Version 6.8 95 Mediant MSBR
Configuration Guide 16. Quality of Service (QoS)
16 Quality of Service (QoS)
In modern networks, different types of traffic are transported over the same infrastructure:
Data, Voice, Video, latency sensitive, application specific and more. In cases of network
congestion, some amount of data may be delayed or dropped and retransmitted, and while
some kinds of traffic are tolerant to this phenomenon, others such as video and voice are
sensitive to it.
QoS is a set of mechanisms to handle the prioritization of some traffic over another to
make sure it gets the amount of network bandwidth it requires, proper latency, etc.
It is important to be familiar with several concepts that are crucial for the QoS process:
Traffic filtering: the first step in the QoS mechanism. You need to filter and define the
preferred traffic”; basically stating which traffic should receive the special priority
handling. This step is usually performed using ACLs, VLAN-Priority or the DSCP
value.
The DiffServ (the system behind DSCP) is a computer networking mechanism for
classifying, managing and providing QoS for data in IP networks in layer 3, while TOS
is quite similar, however uses a slightly different terminology and rating for traffic in
layer 2.
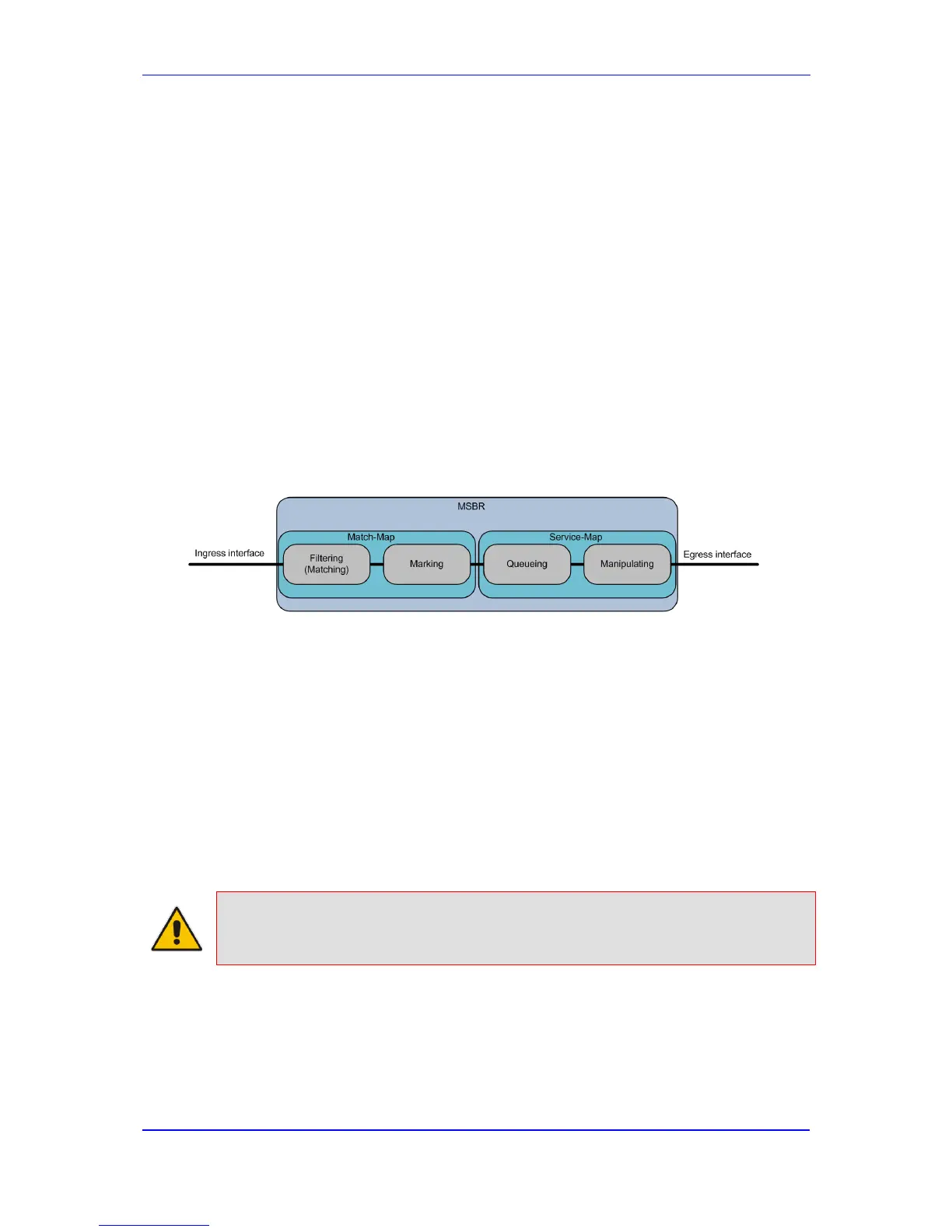
The usual event flow of the QoS mechanism is as follows:
Figure 16-1: QOS Handling Flow-Chart
Match-maps bind the “match” statements with marking rules, meaning that once there are
rules matching the specified traffic, you can mark it for further processing, using the DSCP
system.
After the marking, the actual QoS mechanism is activated using the service-map objects,
which are configured on the physical egress interface and contain the actual queues to
which the different traffic is divided. For each queue the following actions can be
performed:
Shaping: assuring an amount of bandwidth for the specified traffic – usually media
requires minimal bandwidth.
Prioritization: setting different priorities for different traffic associated with different
queues, thus providing lower delay for higher priority traffic.
Drop policy and queue scheduling: setting rules for planned packet drop or sharing
the bandwidth according to user-defined thresholds.
Note: It is considered good practice to perform the matching as close to the ingress
interface as possible, and the manipulation on the physical egress interface.

 Loading...
Loading...