<broadcast/non-broadcast/point-to-
multipoint/point-to-point>
Configures the network type the interface
connects to (has effects on adjacency formation
and message forwarding).
Configures the link state transmit delay.
11.2.2 Example of OSPF Routing
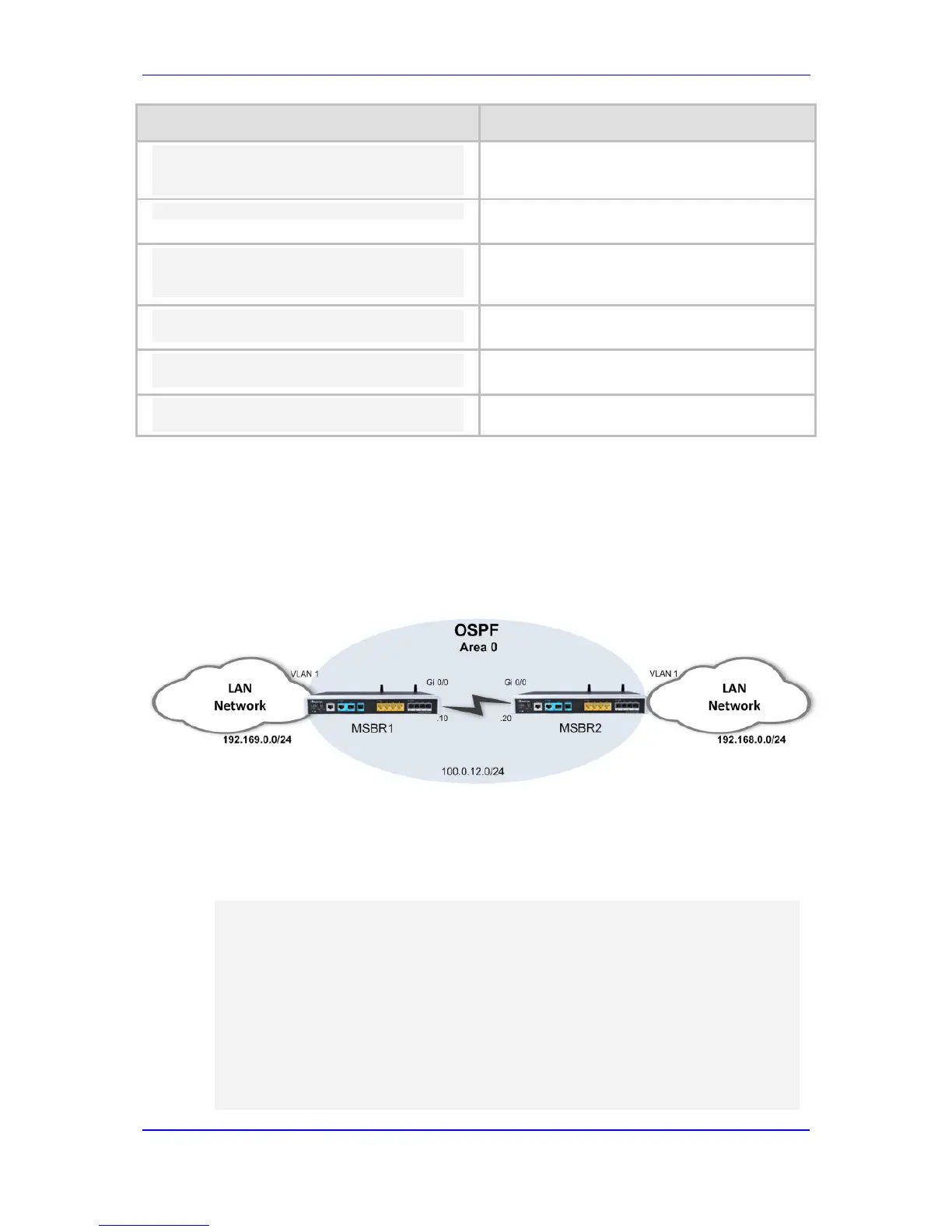
The example shown below demonstrates a typical scenario where an MSBR acts as a
default gateway for a LAN network, and connects to the WAN network using the OSPF
protocol. The example includes a single-area (area 0) OSPF network; however, in more
complex and large-scale networks, multi-area topology may be more adequate in terms of
scalability.
Figure 11-2: OSPF Routing
The following configuration demonstrates a basic OSPF configuration in which OSPF is
activated on the LAN interfaces (for advertisement) and on the WAN interfaces (for
adjacency forming). The router-ids are explicitly configured to the addresses of loopback
interfaces configured on the MSBR. Adjacency change logging is activated for debugging.
The OSPF timers are configured on the WAN interfaces of the MSBRs and should always
be matched on both ends to avoid adjacency flapping.
******************************************************************
IP address configuration is omitted, assume it is as described in
the topology above.
******************************************************************
MSBR1:
MSBR1# configure data
MSBR1(config-data)# router ospf
MSBR1(conf-router)# network 100.0.12.0/24 area 0
MSBR1(conf-router)# network 192.168.12.0/24 area 0
MSBR1(conf-router)# router-id 1.1.1.12

 Loading...
Loading...