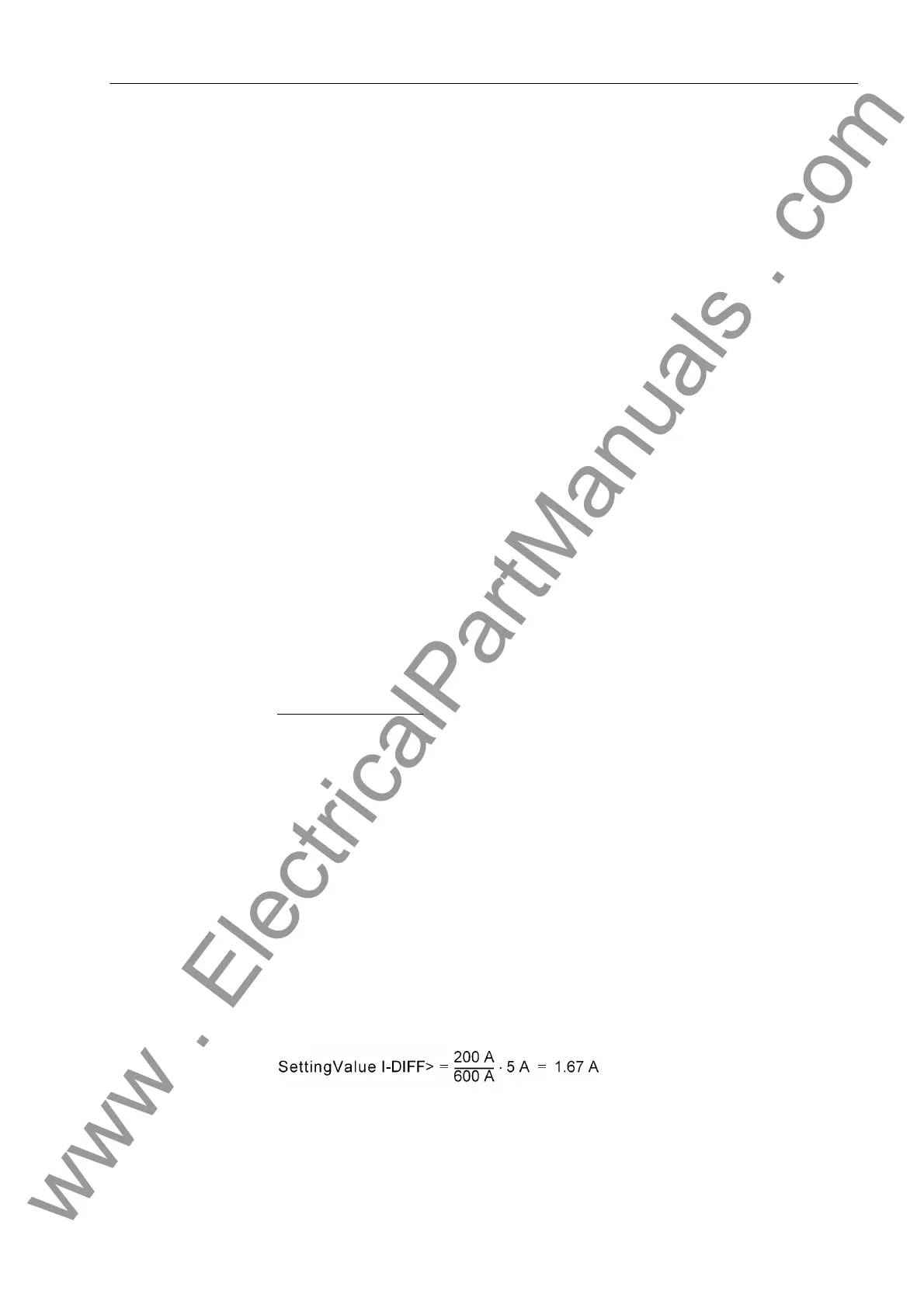
Setting value I-DIFF> = 200
For the setting with secondary values this value has to be converted to secondary
quantity:
If a power transformer with voltage regulation is installed within the protected zone
consider that a differential current may be present even during normal operation, de-
pendent on the position of the tap changer. Please also refer to the notes in chapter
www . ElectricalPartManuals . com

 Loading...
Loading...











