Operating Instructions
1–14
1502C MTDR Service Manual
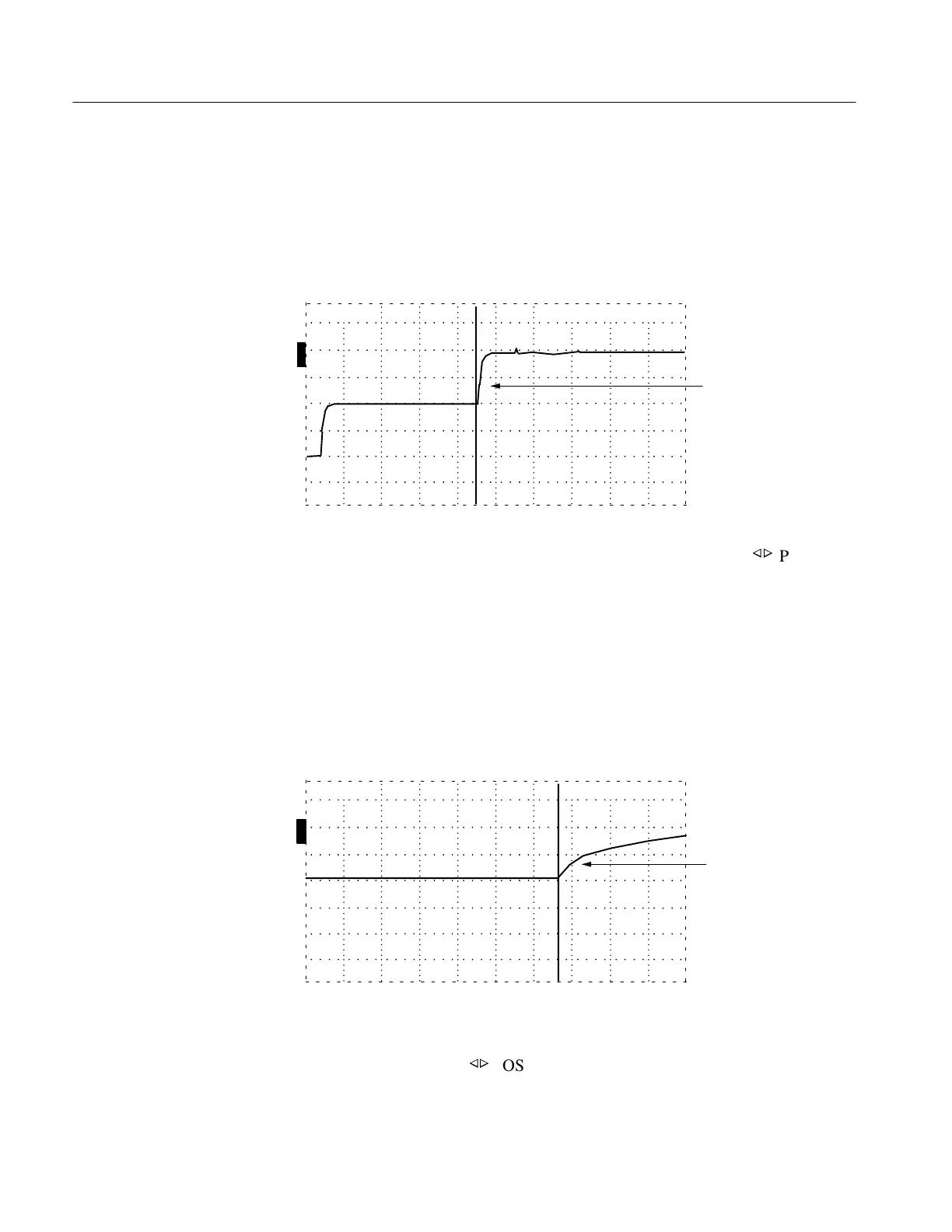
When the entire cable is displayed, you can tell if there is an open or a short.
Essentially, a large downward pulse indicates a short (see Figure 1–9, previous
page), while a large upward pulse indicates an open (see Figure 1–10). Less
catastrophic faults can bee seen as smaller reflections. Bends and kinks, frays, water,
and interweaving all have distinctive signatures.
O
F
F
O
F
F
O
F
F
O
N
ac 20.000 ft
Open
Figure 1–10: Open in the Cable
3. To find the distance to the fault or end of the cable, turn the
POSITION
control until the cursor rests on the leading edge of the rising or falling reflected
pulse (see Figure 1–10). Read the distance in the distance window in the upper
right corner of the display.
A more thorough inspection might be required. This example uses a longer cable:
4. When inspecting a 452-foot cable, a setting of 50 ft/div allows a relatively fast
inspection. If needed, turn VERT SCALE to increase the gain. The higher the
gain, the smaller the faults that can be detected. If noise increases, increase the
NOISE FILTER setting.
O
F
F
O
F
F
O
F
F
O
N
ac 452.000 ft
Open
Figure 1–11: 455-ft Cable
5. Change DIST/DIV to 20 ft/div. The entire cable can now be inspected in detail
on the LCD. Turn the
POSITION control so the cursor travels to the far right
side of the LCD. Keep turning and the cable will be “dragged” across the
display.
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com

 Loading...
Loading...











