IP Networking Configuration
Configuration Guide 38 Document #: LTRT-31657
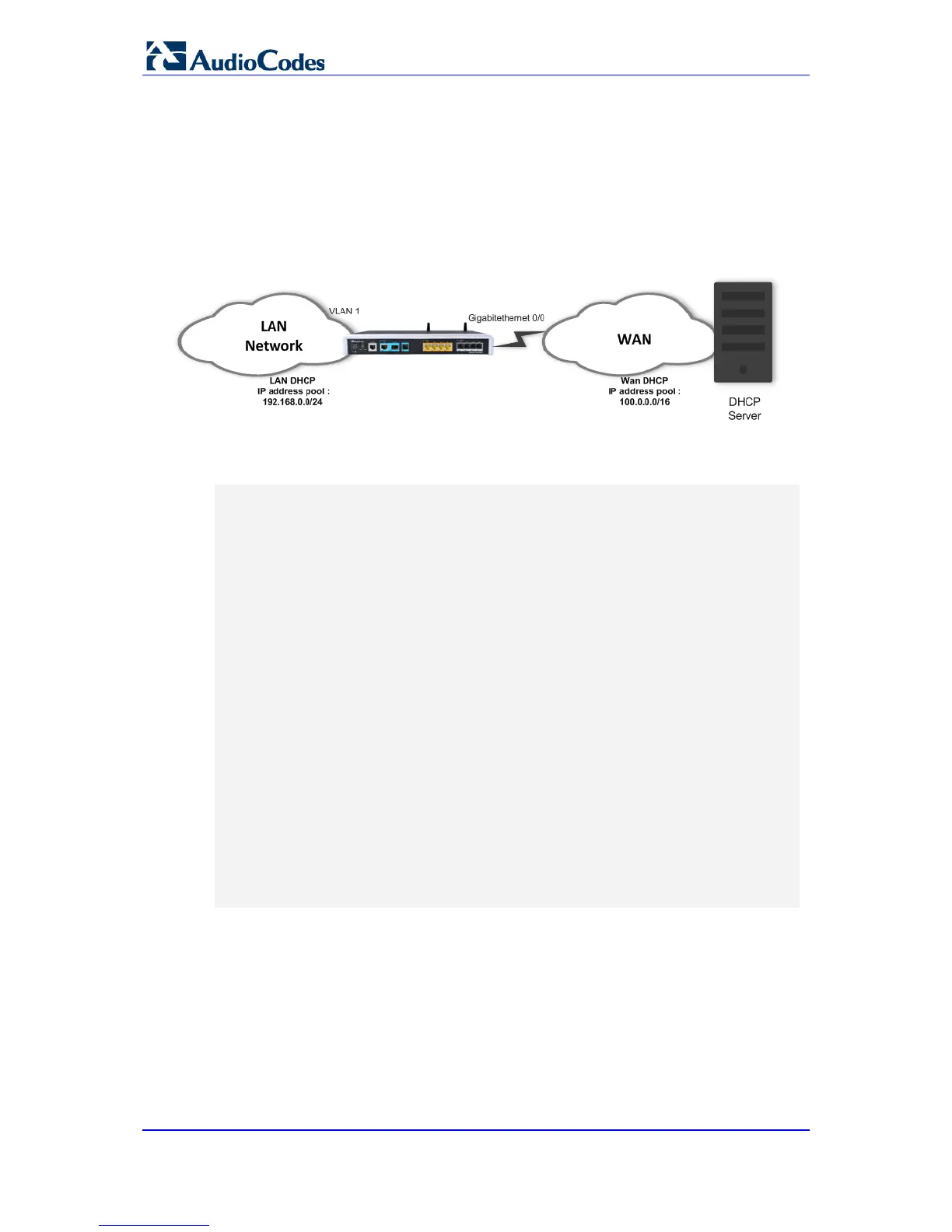
6.2 Example #1 of Basic Dynamic DNS Configuration
In this typical example scenario, the MSBR, acting as an access router for the
organizational network, receives the DNS server’s IP address dynamically through DHCP
on the WAN interface. The MSBR also acts as a DHCP server on the LAN, and by the
configuration ip name-server 0.0.0.0, the MSBR acts as a DNS server, relaying
DNS messages to the DNS server's IP address that it acquires dynamically on the WAN
interface.
Figure 6-1: Dynamic DNS
6.2.1 Configuration
MSBR# configure data
MSBR(conf-data)# interface GigabitEthernet 0/0
# WAN Interface is set as DHCP client
MSBR(conf-if-GE 0/0)# firewall enable
MSBR(conf-if-GE 0/0)# napt
MSBR(conf-if-GE 0/0)# ip address dhcp
MSBR(conf-if-GE 0/0)# ip dhcp-client default-route
MSBR(conf-if-GE 0/0)# ip dns-server auto
MSBR(conf-if-GE 0/0)# no shutdown
MSBR(conf-if-GE 0/0)# exit
MSBR(conf-data)# interface VLAN 1
# LAN Interface is set as DHCP server
MSBR(conf-if-VLAN 1)# ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0
MSBR(conf-if-VLAN 1)# desc "VLAN 1 LAN VOIP"
MSBR(conf-if-VLAN 1)# ip dhcp-server network 192.168.0.10
192.168.0.20 255.255.255.0
MSBR(conf-if-VLAN 1)# ip dhcp-server lease 0 1 0
MSBR(conf-if-VLAN 1)# ip dns server static
MSBR(conf-if-VLAN 1)# ip name-server 0.0.0.0
MSBR(conf-if-VLAN 1)# service dhcp
MSBR(conf-if-VLAN 1)# no shutdown
MSBR(conf-if-VLAN 1)# exit

 Loading...
Loading...