June 11, 2015, 715004754 Rev. A
Page 20
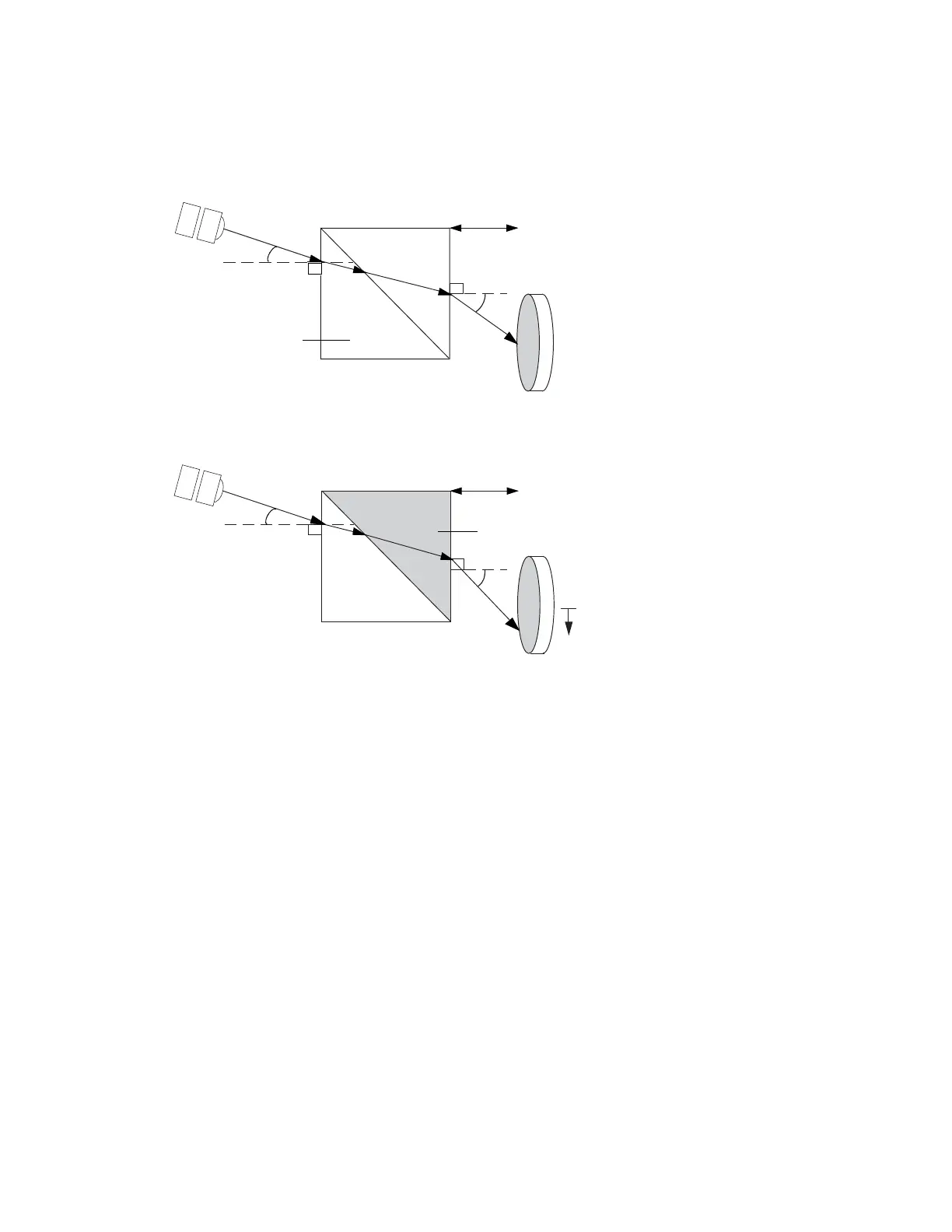
The following figure illustrates the external angle of deflection (φ) and its dependence
on the difference in RIs between the reference and sample sides of the flow cell.
Figure 1–4: How refraction changes the external angle of deflection
1.2.2.2 Effect of refraction on φ
As the beam of light moves along the light path to the photodiode, it encounters and
is refracted by the air in the optics bench assembly, the fused quartz walls of the flow
cell, the solvent in the reference side of the flow cell, and the solution in the sample
side of the flow cell.
Of these refractors, only the solution in the sample side of the flow cell changes over
the course of a run. As a result, the reference external angle of deflection (φ) does not
change until a change in the RI of the sample causes the light beam to be refracted
from its zero position.
The relationship between the external angle of deflection (φ) and the RI of the sample
solution is expressed as:
Δn ≅ φ/tanθ
where:
Δn = Difference in RI between the solvent and the solvent-sample solution
φ = External angle of deflection (in radians)
θ = Angle of incidence (in radians)
θ
φ
n
n
Y
Y
θ
φ
n + Δn
n
= Δx
Reference side
of flow cell
Sample side
of flow cell
 Loading...
Loading...