4
Ion Transmission and Mass Analysis
Ion Optics
Thermo Scientific Orbitrap Fusion Series Hardware Manual 33
Curved Linear Trap
For Orbitrap mass analysis, the mass spectrometer always passes the ions through the gas-free
multipole MP1 and the gas-filled curved linear trap (C-trap) before trapping them in the
IRM. The mass spectrometer then passes the ions back to the C-trap (Figure 19) before
injecting them into the Orbitrap mass analyzer.
Ions that enter the C-trap lose their kinetic energy by colliding with the nitrogen collision gas,
which dissipates their kinetic energy and cools them down to the center axis of the C-trap. See
Figure 13 for its location.
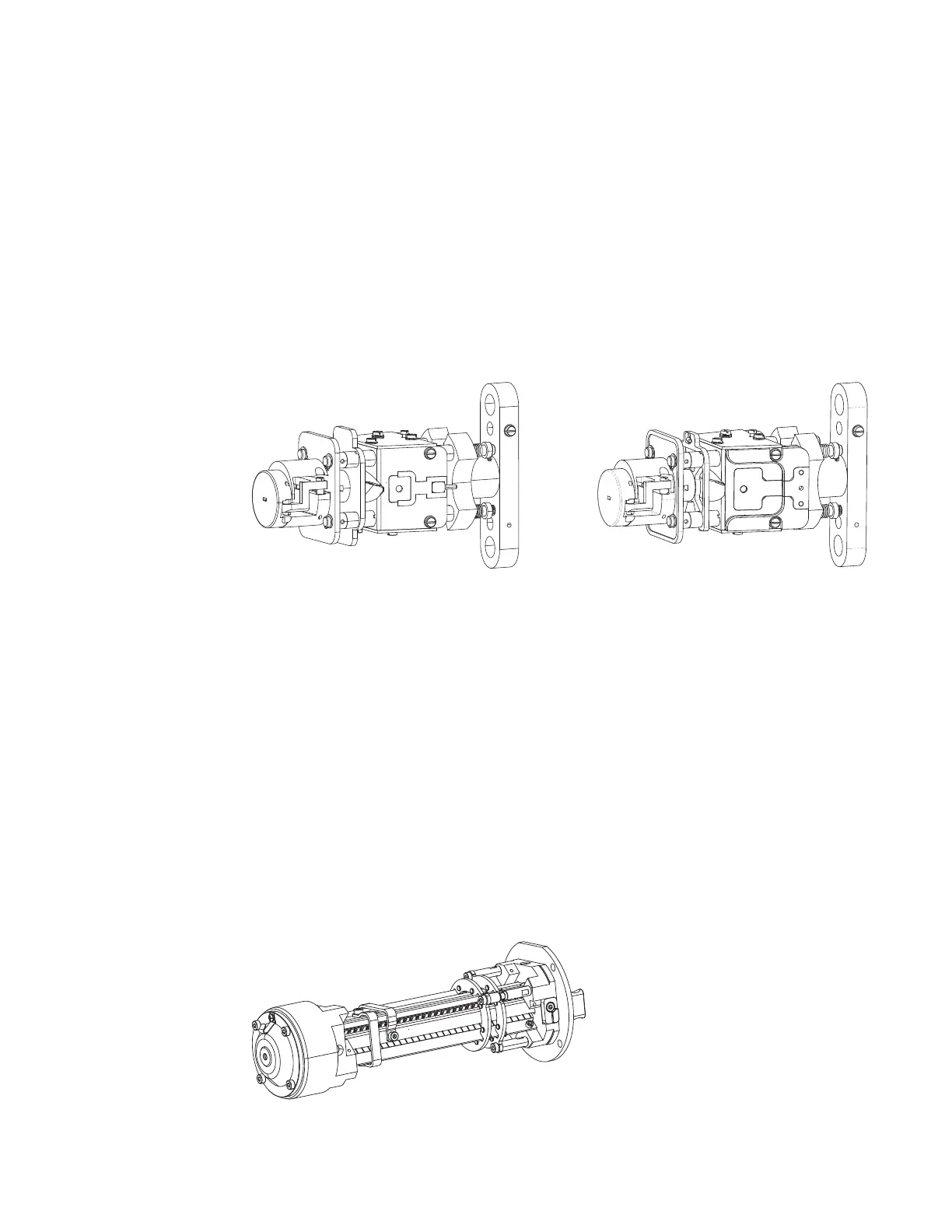
Figure 19. C-trap (Orbitrap Fusion and Orbitrap Fusion Lumos MSs)
Ion-Routing Multipole
The ion-routing multipole (Figure 20) consists of a straight multipole that is mounted inside
a metal tube and has a direct line-of-sight to the C-trap. The mass spectrometer supplies the
IRM with the nitrogen collision gas to increase the multipole’s gas pressure. The C-trap
attaches to the multipole, so part of the collision gas also flows into the C-trap.
To perform HCD, ions pass through the C-trap into the IRM. The offset voltage between the
C-trap and multipole accelerates the precursor ions into the gas-filled multipole. The mass
spectrometer applies a potential gradient to the multipole to provide fast extraction of the
ions. The spectrum of the fragments generated in the IRM and detected in the Orbitrap mass
analyzer shows a fragmentation pattern comparable to the pattern of a typical triple
quadrupole spectrum.
Figure 20. Ion-routing multipole (IRM)
Orbitrap Fusion MS Orbitrap Fusion Lumos MS

 Loading...
Loading...





