June 11, 2015, 715004754 Rev. A
Page 18
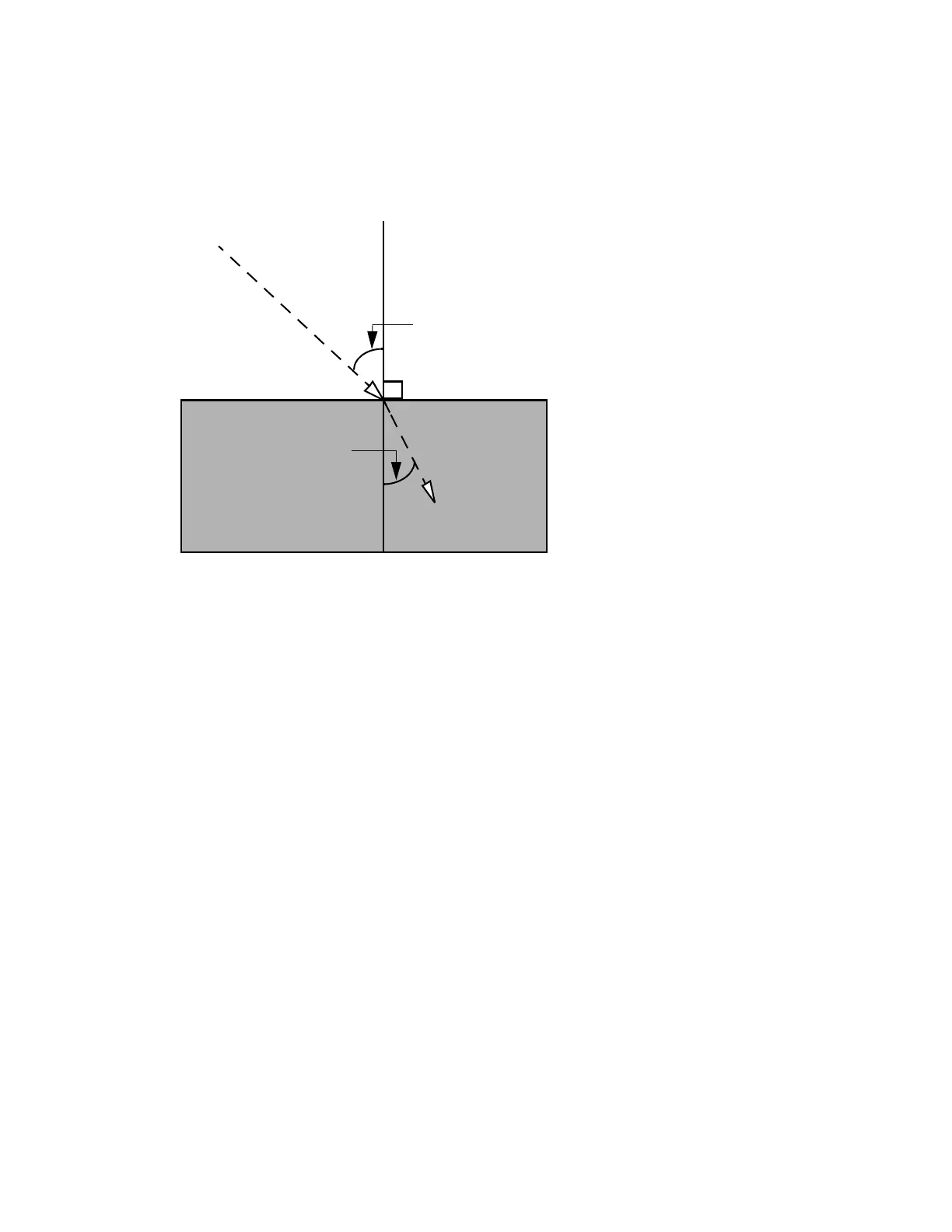
The following figure illustrates the relationship between angle of incidence, angle of
refraction, and refractive index.
Figure 1–2: Refraction of light
The relationship between the refractive indices of the two media and the angles of
incidence and refraction is described by Snell’s Law:
n
1
(sin θ
1
) = n
2
(sin θ
2
)
where:
θ
1
=
Angle of incidence
θ
2
=
Angle of refraction
n
1
=
RI of medium 1
n
2
=
RI of medium 2
You can use Snell’s Law to calculate the RI of a sample solution from the angle of
incidence, the RI of the solvent, and the angle of refraction.
1.2.1.3 Using changes in RI for sample detection
As the separated components of a sample pass through the refractometer flow cell,
these events occur:
• The composition of the sample solution in the flow cell changes.
• The RI of the solution changes.
• The light beam passing through the solution is refracted.
θ
1
Incoming light beam Perpendicular to surface
Medium 1, RI = n
1
Medium 2, RI = n
2
Refracted light beam
Angle of refraction
Angle of incidence
θ
2
 Loading...
Loading...