June 11, 2015, 715004754 Rev. A
Page 105
7.3.1 Hardware troubleshooting
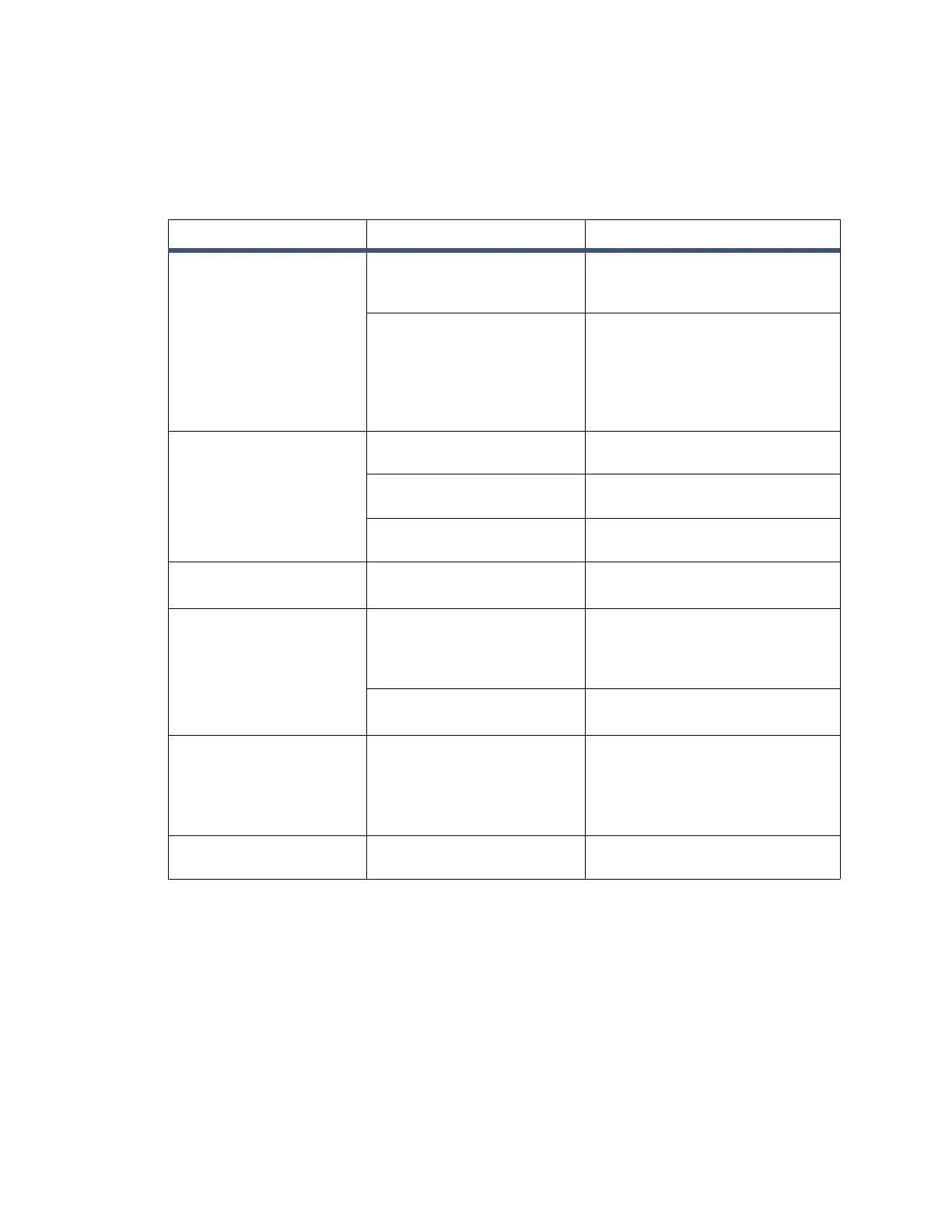
The following table describes hardware troubleshooting for the detector.
7.3.2 Chromatography troubleshooting
Chromatography troubleshooting helps isolate and correct the causes of these
problems:
• Abnormal baseline (drift, noise, or cycling) (see the table on page 107).
• Erratic or incorrect retention times (see the table on page 110).
• Poor peak resolution (see the table on page 112).
• Incorrect qualitative/quantitative results (see the table on page 113).
Table 7–2: General system troubleshooting
Symptom Possible cause Corrective action
Detector inoperative Fuse blown Verify the front panel display is
operational; if it is not, replace
the AC rear panel fuse.
No power at outlet Confirm that the ac outlet is
energized by connecting
another electrical unit known
to be in working order and
determining whether it
operates.
front panel display fails
to illuminate
Broken electrical
connection
Inspect electrical connections.
Fuse blown Inspect and, if necessary,
replace fuse(s).
Bad LCD or control board Contact Waters Technical
Service.
front panel displays odd
characters
Faulty EPROMs
Bad LCD control board
Contact Waters Technical
Service.
IEEE-488 problems IEEE-488 410 mode
configuration disabled
and/or IEEE address set
incorrectly
Set the configuration page
correctly.
Bad IEEE-488 cable Check the IEEE-488 cable.
Replace the IEEE-488 cable.
Keypad not functioning Keypad defective Cycle power to the detector
and run the keypad diagnostic
test.
Contact Waters Technical
Service.
Analog output incorrect RIU-FS setting changed Reset the RIU-FS setting in
RIU mode.
 Loading...
Loading...