6
vacon • 19 EtherNet/IP
Tel. +358 (0) 201 2121 • Fax +358 (0)201 212 205
6.4 Explicit Messaging
Explicit Messaging is used in commissioning and parameterizing of the EtherNet/IP.
The explicit messages provide multipurpose, point-to-point communication paths between two
devices. They provide the typical request/response-oriented network communication used to
perform node configuration and problem diagnosis. The explicit messages typically use low priority
identifiers and contain the specific meaning of the message right in the data field. This includes the
service to be performed and the specific object attribute address.
NOTE! If Class 1 connection (cyclic data) has been established, the Explicit Messages should not be
used to control the Output Data. However this restriction does not apply for the IO Data reading.
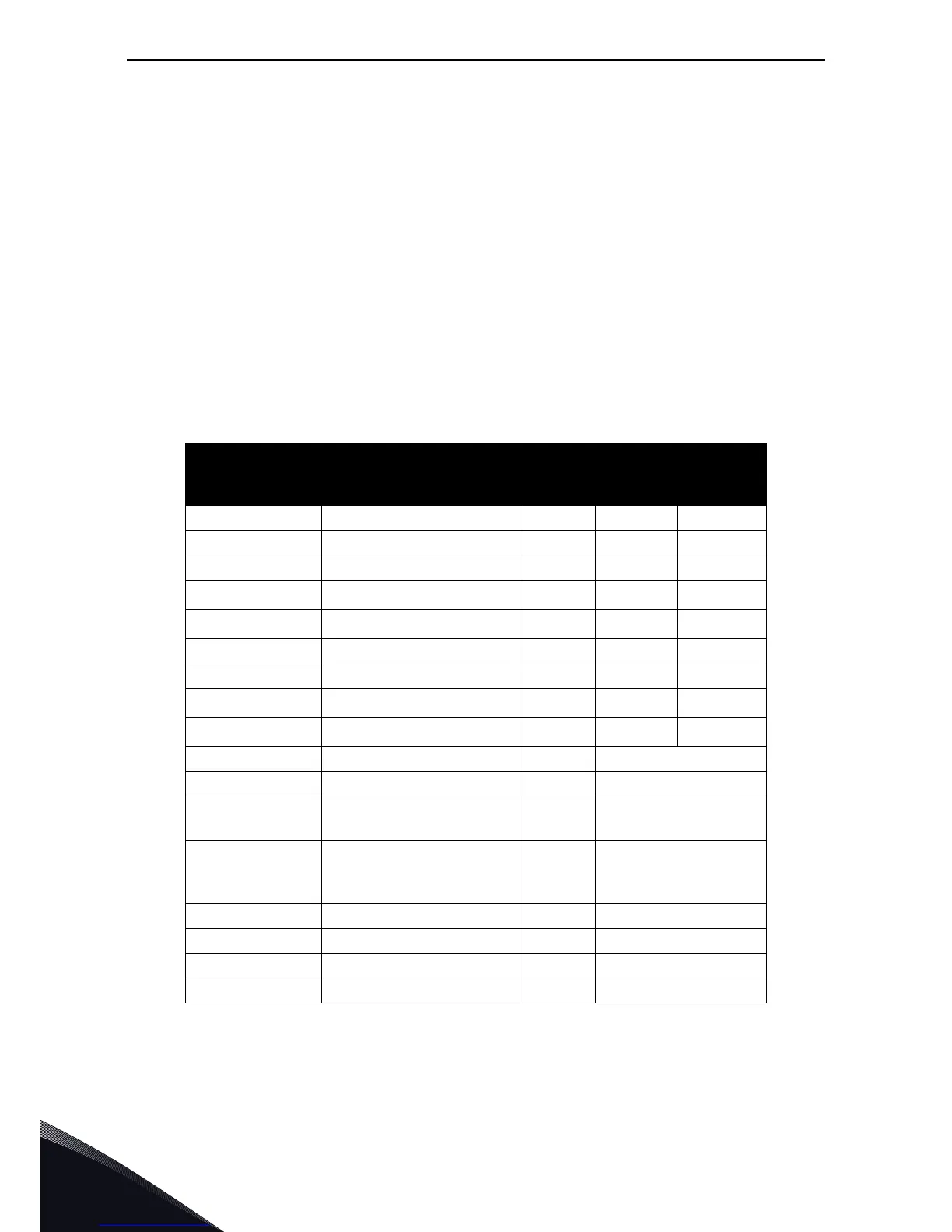
6.4.1 List of data types
The elementary data types in CIP are (among others):
* ISO/IEC-8859-1 encoding.
Table 7. EtherNet/IP datatypes
Name Description Bit size Range
Minimum Maximum
BOOL Boolean 8 0 = FALSE 1 = TRUE
SINT Short Integer 8 -128 127
INT Integer 16 -32768 32767
DINT Double Integer 32
-2
31
2
31
- 1
LINT Long Integer 64
-2
63
2
63
- 1
USINT Unsigned Short Integer 8 0 255
UINT Unsigned Integer 16 0 65535
UDINT Unsigned Double Integer 32 0
2
32
- 1
ULINT Unsigned Long Integer 64 0
2
64
- 1
REAL Floating Point 32 See IEEE 754
LREAL Long Floating Point 64 See IEEE 754
STRING *
Character string (1 octet
per char.)
N
SHORT_STRING *
Character string (1 octet
per char., 1 octet length
indicator)
N+1
BYTE Bit string (8 bits) 8
WORD Bit string (16 bits) 16
DWORD Bit string (32 bits) 32
LWORD Bit string (64 bits) 64
 Loading...
Loading...