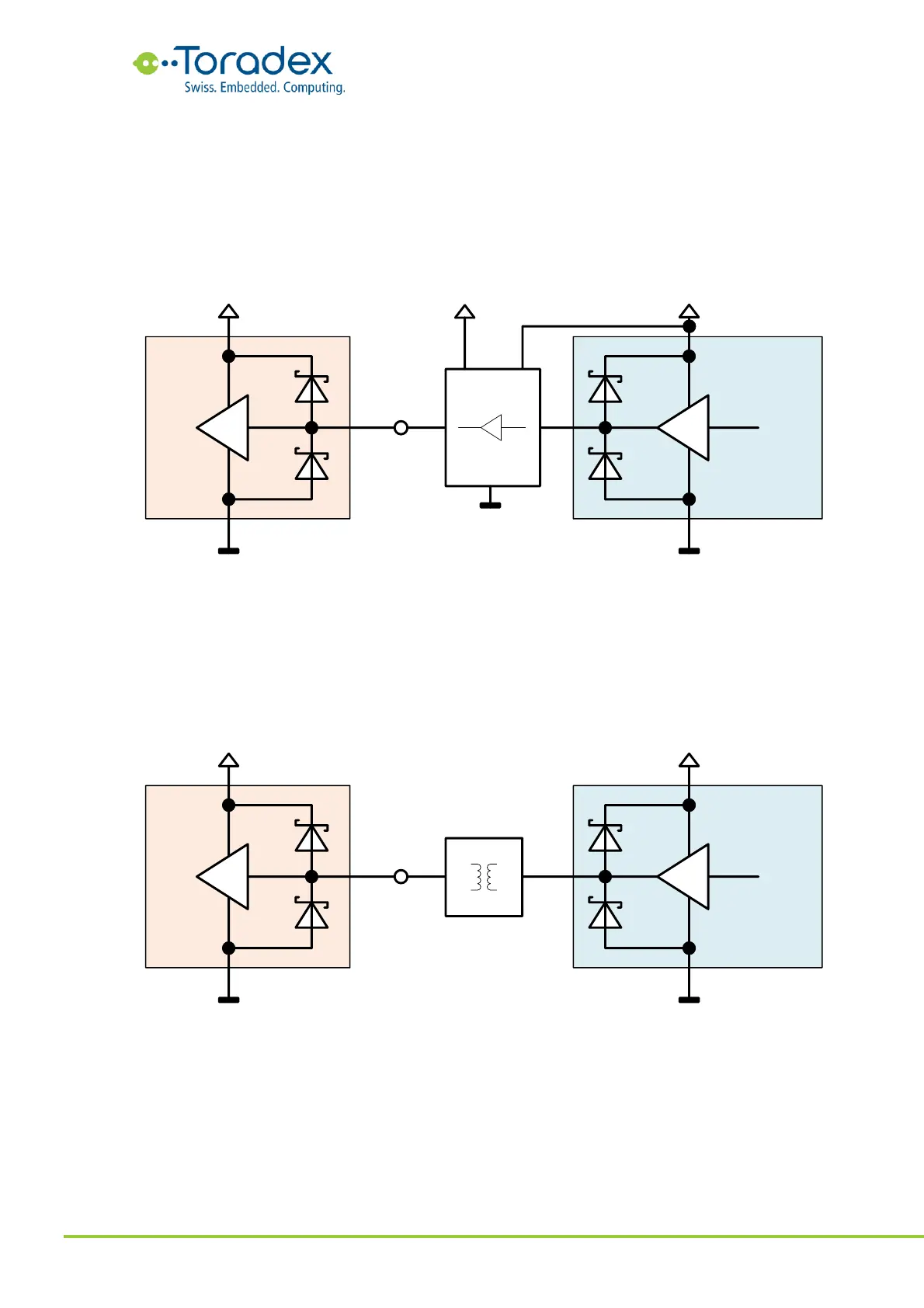
3.5.5.12 Level Shifter
Level shifters can be an effective method for preventing backfeeding. Especially if you anyway need
a level shifter in the signal path. Even if both sides have the same IO voltage level, a level shifter
can still be a good option. It is important to select a level shifter that allows both power rails to be
switched off individually. Not all level shifters allow that without causing backfeeding. A good
candidate for preventing backfeeding is the SN74AVC4T774 from TI. For open-drain signals such
as the I
2
C bus, the FXMA2102L8X from ON Semiconductor prevents backfeeding.
Figure 85: Level shifter for preventing backfeeding
3.5.5.13 Galvanic Isolation
Galvanic isolations in the signal path can be achieved by transformers, optocouplers, or specialized
ICs. Especially in harsh environments, galvanic isolation is a preferred method for isolating power
domains of different devices. The so-called magnetics inside the Ethernet connector is also a
galvanic isolator and prevents backfeeding over the Ethernet cable. Galvanic isolators are also
preferred way for protecting different power domains of CAN interfaces.
Figure 86: Galvanic isolation between input and output
 Loading...
Loading...